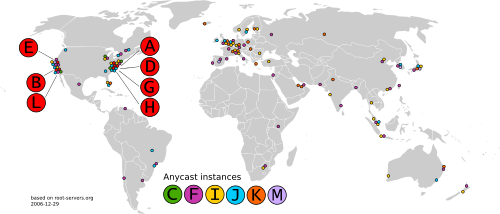
So, you may ask, why are there only 13 root servers? It’s because of the limitations of the original DNS infrastructure, which used only IPv4¹ containing 32 bytes. The IP addresses needed to fit into a single packet, which was limited to 512 bytes at that time.
What are the 13 root server?
The DNS root name servers translate URLs into IP addresses. Each root server is a network of hundreds of servers in countries worldwide. However, they are identified as 13 named authorities in the DNS root zone.
Are there only 13 root servers?
A common misconception is that there are only 13 root servers in the world. In reality there are many more, but still only 13 IP addresses used to query the different root server networks. Limitations in the original architecture of DNS require there to be a maximum of 13 server addresses in the root zone.
How many root servers are there?
In total, there are 13 main DNS root servers, each of which is named with the letters ‘A’ to ‘M’. They all have a IPv4 address and most have an IPv6 address. Managing the root server is ICANN’s responsibility (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers).
What are the 13 root server?
The DNS root name servers translate URLs into IP addresses. Each root server is a network of hundreds of servers in countries worldwide. However, they are identified as 13 named authorities in the DNS root zone.
Are there only 13 root servers?
A common misconception is that there are only 13 root servers in the world. In reality there are many more, but still only 13 IP addresses used to query the different root server networks. Limitations in the original architecture of DNS require there to be a maximum of 13 server addresses in the root zone.
How many DNS servers do I need?
At a minimum, you’ll need two DNS servers for each Internet domain you have. You can have more than two for a domain but usually three is tops unless you have multiple server farms where you would want to distribute the DNS lookup load. It’s a good idea to have at least one of your DNS servers at a separate location.
What do root name servers do?
A Root Name Server is a name server for the domain name server’s root zone that directly answers requests for records in the root zone and also answers other requests, returning a list of the designated authoritative name servers for the appropriate top-level domain; hence, the server to query when looking up a top- …
What DNS 8888?
8.8. 8.8 is the primary DNS server for Google DNS. Google DNS is a public DNS service that is provided by Google with the aim to make the Internet and the DNS system faster, safer, secure, and more reliable for all Internet users.
Who owns domain server?
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) is the non-profit organization that oversees the assignment of both IP addresses and domain names.
Who owns ICANN?
While ICANN began in the U.S. government, it is now and continues to be, an international, community-driven organization independent of any one government.
What is an AAAA record in DNS?
An AAAA record maps a domain name to the IP address (Version 6) of the computer hosting the domain. An AAAA record is used to find the IP address of a computer connected to the internet from a name.
How many servers are there in the world?
There are recent estimates that put the total number of servers in the world to 44 million.
How do I set root hints in DNS?
To update root hints by using the DNS snap-in Click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click DNS. In the right pane, right-click ServerName, where ServerName is the name of the server, and then click Properties. Click the Root Hints tab, and then click Add.
What are the 13 root server?
The DNS root name servers translate URLs into IP addresses. Each root server is a network of hundreds of servers in countries worldwide. However, they are identified as 13 named authorities in the DNS root zone.
Are there only 13 root servers?
A common misconception is that there are only 13 root servers in the world. In reality there are many more, but still only 13 IP addresses used to query the different root server networks. Limitations in the original architecture of DNS require there to be a maximum of 13 server addresses in the root zone.
Which is the fastest DNS in the world?
Cloudflare built 1.1.1.1 to be the “internet’s fastest DNS directory,” and will never log your IP address, never sell your data, and never use your data to target ads. They also have IPv6 public DNS servers: Primary DNS: 2606:4700:4700::1111.
Should I use 8.8 8.8 DNS?
That is not recommended and may even be a violation of your security policies, depending on the level of security required in your organization or by any governing agency. DNS forwarders that only point to 8.8. 8.8 are using your ISP connection to hop to 8.8.
What does changing the DNS to 8.8 8.8 do?
By changing your 8.8. 8.8 DNS, you are switching your operator from your ISP to Google Public DNS. It protects users from DDOS and malware attacks. However, by doing this, Google can see all your DNS queries and collect even more data.
Who hosts DNS servers?
ICANN is the global non-profit organization responsible for coordinating the Internet’s core systems of unique identifiers, most notably the Domain Name System (DNS).
What is a root zone?
Simply put, the root zone of plants is the area of soil and oxygen surrounding the roots of a plant. Roots are the starting point of a plant’s vascular system. Water and nutrients are pulled up from the oxygenated soil around the roots, called the root zone, and pumped into all the aerial parts of the plant.
What is a root domain?
A root domain is the highest level of a domain name hierarchy, and is the starting point for all other domains. A domain is an identification string that defines a realm of administrative autonomy, authority, or control on the Internet. Domains are formed by the rules and procedures of the Domain Name System (DNS).