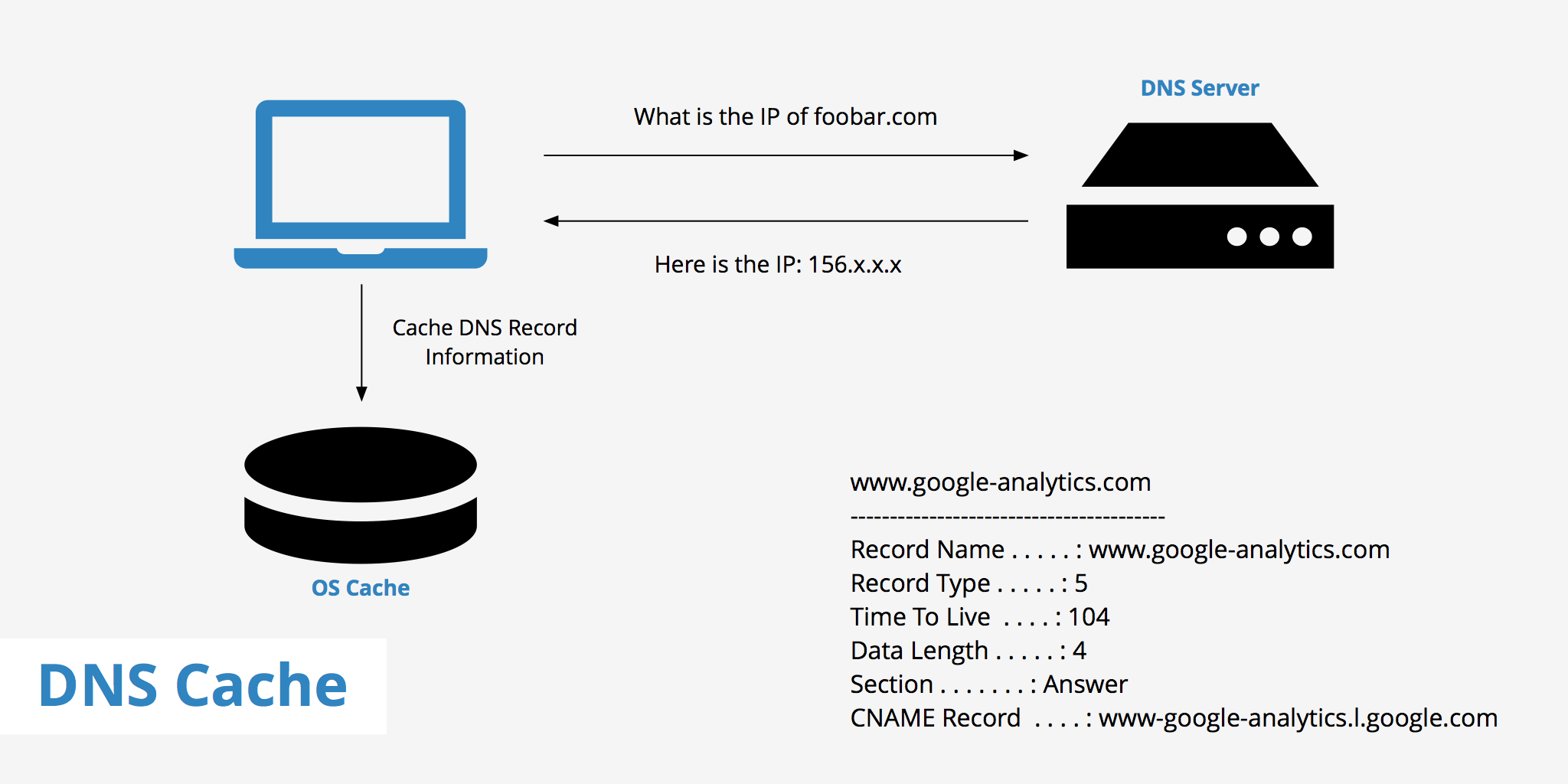
However, DNS record information is usually cached (stored on your local browser, computer or network forwarder) for a specific amount of time; anywhere from 5 minutes to 8 hours is normal.
Does browser keep DNS cache?
Google Chrome is not an operating system of course, but it does keep a DNS cache of its own. This is separate from your operating system’s cache and from Chrome’s browser cache. If Chrome is set as your default web browser, then you’ll need to clear Chrome’s DNS cache as well as your operating system’s DNS cache.
How often does the DNS cache refresh?
When a DNS client creates a record, it is assigned a timestamp. The DNS client attempts to refresh this record every 24 hours. Unless the record is changed (for example, the client receives a new IP address), the timestamp cannot be refreshed for a default period of seven days.
Does DNS cache flush automatically?
The DNS cache doesn’t ever flush, unless you explicitly tell it to or you make a DNS/networking related configuration change. DNS records have a Time To Live (TTL) value associated with them which tells a DNS cache how long the particular record is good for. Records in the cache are kept for their TTL, then re-queried.
How long is a DNS valid?
This is because those records are handled by the zone parent DNS servers (for example, the .com DNS servers if your domain is example.com), which typically cache those records for 48 hours. However, those DNS changes are immediately available for any DNS servers that do not have them cached.
Does Chrome keep DNS cache?
Google Chrome also keeps a DNS cache of its own, and it is separate from the DNS cache stored by your operating system. If you use Google Chrome as your main browser, then you’ll need to clear Chrome’s DNS cache as well.
Does Google Chrome cache DNS?
Yes, Google Chrome browser has inbuilt DNS and proxy caching server to improve performance. You can quickly clean out or flush out DNS entries manually on Google Chrome browser.
How long does it take for DNS to flush?
A DNS change requires up to 72 hours to propagate worldwide, although most often this happens in a matter of hours.
How long do DNS changes take?
DNS propagation is the time frame it takes for DNS changes to be updated across the Internet. A change to a DNS record—for example, changing the IP address defined for a specific hostname—can take up to 72 hours to propagate worldwide, although it typically takes a few hours.
How often should I flush my DNS cache?
The TTL was defined in SOA record of specific zone in DNS server. If you need clear DNS cache from client side for every 15 minutes, it is OK. After these caches were cleared, if needed, the client will re-query these records from DNS server. TTL times are always represented in seconds.
How do I completely flush my DNS?
To Flush the DNS Cache: 1.At the bottom left corner, type ‘cmd’ in the Start menu’s search bar, and press Enter. 2. Type ‘ipconfig /flushdns’ in the Command Prompt, and press Enter.
How do I refresh my DNS cache?
Navigate to All Programs > Accessories and select Command Prompt. In the command line interface, run ipconfig /flushdns . You should receive a confirmation message once the DNS cache is flushed.
Who is DNS record?
What is a DNS record? DNS records (aka zone files) are instructions that live in authoritative DNS servers and provide information about a domain including what IP address is associated with that domain and how to handle requests for that domain.
Who hosts DNS servers?
ICANN is the global non-profit organization responsible for coordinating the Internet’s core systems of unique identifiers, most notably the Domain Name System (DNS).
What happens when DNS TTL expires?
Once the TTL on a cached record expires, a recursive DNS resolver must begin the lookup process anew. It will have to resolve the DNS query via an authoritative nameserver. Separate from DNS caching, TTL is also used to ensure IP packets have a limited lifetime on a network.
How do I clear my DNS cache in my browser?
In the address bar, type chrome://net-internals/#dns. Google Chrome displays a list of hosts in its internal DNS cache. Click Clear host cache.
Does Firefox cache DNS?
Firefox is an Internet browser which integrates a DNS cache feature. This feature automatically saves the DNS settings of websites that you frequently visit. DNS settings are records that contain a website’s domain name and its corresponding Internet Protocol address.
How does browser do DNS lookup?
The browser checks the cache for a DNS record to find the corresponding IP address of maps.google.com. DNS(Domain Name System) is a database that maintains the name of the website (URL) and the particular IP address it links to. Every single URL on the internet has a unique IP address assigned to it.
What is Google Chrome DNS?
Simply put, DNS is an online directory matching domain names (like google.com) to their respective IP addresses. DNS servers are publicly accessible and are routinely used by web browsers to determine the correct IP addresses of websites.
Does Firefox cache DNS?
Firefox is an Internet browser which integrates a DNS cache feature. This feature automatically saves the DNS settings of websites that you frequently visit. DNS settings are records that contain a website’s domain name and its corresponding Internet Protocol address.
How do I check my DNS cache in chrome?
Additionally, you can also check your DNS cache entries on certain browsers. For example, if you’re using Chrome, you can enter: chrome://net-internals/#dns into your address bar which will return your browser’s current list of cached DNS records.
What does Flushing DNS mean?
Operating systems such as Windows automatically generate temporary entries of visited websites in a so-called DNS cache. The information contained in the cache is valid for a defined period of time. A DNS flush, i.e. emptying of the cache, removes the data from the system before the time limit expires.