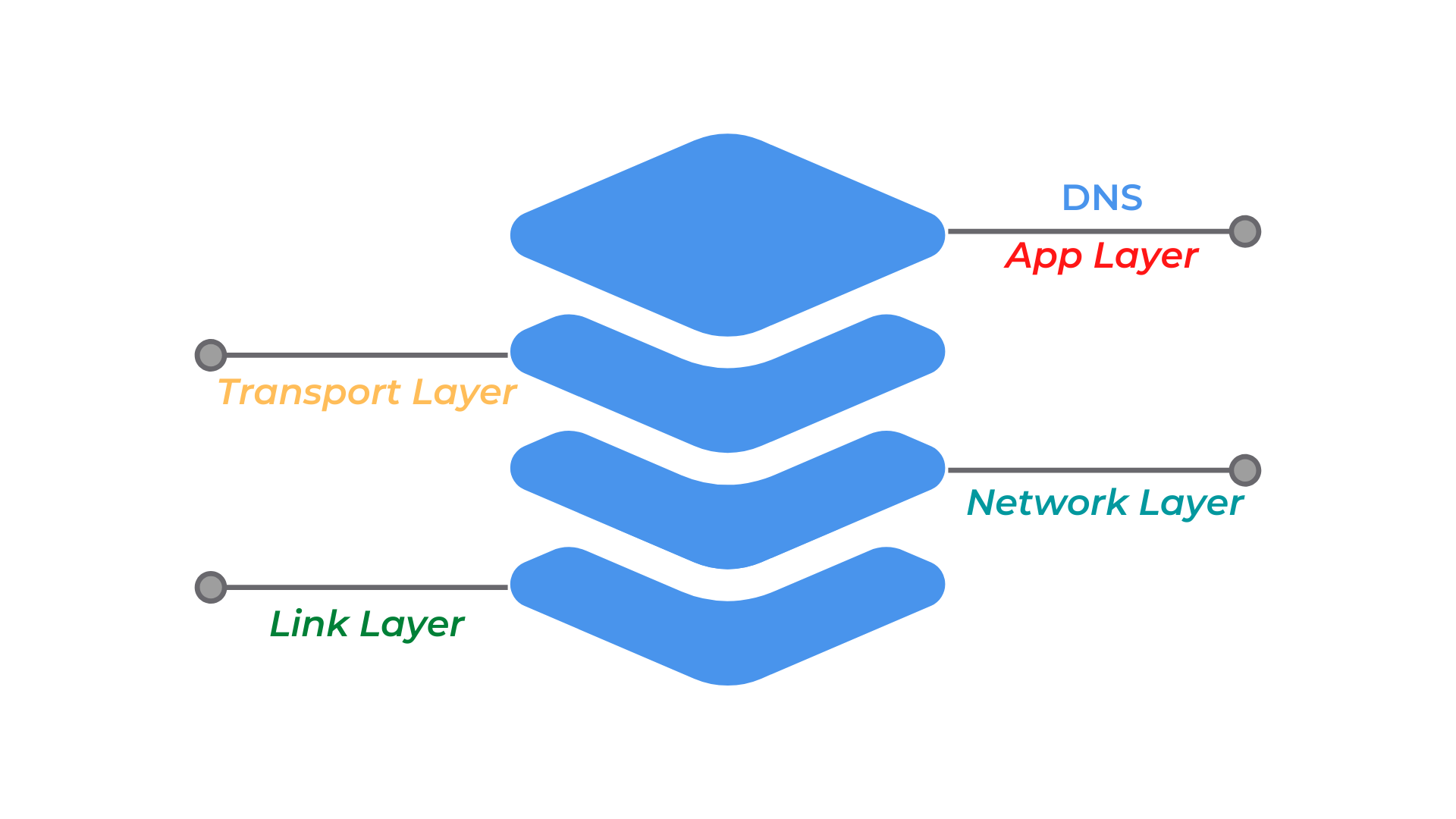
At a high level, the DNS protocol operates (using OSI model terminology) at the application level, also known as Layer 7. This layer is shared by HTTP, POP3, SMTP, and a host of other protocols used to communicate across an IP network.
Is DNS a layer 3 or 4?
DNS is a application layer protocol, because DNS query and answer is the application level communications. Application layer only understand the query and answer section in the DNS packet. so application layer DNS query/answer is encapsulated in layer 4 udp then layer 3 IP…..and so on.
What layer is DHCP and DNS?
DHCP runs at the application layer of the Transmission Control Protocol/IP (TCP/IP) stack to dynamically assign IP addresses to DHCP clients and to allocate TCP/IP configuration information to DHCP clients. This includes subnet mask information, default gateway IP addresses and domain name system (DNS) addresses.
Where does DNS fit in the OSI model?
In OSI stack terms, DNS runs in parallel to HTTP in the Application Layer (layer 7). DNS is in effect an application that is invoked to help out the HTTP application, and therefore does not sit “below” HTTP in the OSI stack. DNS itself also makes use of UDP and more rarely TCP, both of which in turn use IP.
Does DNS use TCP or UDP or both?
DNS uses TCP for Zone transfer and UDP for name, and queries either regular (primary) or reverse. UDP can be used to exchange small information whereas TCP must be used to exchange information larger than 512 bytes.
Is DNS a layer 3 or 4?
DNS is a application layer protocol, because DNS query and answer is the application level communications. Application layer only understand the query and answer section in the DNS packet. so application layer DNS query/answer is encapsulated in layer 4 udp then layer 3 IP…..and so on.
Where does DNS fit in the OSI model?
In OSI stack terms, DNS runs in parallel to HTTP in the Application Layer (layer 7). DNS is in effect an application that is invoked to help out the HTTP application, and therefore does not sit “below” HTTP in the OSI stack. DNS itself also makes use of UDP and more rarely TCP, both of which in turn use IP.
Is DNS a layer 3 protocol?
At a high level, the DNS protocol operates (using OSI model terminology) at the application level, also known as Layer 7. This layer is shared by HTTP, POP3, SMTP, and a host of other protocols used to communicate across an IP network.
What is Layer 4 networking?
Layer 4 of the OSI model, also known as the transport layer, manages network traffic between hosts and end systems to ensure complete data transfers. Transport-layer protocols such as TCP, UDP, DCCP, and SCTP are used to control the volume of data, where it is sent, and at what rate.
Is DHCP same as DNS?
Domain Name System (DNS) is an Internet service that translates domain names (e.g., its.umich.edu) into IP addresses. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a protocol for automatically assigning IP addresses and other configurations to devices when they connect to a network.
Is DHCP part of DNS?
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) and DNS (Domain Name System) both work across the client-server architecture though they are different terms. While DNS maps the name of the domain to the IP address, DHCP is a protocol that assigns the IP address to the host in a network either dynamically or statically.
What is a layer 7 protocol?
Layer 7 is responsible for the data manipulation and protocols that software needs to present data so it is meaningful to humans. For example, layer 7 protocols include HTTP which enables internet communication and SMTP which enables email communications.
What is DNS in TCP IP?
Domain Name System (DNS) is one of the industry-standard suite of protocols that comprise TCP/IP, and together the DNS Client and DNS Server provide computer name-to-IP address mapping name resolution services to computers and users.
Is DNS an IP address?
The Domain Name System (DNS) turns domain names into IP addresses, which browsers use to load internet pages. Every device connected to the internet has its own IP address, which is used by other devices to locate the device.
Is DHCP a TCP or UDP?
The DHCP employs a connectionless service model, using the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). It is implemented with two UDP port numbers for its operations which are the same as for the bootstrap protocol (BOOTP). UDP port number 67 is the port used by the server, and UDP port number 68 is used by the client.
Why is UDP used for DNS?
DNS uses the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) on port 53 to serve DNS queries. UDP is preferred because it is fast and has low overhead. A DNS query is a single UDP request from the DNS client followed by a single UDP reply from the server.
Is port 53 TCP or UDP?
The answer is DNS is mostly UDP Port 53, but as time progresses, DNS will rely on TCP Port 53 more heavily.
What is Layer 2 layer 3 and Layer 4?
The layers are: Layer 1—Physical; Layer 2—Data Link; Layer 3—Network; Layer 4—Transport; Layer 5—Session; Layer 6—Presentation; Layer 7—Application.
What is ip3 layer?
The most significant protocol at layer 3 (also called the network layer) is the Internet Protocol, or IP. IP is the standard for routing packets across interconnected networks–hence, the name internet. It is an encapsulating protocol similar to the way Ethernet is an encapsulating protocol.
What is a Layer 4 header?
Layer 4 – The Transport Layer The Transport Layer provides transparent transfer of data between hosts and is responsible for end-to-end error recovery and flow control. Flow control is the process of adjusting the flow of data from the sender to ensure that the receiving host can handle all of it.
Is DNS a layer 3 or 4?
DNS is a application layer protocol, because DNS query and answer is the application level communications. Application layer only understand the query and answer section in the DNS packet. so application layer DNS query/answer is encapsulated in layer 4 udp then layer 3 IP…..and so on.
Where does DNS fit in the OSI model?
In OSI stack terms, DNS runs in parallel to HTTP in the Application Layer (layer 7). DNS is in effect an application that is invoked to help out the HTTP application, and therefore does not sit “below” HTTP in the OSI stack. DNS itself also makes use of UDP and more rarely TCP, both of which in turn use IP.