What is another name for DNS poisoning?
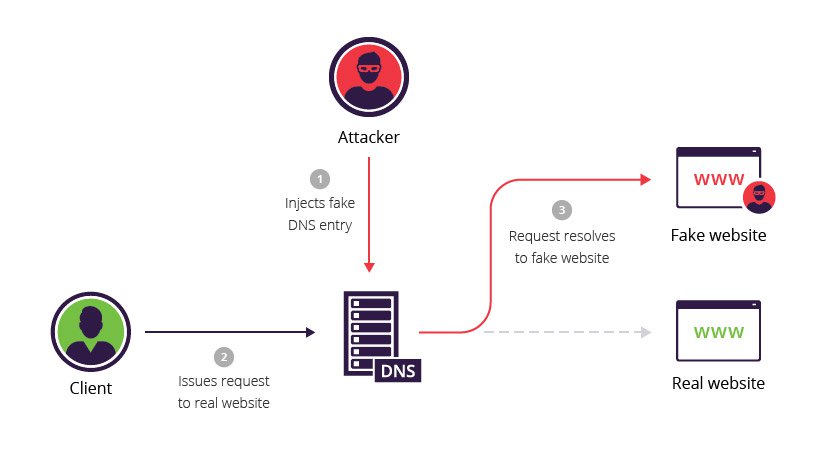
DNS cache poisoning is the act of entering false information into a DNS cache, so that DNS queries return an incorrect response and users are directed to the wrong websites. DNS cache poisoning is also known as ‘DNS spoofing.
What is DNS explain DNS cache poisoning?
Cache poisoning is a type of cyber attack in which attackers insert fake information into a domain name system (DNS) cache or web cache for the purpose of harming users. In DNS cache poisoning or DNS spoofing, an attacker diverts traffic from a legitimate server to a malicious/dangerous server.
How do I know if my DNS is poisoned?
A sudden increase in DNS activity from a single source about a single domain indicates a potential Birthday attack. An increase in DNS activity from a single source that is querying your DNS server for multiple domain names without recursion indicates an attempt to find an entry to use for poisoning.
What is another name for DNS poisoning?
DNS cache poisoning is the act of entering false information into a DNS cache, so that DNS queries return an incorrect response and users are directed to the wrong websites. DNS cache poisoning is also known as ‘DNS spoofing.
What are the 3 types of DNS?
There are three main kinds of DNS Servers — primary servers, secondary servers, and caching servers.
What are 3 types of DNS records?
The three DNS server types server are the following: DNS stub resolver server. DNS recursive resolver server. DNS authoritative server.
What is the difference between DNS poisoning and ARP poisoning?
While DNS poisoning spoofs IP addresses of legitimate sites and its effect can spread across multiple networks and servers, ARP poisoning spoofs physical addresses (MAC addresses) within the same network segment (subnet).
What is difference between DNS spoofing and DNS poisoning?
While the terms DNS poisoning and DNS spoofing are used interchangeably, there’s a difference between the two. DNS Poisoning is the method attackers use to compromise and replace DNS data with a malicious redirect. DNS Spoofing is the end result, where users are redirected to the malicious website via a poisoned cache.
What are common DNS issues?
High DNS latency equals high loading times. High DNS latency can be as a result of the DNS name servers not being in close geographic proximity to a large percentage of users who visit your site. Another reason might be network congestion.
How do I know if my DNS is leaking?
There are easy ways to test for a leak, again using websites like Hidester DNS Leak Test(Opens in a new window), DNSLeak.com(Opens in a new window), or DNS Leak Test.com(Opens in a new window). You’ll get results that tell you the IP address and owner of the DNS server you’re using.
What is DNS also known as?
DNS, or the Domain Name System, translates human readable domain names (for example, www.amazon.com) to machine readable IP addresses (for example, 192.0. 2.44).
What is the correct term for a DNS?
It points to the exact location of a domain name in the domain name system (DNS) tree hierarchy. This is expressed through the three parts that shape every domain name: hostname, second-level domain name, and top-level domain name (TLD).
What is the difference between ARP and DNS poisoning?
While DNS poisoning spoofs IP addresses of legitimate sites and its effect can spread across multiple networks and servers, ARP poisoning spoofs physical addresses (MAC addresses) within the same network segment (subnet).
What is a DNS entry called?
DNS (which stands for domain name system) records are officially called resource records.
What is another name for DNS poisoning?
DNS cache poisoning is the act of entering false information into a DNS cache, so that DNS queries return an incorrect response and users are directed to the wrong websites. DNS cache poisoning is also known as ‘DNS spoofing.
What is a DNS Example?
DNS, or the Domain Name System, translates human readable domain names (for example, www.amazon.com) to machine readable IP addresses (for example, 192.0. 2.44).
What is DNS protocol example?
The DNS protocol works when your computer sends out a DNS query to a name server to resolve a domain. For example, you type “www.firewall.cx” in your web browser, this triggers a DNS request, which your computer sends to a DNS server in order to get the website’s IP Address !
What is DNS zone example?
DNS zones are not necessarily physically separated from one another, zones are strictly used for delegating control. For example, imagine a hypothetical zone for the cloudflare.com domain and three of its subdomains: support.cloudflare.com, community.cloudflare.com, and blog.cloudflare.com.
What are the two types of DNS message?
The DNS protocol uses two types of DNS messages, queries and replies; both have the same format. Each message consists of a header and four sections: question, answer, authority, and an additional space.
What are the two types of DNS zones?
There are two types of DNS zones – Primary (Master) DNS zone for control and Secondary (Slave) DNS zone for redundancy and better performance. The first contains all the original DNS records, and the second gets them from the Primary DNS zone. The process is called DNS zone transfer.
Is DNS a layer 3 or 4?
From a functionality perspective, DNS is pretty clearly part of the application layer (that’s layer 4). It’s invoked by the application layer and rides on top of the transport layer (UDP).