Spindle fiber is most abundantly composed of the microtubule, which is a polymer of 𝜶 and 𝞫-tubulin dimer. Also, the spindle fiber is made up of several hundreds of associated proteins.
Are spindles made of tubulin?
The mitotic spindle is a highly dynamic molecular machine composed of tubulin, motors, and other molecules. It assembles around the chromosomes and distributes the duplicated genome to the daughter cells during mitosis.
What are spindles made of in mitosis?
The spindle is built of microtubules that are used as tracks to move chromosomes precisely during cell division. In the spindle, microtubules are arranged in two antiparallel arrays with their plus ends at the equator and their minus ends at the poles, whatever the detailed shape of the spindle (Fig.
How are spindle fibers formed?
Spindle fibers are formed from microtubules with many accessory proteins which help guide the process of genetic division. Each spindle fiber forms during cellular division near the poles of the dividing cell. As they extend across the cell, they search for the centromere of each chromosome.
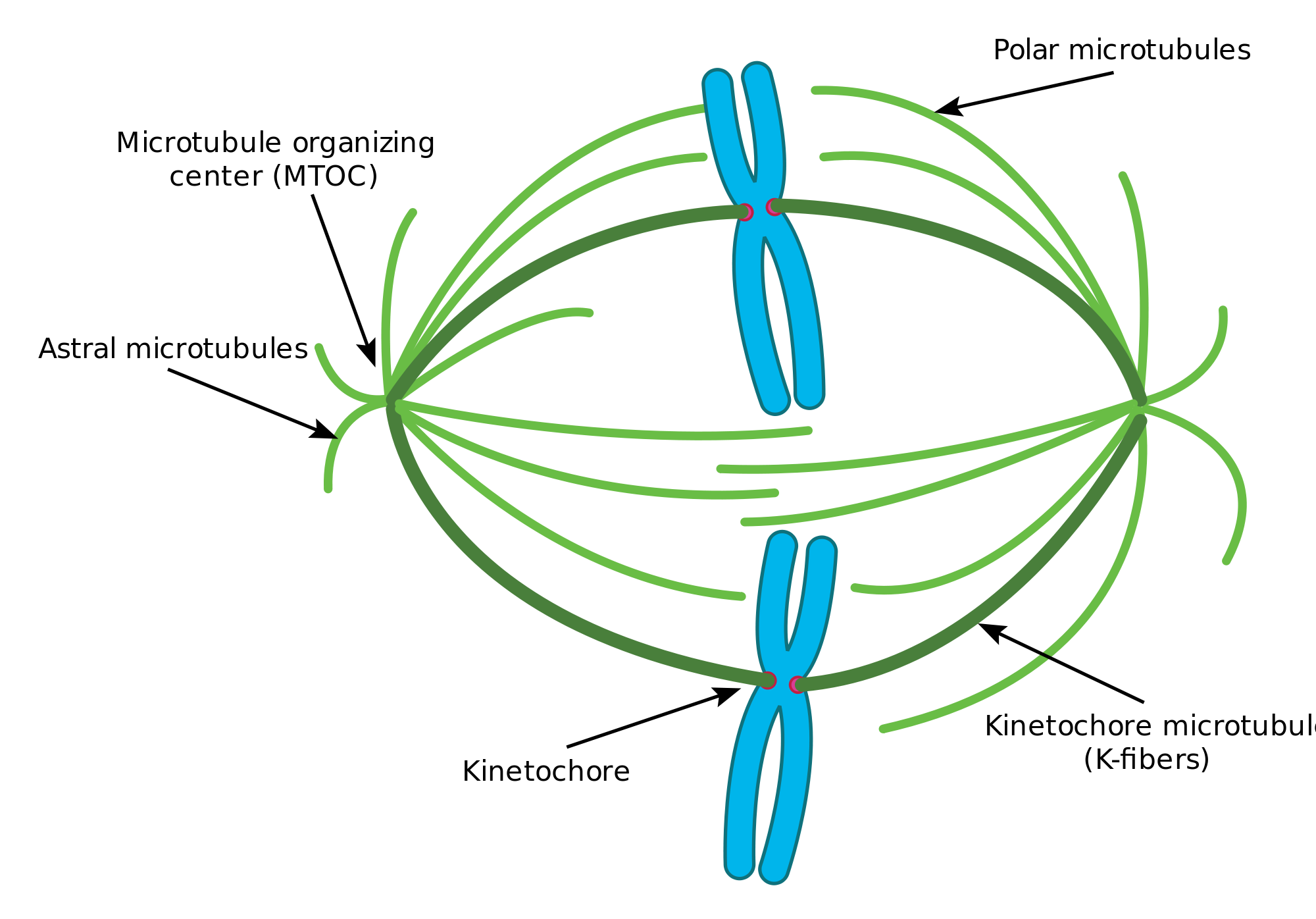
What are the 3 types of spindle microtubules?
Spindle microtubules can be divided into three major classes: kinetochore microtubules, which form k-fibers ending at the kinetochore; interpolar microtubules, which extend from the opposite sides of the spindle and interact in the middle; and astral microtubules, which extend towards the cell cortex.
How many microtubules are in a spindle?
Extra kinetochores increase microtubule number. ). Postreplication chromosomes consist of two chromatids each with a centromere that recruits a kinetochore (Figure 1A), so 2 microtubules are required to attach a single replicated chromosome to the spindle, and 32 are required to attach all 16 replicated chromosomes.
What proteins make the mitotic spindle?
Mitotic spindle is mainly made of microtubules. These microtubules are made by polymerisation of globular tubulin proteins.
What is a spindle?
1 : a slender round rod or stick with narrowed ends by which thread is twisted in spinning and on which it is wound. 2 : something (as an axle or shaft) which has a slender round shape and on which something turns. spindle. noun. spin·dle | \ ˈspin-dᵊl \
How many types of spindle fibres are there?
There are 2 types of spindle fibres which are identified – the interpolar fibre, stretching continuously from one to another of the spindle; kinetochore fibre. It stretches from the pole to the kinetochore of a chromosome.
What are spindle fibers attached to?
During metaphase, spindle fibers attach to the centromere of each pair of sister chromatids (see Figure below). The sister chromatids line up at the equator, or center, of the cell. This is also known as the metaphase plate.
Are spindle fibres made of protein?
Spindle fibres are the cytoskeletal structure of eukaryotic cells, that are formed during cell division. It contracts and expands to separate sister chromatids between daughter cells. It is made up of microtubules, which are composed of protein tubulin.
Why is tubulin used in Western blots?
Beta-Tubulin, is usually used as loading control for Western Blot to normalize the levels of protein detected by confirming that protein loading is the same across the gel.
What is the role of tubulin in mitosis?
Tubulin is the protein that polymerizes into long chains or filaments that form microtubules, hollow fibers which serve as a skeletal system for living cells. Microtubules have the ability to shift through various formations which is what enables a cell to undergo mitosis or to regulate intracellular transport.
Where is tubulin found in a cell?
It is found primarily in centrosomes and spindle pole bodies, since these are the areas of most abundant microtubule nucleation.
Where is tubulin found in the body?
The tubulin family of proteins are vital components of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton and are the main constituent of microtubules in living cells. The tubulin proteins α- and β polymerize into long chains or filaments that form microtubules, an essential element of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton.
What are microtubules made of?
In contrast to intermediate filaments, which are composed of a variety of different fibrous proteins, microtubules are composed of a single type of globular protein, called tubulin. Tubulin is a dimer consisting of two closely related 55-kd polypeptides, α-tubulin and β-tubulin.
What does a spindle fiber look like?
When viewed using a light microscope, the “spindle” (named after a device used for spinning thread) looks like a hairy, elongated ball originating (in animal cells) from the asters around the centrioles, or from opposite sides of the plant cell.
Where are spindle fibers located?
Spindle fibers work by growing toward chromosomes lined up in the middle of a cell during metaphase of either mitosis or meiosis. They extend out of centrosomes and centrioles that are a part of animal cells.
What is the role of the spindle during mitosis?
The mitotic spindle is the macromolecular machine that segregates chromosomes to two daughter cells during mitosis. The major structural elements of the spindle are microtubule polymers, whose intrinsic polarity and dynamic properties are critical for bipolar spindle organization and function.
Are mitotic spindles microtubules?
The mitotic spindle is a microtubule-made machine required for chromosome segregation during mitosis. Several pathways and molecules contribute to the assembly of this structure, which shows intrinsic dynamic properties.
Where are spindles used?
On a lathe (whether wood lathe or metal lathe), the spindle is the heart of the headstock. In rotating-cutter woodworking machinery, the spindle is the part on which shaped milling cutters are mounted for cutting features (such as rebates, beads, and curves) into mouldings and similar millwork.
What is a cotton spindle?
Spindles are machine tools which rotate on an access. They are present in wood lathes, milling equipment and drill presses, as well as cotton pickers. On a spindle harvester, their job is to rotate at high-speeds to remove the seeds from the cotton.