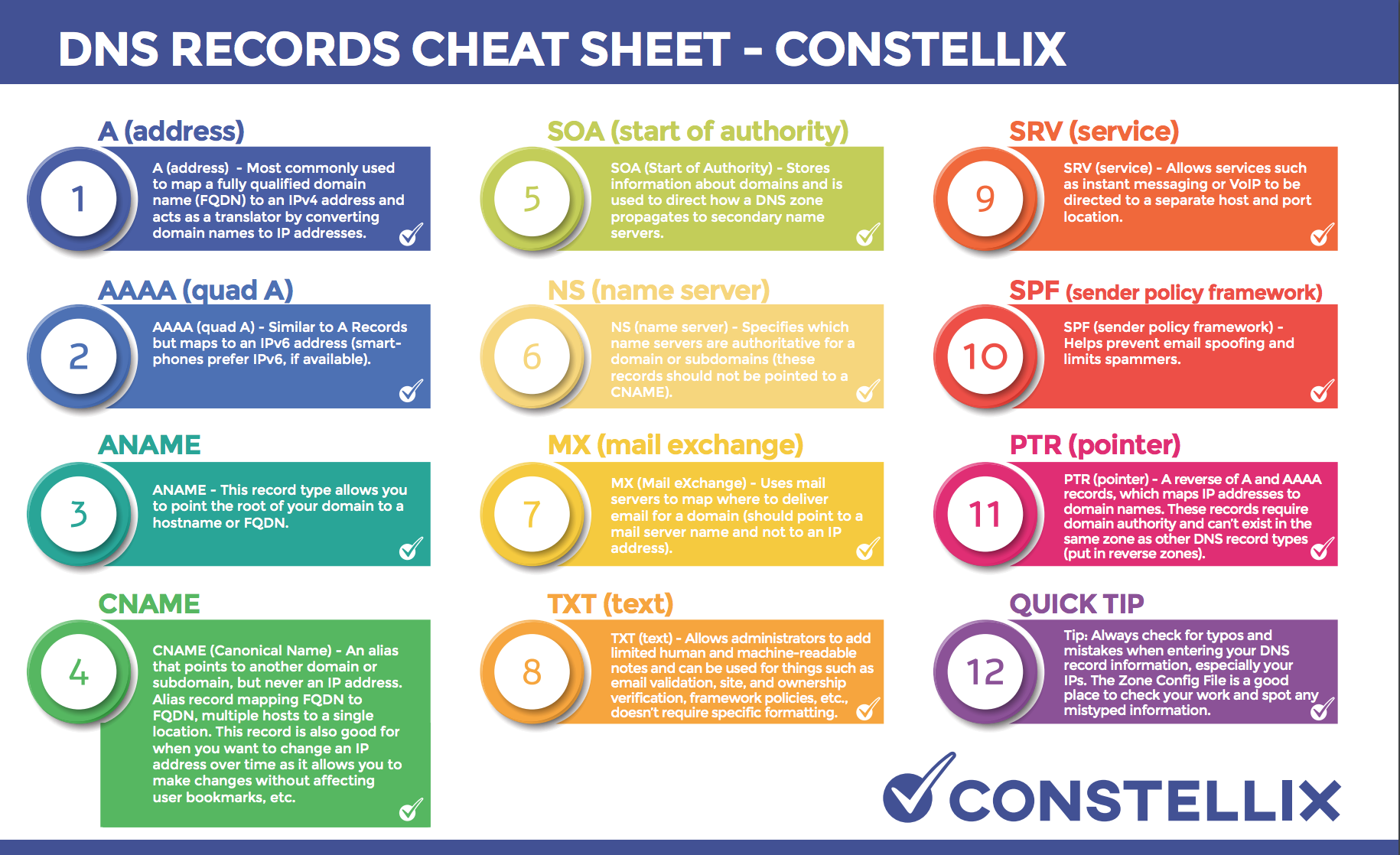
What is a DNS record? DNS records (aka zone files) are instructions that live in authoritative DNS servers and provide information about a domain including what IP address is associated with that domain and how to handle requests for that domain.
What Are Records in DNS?
What is a DNS record? DNS records (aka zone files) are instructions that live in authoritative DNS servers and provide information about a domain including what IP address is associated with that domain and how to handle requests for that domain.
What is a DNS A record example?
As an example, an A Record is used to point a logical domain name, such as “google.com”, to the IP address of Google’s hosting server, “74.125. 224.147”. These records point traffic from example.com (indicated by @) and ftp.example.com to the IP address 66.147. 224.236.
What Are Records in DNS?
What is a DNS record? DNS records (aka zone files) are instructions that live in authoritative DNS servers and provide information about a domain including what IP address is associated with that domain and how to handle requests for that domain.
Why do we need DNS records?
This allows you to change web hosts without changing domain names. Each website has a specific IP address, and the DNS records pair that IP address to the domain name so users don’t need to remember the numeric line. DNS records hold information about every single website on the internet.
Why are DNS records important?
DNS records tell servers precisely how to respond to a DNS query. There are dozens of record types. And more deeply understanding at least some of them can help you better understand what’s happening on your network.
Where are DNS records stored?
DNS records are stored in authoritative servers. These records provide information about a domain, including its associated IP address for each domain. It is mandatory for all domains to have a specific set of default records.
Who keeps DNS records?
Root nameservers are designated servers around the world that are responsible for storing DNS data and keeping the system working smoothly. Once the DNS record is found on the root nameserver, it’s cached by your computer. 4.
What is the most commonly used DNS record?
The most common DNS record types are: Address Mapping record (A Record)—also known as a DNS host record, stores a hostname and its corresponding IPv4 address. IP Version 6 Address record (AAAA Record)—stores a hostname and its corresponding IPv6 address.
How do I create a DNS record?
Right-click the zone where you want to add a resource record, and then click Add DNS resource record. The Add DNS Resource Records dialog box opens. In Resource record properties, click DNS server and select the DNS server where you want to add one or more new resource records.
What is A record used for?
DNS records are used to control the location of a resource on the Internet. As an example, an A Record is used to point a logical domain name, such as “google.com”, to the IP address of Google’s hosting server, “74.125. 224.147”.
How do DNS work?
DNS resolves names to numbers, to be more specific it resolves domain names to IP addresses. So if you type in a web address in your web browser, DNS will resolve the name to a number because the only thing computers know are numbers.
What is DNS and its types?
DNS is a core internet technology that translates human-friendly domain names into machine-usable IP addresses, such as www.example.com into 192.0. 2.1. The DNS operates as a distributed database, where different types of DNS servers are responsible for different parts of the DNS name space.
What is DNS server types?
There are three main kinds of DNS Servers — primary servers, secondary servers, and caching servers.
Are DNS records public?
Public DNS and Private DNS For a server to be accessible on the public internet, it needs a public DNS record, and its IP address needs to be reachable on the internet – that means it’s not blocked by a firewall. Public DNS servers are accessible to anyone that can connect to them and don’t require authentication.
What is A record used for?
DNS records are used to control the location of a resource on the Internet. As an example, an A Record is used to point a logical domain name, such as “google.com”, to the IP address of Google’s hosting server, “74.125. 224.147”.
What is Cname and A record?
A Canonical Name or CNAME record is a type of DNS record that maps an alias name to a true or canonical domain name. CNAME records are typically used to map a subdomain such as www or mail to the domain hosting that subdomain’s content.
Where are DNS records stored?
DNS records are stored in authoritative servers. These records provide information about a domain, including its associated IP address for each domain. It is mandatory for all domains to have a specific set of default records.
What Are Records in DNS?
What is a DNS record? DNS records (aka zone files) are instructions that live in authoritative DNS servers and provide information about a domain including what IP address is associated with that domain and how to handle requests for that domain.
How do I check my DNS records?
Use a website that gathers domain information, like WHOIS lookup, to look up public information about your name server. Search your domain name. Enter your domain name in the search field, such as mywebsite.com, and look up the domain information. Look for Name Server information in search results.
How many A records can a domain have?
maximum:13 A domain name can point to multiple IP addresses. You can have unlimited number of IP address or A records for your domain name or sub-domains. The dns query in this case will be served in a round-robin fashion. Nameserver limits have no bearing on A record limits.
Who hosts DNS servers?
ICANN is the global non-profit organization responsible for coordinating the Internet’s core systems of unique identifiers, most notably the Domain Name System (DNS).