It doesn’t decide randomly. You’re connected to a router which gets it IP from a company which has DNS servers. They get your request unless you alter the IP manually to another DNS, for instance: OpenDns. Or perhaps you decide on having your own DNS servers.
How does computer know which DNS server?
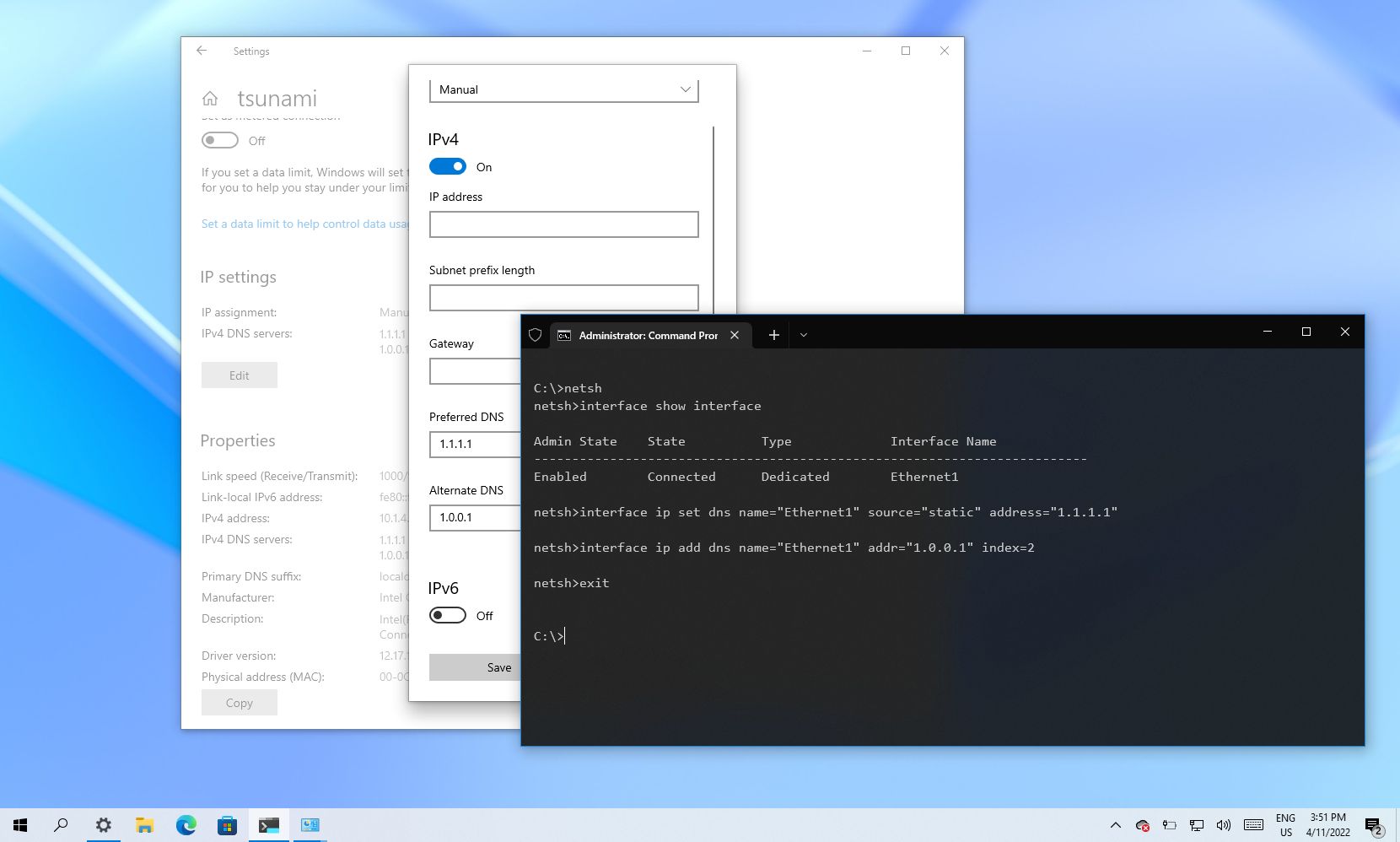
Your computer can locate a DNS server because it’s told the address of one (or preferably more) DNS servers in it’s networking configuration. That info is either obtained dynamically (from another protocol called DHCP) or it’s configured statically for a specific network interface.
How are DNS servers assigned?
The DNS system provides a domain name to IP address mapping for devices connected to the Internet, and it is crucial to the working of the Internet. Usually you don’t need to worry about it as your are automatically assigned the address of the DNS server by your ISP and Home router.
What order does Windows use DNS servers?
The standard order in which Windows resolves names to IP addresses is as follows: 1. Host name (the host itself) 2. DNS resolver cache (the Windows service “DNS Client”) 3.
What DNS server should I use Windows 10?
If you want to use a third-party DNS server, some of the best options are the Google Public DNS, Cloudflare, and OpenDNS. Each of these providers has a primary and secondary DNS address that you can use. Google’s Public DNS is one of the most popular addresses because it is so easy to remember.
What order does Windows use DNS servers?
The standard order in which Windows resolves names to IP addresses is as follows: 1. Host name (the host itself) 2. DNS resolver cache (the Windows service “DNS Client”) 3.
How does a computer find a server?
Computers actually find each other using unique IP addresses, Internet Protocol addressses. IP addresses are defined in the TCP/IP suite, the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP). TCP/IP defines how data is transferred between networks and over the Internet.
Can I use 8.8 8.8 DNS?
8.8. 8.8 is the primary DNS, 8.8. 4.4 is the secondary one. Google DNS service is free to use and can be used by anyone who has access to the Internet.
What does changing the DNS to 8.8 8.8 do?
By changing your 8.8. 8.8 DNS, you are switching your operator from your ISP to Google Public DNS. It protects users from DDOS and malware attacks. However, by doing this, Google can see all your DNS queries and collect even more data.
Why do companies have their own DNS server?
A local DNS is vital for enterprise level and larger companies. A DNS server keeps IP addresses inside a company network private. They are invisible to the outside world. It also helps to add zest to your network speeds.
What is the 8.8 4.4 DNS server?
8.8. 4.4 is the secondary DNS server for Google Public DNS. Google Public DNS is a global DNS service that is run by Google for the purpose of making the Internet and the DNS system faster, safer, secure, and more reliable for everyone online.
How does a Windows DNS server work?
A DNS Server contains Forward Lookup Zone and Reverse Lookup Zone. Each zone contains different types of resource records. A Forward Lookup Zone maps host name to an IP address while Reverse Lookup Zone maps the IP address of the host name. The DNS Zone is stored in a file or in the Active Directory database.
Does Windows 10 still use NetBIOS?
NetBIOS is a somewhat obsolete broadband protocol. Yet, despite its vulnerabilities, NetBIOS is still enabled by default for network adapters in Windows.
Is changing DNS server safe?
Switching from your current DNS server to another one is very safe and will never harm your computer or device. However, ensure you are changing to a known and reliable server, such as Cloudflare or another third-party server that does not sell your data.
What is the fastest DNS server?
Cloudflare built 1.1.1.1 to be the “internet’s fastest DNS directory,” and will never log your IP address, never sell your data, and never use your data to target ads. They also have IPv6 public DNS servers: Primary DNS: 2606:4700:4700::1111.vor 4 Tagen
Should you change your DNS server?
Which DNS (Domain Name System) server do you use? If you don’t know the answer, it’s a good bet that you’re using your ISP’s (Internet Service Provider’s) servers, and you can do better. Changing your default DNS server can boost your security, privacy, and speed (by a few milliseconds, but hey, why not?).
When your computer requests a DNS lookup which DNS server holds the most reliable information for that DNS record?
An authoritative DNS server holds and maintains DNS records. It is the last server in a DNS lookup chain that responds with the queried DNS record. An authoritative DNS ultimately allows a web browser with the URL request to reach the IP address needed to access a website or other web resources.
When you make a DNS query Where does your computer first check to find an IP address?
When you make a DNS query, where does your computer first check to find an IP address to name mapping? Your local machine.
What order does Windows use DNS servers?
The standard order in which Windows resolves names to IP addresses is as follows: 1. Host name (the host itself) 2. DNS resolver cache (the Windows service “DNS Client”) 3.
Who hosts DNS servers?
ICANN is the global non-profit organization responsible for coordinating the Internet’s core systems of unique identifiers, most notably the Domain Name System (DNS).
Where are DNS servers located?
These servers reside in your ISP’s data centers, and they handle requests as follows: If it has the domain name and IP address in its database, it resolves the name itself. If it doesn’t have the domain name and IP address in its database, it contacts another DNS server on the internet.
Is 1.1.1.1 still the fastest DNS?
The independent DNS monitor DNSPerf ranks 1.1.1.1 the fastest DNS service in the world. Since nearly everything you do on the Internet starts with a DNS request, choosing the fastest DNS directory across all your devices will accelerate almost everything you do online.