Boot manager is essentially your drive where your OS is installed on. You should see something like Windows Boot Manager (name of your SSD). So yeah it’s normal that if you disable it, your OS won’t load. You are disabling your main drive.
What is Windows Boot Manager in BIOS?
The Windows Boot Manager is a Microsoft-provided UEFI application that sets up the boot environment. Inside the boot environment, individual boot applications started by the Boot Manager provide functionality for all customer-facing scenarios before the device boots.
How do I get rid of Windows Boot Manager in BIOS?
From the System Utilities screen, select System Configuration > BIOS/Platform Configuration (RBSU) > Boot Options > Advanced UEFI Boot Maintenance > Delete Boot Option and press Enter.
Why do I get Windows Boot Manager?
Windows Boot Manager is used on recent versions of Windows to handle the startup process when you turn on or restart your computer. Earlier versions, prior to Windows 7, used a similar tool called NTLDR.
Why does my computer say boot manager?
The software that walks you through the startup process comes preinstalled with your Windows device and is called the Windows Boot Manager, or “bootmgr”. It is necessary for Windows to function properly as without it, you won’t be able to automatically load up your operating system (OS).
Is it OK to disable Windows Boot Manager?
The Need to Disable Windows Boot Manager If you are using dual OS, Windows Boot Manager gives an option to choose the operating system. However, when there’s only one OS this slows down the boot process. Therefore, to reduce the wait time we should disable the Windows Boot Manager.
Should you boot with Windows Boot Manager?
Without it your windows won’t load. Boot manager is essentially your drive where your OS is installed on. You should see something like Windows Boot Manager (name of your SSD). So yeah it’s normal that if you disable it, your OS won’t load.
What happens if you delete Windows Boot Manager?
Deleting the boot loader entry of an installed operating system (ex: “Windows 7”) will not uninstall the operating system. It will only remove the boot loader entry (ex: “Windows 7”) from being displayed on the boot options menu.
Is Windows Boot Manager the hard drive?
The Windows Boot Manager is also known as Boot loader occasionally. The reason is technical. All your files—including the operating system and other critical system data—are stored on the hard drive when it’s powered off.
What does a boot manager do?
A boot manager is a software utility for choosing what operating system to load from a list of operating systems installed on a hard drive.
Is Windows Boot Manager the hard drive?
The BOOTMGR file itself is both read-only and hidden, which is located in the root directory of the partition. It is marked as “Active” in Disk Management. In most Windows PCs, this partition is labelled as “System Reserved” without hard drive letter.
How do I use Windows Boot Manager?
On most computers, this can be accomplished by pressing the “F8” key as soon as your computer turns on. When the Windows Boot Manager menu opens, you can use the arrow keys to select an operating system or external boot source and then press “ENTER” to load it.
What does a boot manager do?
A boot manager is a software utility for choosing what operating system to load from a list of operating systems installed on a hard drive.
How do I remove the boot manager from my HP laptop?
When you launch it, click the Edit Boot Menu button. You should see the list of boot options. Remove the one you no longer want and click Save Settings.
Where is the Windows Boot Manager located?
It is located in the root directory of the partition marked as Active in Disk Management. On most Windows computers, this partition is labeled as System Reserved and doesn’t obtain a drive letter. If you don’t have a System Reserved partition, BOOTMGR is probably located on your primary drive, which is usually C:.
What should your boot option be?
What should my boot sequence be? Your boot sequence should be set to how you want the computer to boot. For example, if you never plan on booting from a disc drive or a removable device, the hard drive should be the first boot device.
How do I manage Windows Boot Manager?
You can manage the Boot Manager from Advanced System Properties, System Configuration (MSConfig.exe) tool, or Windows command Prompt (BCDEdit command). BOOTMGR provides useful information for troubleshooting and resolving Windows boot errors.
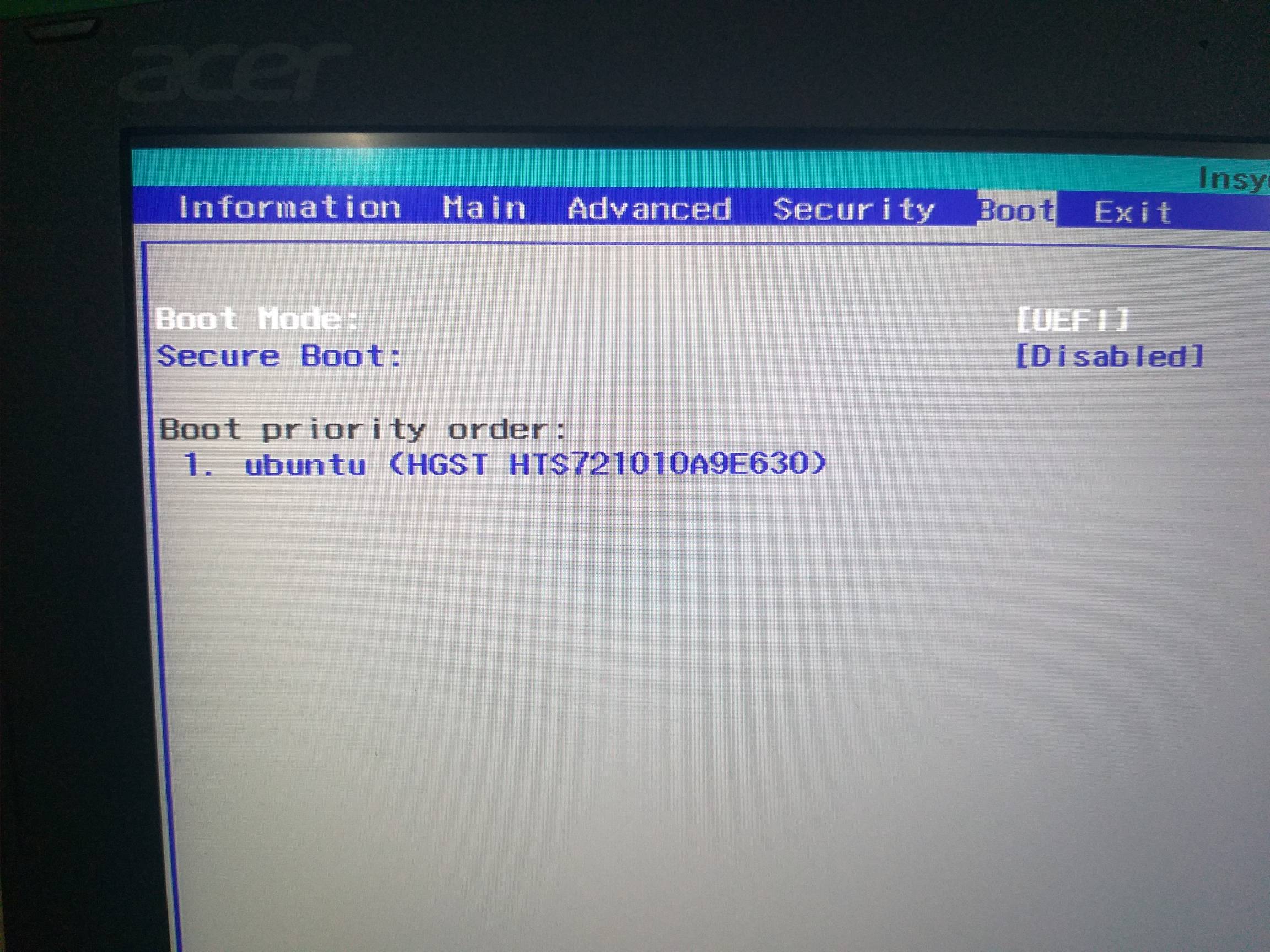
What should be the boot priority order?
The first device in the order list has the first boot priority. For example, to boot from a CD-ROM drive instead of a hard drive, place the CD-ROM drive ahead of it in the priority list. While you are in the BIOS Setup Utility, you will not be able to use your mouse.
Which file is the Windows Boot Manager?
The Boot. ini file is a text file that contains the boot options for computers with BIOS firmware running NT-based operating system prior to Windows Vista. It is located at the root of the system partition, typically c:\Boot. ini.
How do I update Windows Boot Manager?
Editing Boot Options You can also use the System Configuration utility (MSConfig.exe) to change boot settings. In addition, many options can be set using the Advanced Startup settings UI. To change boot options programmatically in Windows, use the Windows Management Instrument (WMI) interface to boot options.
Why do I have two Windows 10 boot options?
This may occur because you previously used multiple operating systems or because of a mistake during an operating system upgrade. Previously, Windows used a simple text file to create these boot options; however, the latest Window operating systems require the modification of the bootmgr.
What is UEFI boot mode?
UEFI Mode (default)—Configures the system to boot to a UEFI compatible operating system. Legacy BIOS Mode—Configures the system to boot to a traditional operating system in Legacy BIOS compatibility mode.