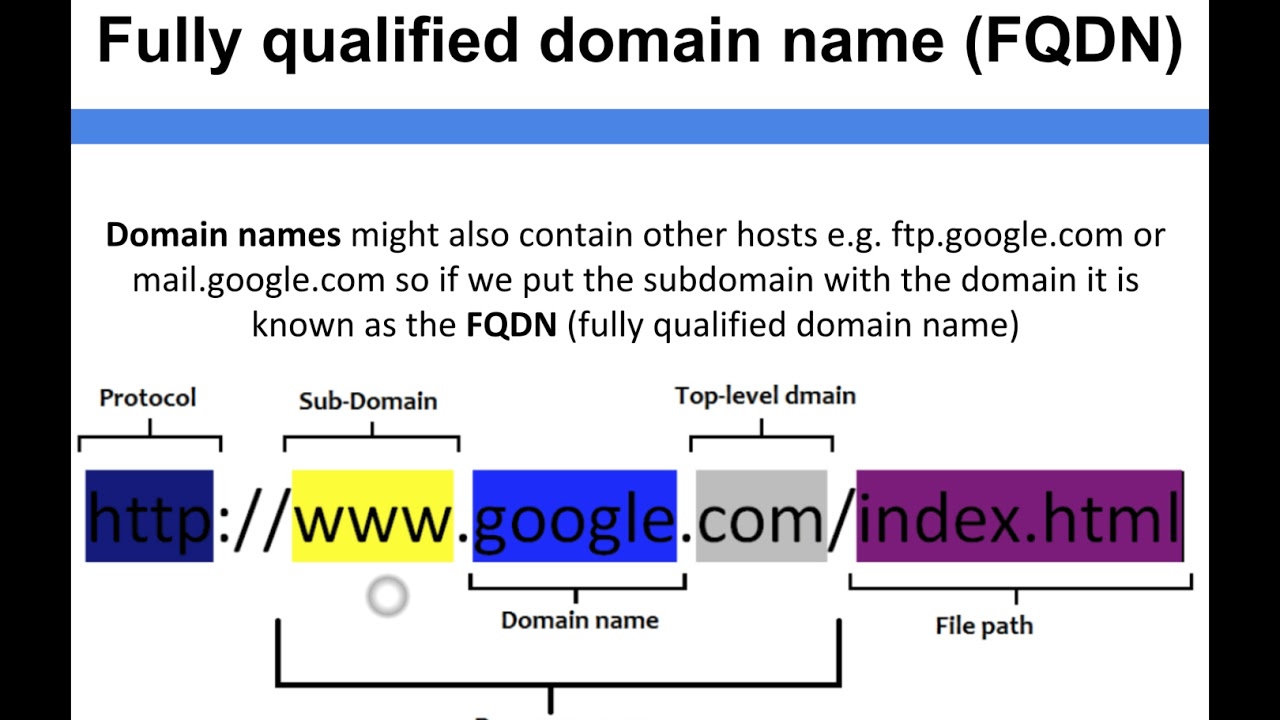
A fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) is that portion of an Internet Uniform Resource Locator (URL) that fully identifies the server program that an Internet request is addressed to.
What is a FQDN example?
A fully qualified domain name (FQDN) is the complete domain name for a specific computer, or host, on the internet. The FQDN consists of two parts: the hostname and the domain name. For example, an FQDN for a hypothetical mail server might be mymail.somecollege.edu .
Whats is my FQDN?
Where to Find the FQDN? On your Windows PC, follow these steps to find your FQDN: Launch the Control Panel by searching for “Control Panel” in the Start Menu, or by typing Win+R and typing “control.exe” in the Run menu. On the System Information screen, you will see both the hostname and FQDN of your machine.
Is FQDN and DNS name the same?
A fully qualified domain name (FQDN), sometimes also referred to as an absolute domain name, is a domain name that specifies its exact location in the tree hierarchy of the Domain Name System (DNS).
Is an FQDN an IP address?
The FQDN represents the absolute address of the internet presence. “Fully qualified” refers to the unique identification that guarantees that all of the domain levels are specified. The FQDN contains the host name and domain, including the top level domain, and can be uniquely assigned to an IP address.
What is a FQDN example?
A fully qualified domain name (FQDN) is the complete domain name for a specific computer, or host, on the internet. The FQDN consists of two parts: the hostname and the domain name. For example, an FQDN for a hypothetical mail server might be mymail.somecollege.edu .
Is FQDN and DNS name the same?
A fully qualified domain name (FQDN), sometimes also referred to as an absolute domain name, is a domain name that specifies its exact location in the tree hierarchy of the Domain Name System (DNS).
Is an FQDN an IP address?
The FQDN represents the absolute address of the internet presence. “Fully qualified” refers to the unique identification that guarantees that all of the domain levels are specified. The FQDN contains the host name and domain, including the top level domain, and can be uniquely assigned to an IP address.
How do I create a FQDN?
To configure an FQDN on your server, you should have: An A Record configured in your DNS pointing the host to your server’s public IP address. A line in your /etc/hosts file referencing the FQDN. See our documentation on the system’s host file: Using Your System’s hosts File.
Does every computer have a FQDN?
Workgroup computers don’t have an FQDN unless you specifically configure them to have one. They have only a NetBIOS (single label) name. Also, don’t confuse the Primary DNS suffix with the DNS suffix search list as assigned by DHCP because they’re two different things. Save this answer.
How do I use FQDN instead of IP address?
Using a FQDN instead of an IP address provides the capability to reduce or eliminate outages stemming from IP address changes, caused either by the migration of services from one host/server to another, or by a change of the virtual host or service.
How do I ping FQDN?
A quick way to view the fully qualified domain name is using the “ping” command in the Windows command line utility. The fully qualified domain name (FQDN) is the standard “computer_name.domain.com” format where “computer_name” is the name given to your server when you installed Windows.
Does FQDN include port number?
A FQDN is not the same as a URL (universal resource locator), but rather it is a part of it. This is because a FQDN lacks the TCP/IP protocol name (e.g., http or ftp) that is always used at the start of a URL. Moreover, a URL can also include a directory path, a file name and a TCP port number.
Why do we need FQDN?
An FQDN enables each entity connected to the internet (computer, server, etc.) to be uniquely identified and located within the internet framework. Think of the DNS as the address book of the internet, which locates and translates domain names into IP addresses.
What is my host name?
In the window the window that appears on the bottom-left hand corner of your screen, type in cmd and click OK. The command prompt window will appear. In this window, type hostname and press Enter. The name of your computer will be displayed.
What is hostname and domain name?
A host, or website, on the Internet is identified by a host name, such as www.example.com . Host names are sometimes called domain names. Host names are mapped to IP addresses, but a host name and an IP address do not have a one-to-one relationship. A host name is used when a web client makes an HTTP request to a host.
Why would you ping an Internet site using FQDN?
Using a FQDN instead of an IP address means that, if you were to migrate your service to a server with a different IP address, you would be able to simply change the record in DNS rather than try and find everywhere that the IP address is used.
How do I find hostname from IP address?
Querying DNS Click the Windows Start button, then “All Programs” and “Accessories.” Right-click on “Command Prompt” and choose “Run as Administrator.” Type “nslookup %ipaddress%” in the black box that appears on the screen, substituting %ipaddress% with the IP address for which you want to find the hostname.
Can I use hostname instead of IP?
When a host name is defined, you can specify a machine by host name instead of IP address. The host names vary depending on the network environment. Use the host name set to the data file on the DNS server.
How do I know if my FQDN is valid?
The validation of FQDN object is performed using RegEx pattern ^([a-zA-Z0-9. _-])+$ by the system to determine if a given hostname uses valid characters. Where ^ specifies start of a string, and $ specifies end of a string and + indicates one or more strings in the Round Brackets. [a-zA-Z0-9.
How do I use FQDN instead of IP address?
Using a FQDN instead of an IP address provides the capability to reduce or eliminate outages stemming from IP address changes, caused either by the migration of services from one host/server to another, or by a change of the virtual host or service.
What is PQDN example?
A PQDN is a domain name on an internal network that may include a host name and a domain name but does not include an ICANN registered TLD if any at all. For example, on local network if the name of your computer is (batman), and your company’s domain is (. centre.