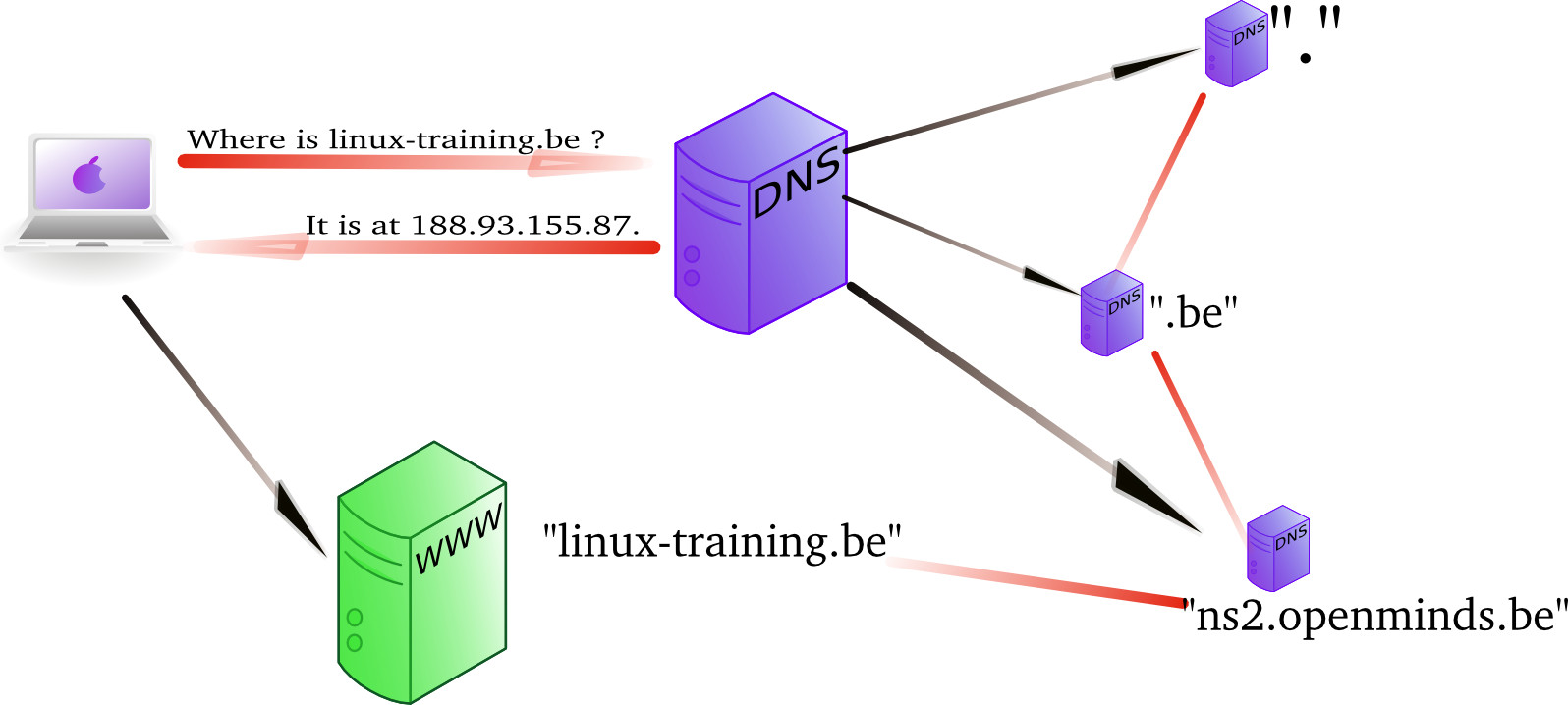
There’s a few reason for using caching-only DNS servers: Better security – internal servers can do dns lookup within the internal network, so can close the dns port from network to the public. Better performance – you get faster response times if dns lookup a server want is already cached.
Why do we use DNS caching?
DNS caching allows any DNS server or client to locally store the DNS records and re-use them in the future – eliminating the need for new DNS queries. The Domain Name System implements a time-to-live (TTL) on every DNS record. TTL specifies the number of seconds the record can be cached by a DNS client or server.
What is caching-only server in DNS?
A cache-only server is a server that is not a master server for any zone other than the in-addr.arpa. domain. A cache-only server handles the same kind of queries from clients that authoritative name servers perform. But the cache-only server does not maintain any authoritative data itself.
Why do we use DNS caching?
DNS caching allows any DNS server or client to locally store the DNS records and re-use them in the future – eliminating the need for new DNS queries. The Domain Name System implements a time-to-live (TTL) on every DNS record. TTL specifies the number of seconds the record can be cached by a DNS client or server.
How does DNS caching affect the network?
Ultimately, the DNS enables human users to keep track of more web pages and to access them as required, and DNS caching expedites the DNS lookup process to more quickly resolve a domain name to an IP address when the OS has visited a web page before.
What is a caching only DNS server quizlet?
cache-only DNS server. A cache-only DNS server obtains all DNS information from other DNS servers. It does not store host information in domain files and does not perform zone transfers. A cache-only DNS server must have at least one root server or forwarder listed, or it cannot resolve domain names.
How does caching only server differ from a normal DNS server?
Caching servers have the advantage of answering recursive requests from clients. While authoritative-only servers may be ideal for serving specific zone information, caching DNS servers are more broadly useful from a client’s perspective.
What does clearing DNS cache do?
Flushing DNS will clear any IP addresses or other DNS records from your cache. This can help resolve security, internet connectivity, and other issues. It’s important to understand that your DNS cache will clear itself out from time to time without your intervention.
Where is the DNS cache?
To display the contents of the DNS resolver cache: Type ipconfig /displaydns and press Enter. Observe the contents of the DNS resolver cache. It is generally not necessary to view the contents of the DNS resolver cache, but this activity may be performed as a name resolution troubleshooting method.
Where DNS cache is stored?
It is maintained by your computer, and it contains records of all the recently visited websites and their IP addresses. It serves as a database that keeps a copy of a DNS lookup, locally stored on your browser or operating system. Your computer can quickly refer to it whenever trying to load a website.
Which would be the best place to cache DNS data?
The answer is DNS cache. DNS cache would be the best place to cache DNS data. A DNS cache or a DNS resolver cache can be considered as a temporary database that is being maintained by a computer’s operating system.
Why do we use DNS caching?
DNS caching allows any DNS server or client to locally store the DNS records and re-use them in the future – eliminating the need for new DNS queries. The Domain Name System implements a time-to-live (TTL) on every DNS record. TTL specifies the number of seconds the record can be cached by a DNS client or server.
Which would be the best place to cache DNS data?
The answer is DNS cache. DNS cache would be the best place to cache DNS data. A DNS cache or a DNS resolver cache can be considered as a temporary database that is being maintained by a computer’s operating system.
What is DNS zone What is DNS cache and how it works?
The DNS cache (also known as DNS resolver cache) is a temporary DNS storage on a device (your computer, smartphone, server, etc.) that contains DNS records of already visited domain names (A records for IPv4 addresses, AAAA records for IPv6, etc.). It keeps those records, depending on their time-to-live (TTL).
What strategy does a local caching DNS server use to look up records?
What strategy does a local, caching DNS server use to look up records when asked? DNS requests from a local caching server start with the cache, then move to root servers and then subsequent servers, always getting closer to the final destination.
What is the purpose of a DNS server quizlet?
What do DNS servers do? Store, maintain, & update parts of the database for which they have authority, & consult them when responding to requests to resolve specified host names into IP addresses.
What is the function of a DNS server?
DNS servers convert URLs and domain names into IP addresses that computers can understand and use. They translate what a user types into a browser into something the machine can use to find a webpage.
What statement regarding DNS implementation is accurate quizlet?
What statement regarding DNS implementation is accurate? A domain should ideally have two or more DNS servers to take advantage of load balancing and multimaster relationships, as well as fault tolerance.
How does cache server work?
How does Caching work? The data in a cache is generally stored in fast access hardware such as RAM (Random-access memory) and may also be used in correlation with a software component. A cache’s primary purpose is to increase data retrieval performance by reducing the need to access the underlying slower storage layer.
How do DNS servers determine how long to cache records?
DNS TTL (time to live) is a setting that tells the DNS resolver how long to cache a query before requesting a new one. The information gathered is then stored in the cache of the recursive or local resolver for the TTL before it reaches back out to collect new, updated details.
What is DNS cache manager?
The DNS Cache Manager caches the IP address and DNS hostname pairs and returns the cached value if the DNS hostname has a match in its internal cache. If this checkbox is ticked, the cache will be cleared at the start of the thread.
What happens when you clear DNS cache?
Flushing DNS will clear any IP addresses or other DNS records from your cache. This can help resolve security, internet connectivity, and other issues. It’s important to understand that your DNS cache will clear itself out from time to time without your intervention.