Windows: Open your command prompt and enter the command “ipconfig /displaydns.” You should then be able to see the records. Mac: Open the Terminal app, enter the command “sudo discoveryutil udnscachestats,” and input your password. This will display the Unicast DNS cache.
Where is the DNS cache located?
Windows: Open your command prompt and enter the command “ipconfig /displaydns.” You should then be able to see the records. Mac: Open the Terminal app, enter the command “sudo discoveryutil udnscachestats,” and input your password. This will display the Unicast DNS cache.
Are DNS records cached?
In fact, as mentioned above, a DNS lookup involves various steps. During a new DNS lookup, the lookup passes through the resolver, root server, and TLD server. At each step, information is gathered and cached for later use.
Where are my DNS records stored?
DNS records are stored in authoritative servers. These records provide information about a domain, including its associated IP address for each domain. It is mandatory for all domains to have a specific set of default records.
Who caches DNS records?
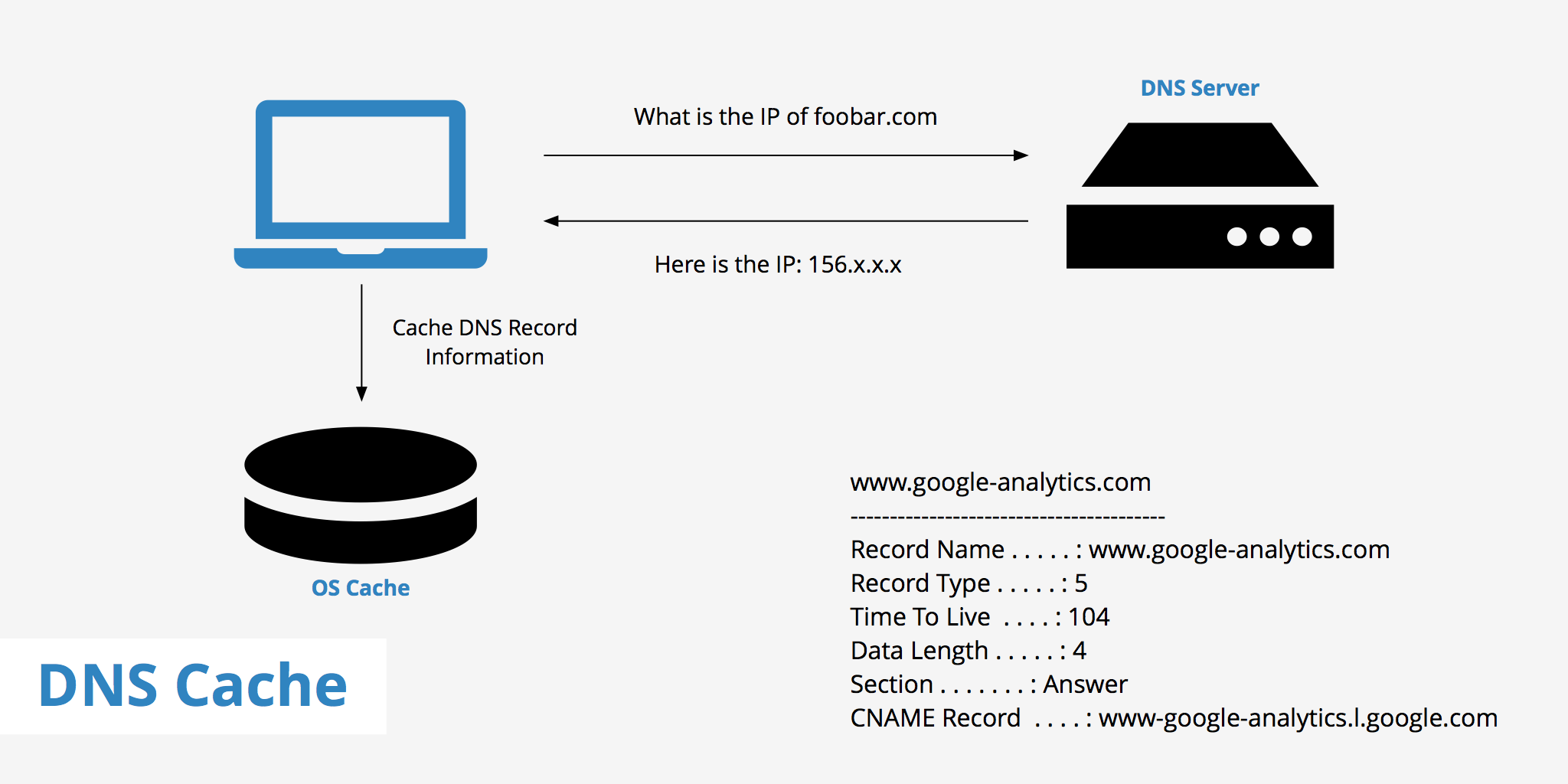
A DNS cache (sometimes called a DNS resolver cache) is a temporary database, maintained by a computer’s operating system, that contains records of all the recent visits and attempted visits to websites and other internet domains.
Where is the DNS cache located?
Windows: Open your command prompt and enter the command “ipconfig /displaydns.” You should then be able to see the records. Mac: Open the Terminal app, enter the command “sudo discoveryutil udnscachestats,” and input your password. This will display the Unicast DNS cache.
Are DNS records cached?
In fact, as mentioned above, a DNS lookup involves various steps. During a new DNS lookup, the lookup passes through the resolver, root server, and TLD server. At each step, information is gathered and cached for later use.
Who caches DNS records?
A DNS cache (sometimes called a DNS resolver cache) is a temporary database, maintained by a computer’s operating system, that contains records of all the recent visits and attempted visits to websites and other internet domains.
Where are DNS entries stored in Windows?
They are stored in the Application Directory Partition.
How long is DNS cache stored?
By default, Windows stores positive responses in the DNS cache for 86,400 seconds (i.e., 1 day) and stores negative responses for 300 seconds (5 minutes). To modify these values, perform the following steps: Start a registry editor (e.g., regedit.exe).
How do DNS records disappear?
DNS records are deleted when a given Windows client dynamic lease is changed to a reservation. DNS records that are currently registered by a DHCP-enabled Windows client are deleted by the DHCP server.
Does clearing DNS cache delete history?
If the domain name in the cache points to an old or incorrect IP address, the website won’t return the correct information. Even if you clear your browser history, the DNS cache will still have the old information, and the server needs to be flushed to get the updated results.
Which would be the best place to cache DNS data?
The answer is DNS cache. DNS cache would be the best place to cache DNS data. A DNS cache or a DNS resolver cache can be considered as a temporary database that is being maintained by a computer’s operating system.
How do I clear the DNS cache?
Android (version 12) Open Chrome. In the URL bar type in chrome://net-internals/#dns: In the left pane select DNS. In the right pane tap the Clear host cache button.
How do I clear the DNS cache?
Android (version 12) Open Chrome. In the URL bar type in chrome://net-internals/#dns: In the left pane select DNS. In the right pane tap the Clear host cache button.
What happens when you delete DNS cache?
Clearing the DNS server will remove any invalid addresses, whether because they’re outdated or because they’ve been manipulated. It’s also important to note flushing the cache doesn’t have any negative side effects.
What happens if I flush my DNS cache?
Flushing DNS will clear any IP addresses or other DNS records from your cache. This can help resolve security, internet connectivity, and other issues. It’s important to understand that your DNS cache will clear itself out from time to time without your intervention.
Where is the DNS cache located?
Windows: Open your command prompt and enter the command “ipconfig /displaydns.” You should then be able to see the records. Mac: Open the Terminal app, enter the command “sudo discoveryutil udnscachestats,” and input your password. This will display the Unicast DNS cache.
Are DNS records cached?
In fact, as mentioned above, a DNS lookup involves various steps. During a new DNS lookup, the lookup passes through the resolver, root server, and TLD server. At each step, information is gathered and cached for later use.
Who caches DNS records?
A DNS cache (sometimes called a DNS resolver cache) is a temporary database, maintained by a computer’s operating system, that contains records of all the recent visits and attempted visits to websites and other internet domains.
Does DNS cache flush automatically?
Flushing DNS will clear any IP addresses or other DNS records from your cache. This can help resolve security, internet connectivity, and other issues. It’s important to understand that your DNS cache will clear itself out from time to time without your intervention.
Does restarting flush DNS cache?
A DNS Server’s cache is cleared at reboot. Other than that you can manually clear the cache at any time by using the DNS Admin console. If you leave the cache alone, the individual records are removed from the DNS cache as the TTL (time-to-live) expires.