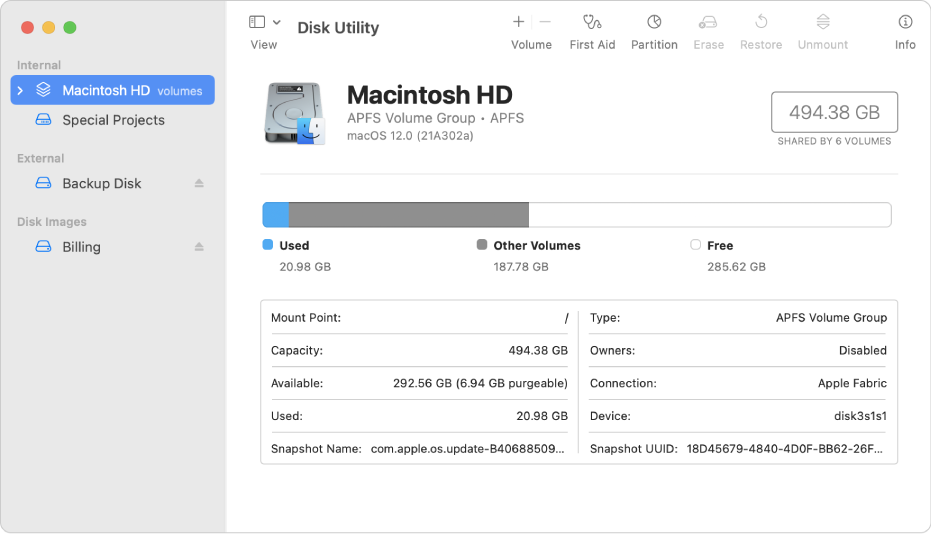
You can use Disk Utility on your Mac to manage internal and external storage devices. Using Disk Utility, you can: Format and manage volumes on physical storage devices. Create a disk image, a single file you can use to move files from one computer to another or to back up and archive your work.
How often should I run Disk Utility on my Mac?
Run Disk Utility The Disk Utility tool can be used for repairing disk permissions and it is important to run it once every 2-3 months to keep your Mac storage healthy and fully functional.
Is Disk Utility good for Mac?
Use the First Aid feature of Disk Utility to find and repair disk errors. Disk Utility can find and repair errors related to the formatting and directory structure of a Mac disk. Errors can lead to unexpected behavior when using your Mac, and significant errors might even prevent your Mac from starting up completely.
Does Disk Utility erase everything Mac?
In Disk Utility on Mac, you can erase and reformat storage devices to use with your Mac. Erasing a storage device deletes everything on it. If you have any files you want to save, copy them to another storage device.
What happens if you restore in Disk Utility in Mac?
You can restore a volume from another volume. When you restore from one volume to another volume, an exact copy of the original is created. WARNING: When you restore one volume to another, all the files on the destination volume are erased.
Is Disk Utility good for Mac?
Use the First Aid feature of Disk Utility to find and repair disk errors. Disk Utility can find and repair errors related to the formatting and directory structure of a Mac disk. Errors can lead to unexpected behavior when using your Mac, and significant errors might even prevent your Mac from starting up completely.
Does reinstalling macOS delete data?
No. Reinstalling macOS does not have to wipe all other data that you have stored. It is often recommended to reinstall macOS on top of the current installation. It is done from the Recovery partition using the same Command-R reboot.
What is the best format for a Mac external hard drive?
If you need to format a drive, use the APFS or Mac OS Extended (Journaled) format for best performance. If your Mac is running macOS Mojave or later, use the APFS format.
Do I erase Macintosh HD or HD data?
You should erase the Macintosh HD volume together with the Macintosh HD – Data volume when downgrading macOS. Why should you delete the Macintosh HD – Data? Because the Macintosh HD – Data volume of the previous macOS will be retained after downgrading macOS.
What’s the difference between Macintosh HD and Macintosh HD data?
Your files and data are stored in another volume named Macintosh HD – Data. In the Finder, both volumes appear as Macintosh HD. The Disk Utility app in macOS Catalina shows that Macintosh HD is the read-only system volume and Macintosh HD – Data contains the the rest of your files and data.
How do I check the health of my SSD Mac?
To check your Mac’s SSD, click the Apple menu and select About This Mac. On the Overview tab of the About This Mac window, click System Report. In the left sidebar of System Report, scroll down to and click on Storage. The “Verified” S.M.A.R.T status indicates the drive is working properly.
How do I know if my Mac is running properly?
Turn on your Mac and then immediately press and hold the D key on your keyboard as your Mac starts up. Release when you see a progress bar or you’re asked to choose a language.
Is Disk Utility good for Mac?
Use the First Aid feature of Disk Utility to find and repair disk errors. Disk Utility can find and repair errors related to the formatting and directory structure of a Mac disk. Errors can lead to unexpected behavior when using your Mac, and significant errors might even prevent your Mac from starting up completely.
Your Mac may be slow due to an outdated macOS or an overloaded cache. Malware can also infect your Mac and slow it down by hogging system resources. If your Mac is old, it might struggle to run modern software, and you may need to replace it.
What is slowing down my Mac?
If you find your Mac is running slowly, there are a number of potential causes that you can check. Your computer’s startup disk may not have enough free disk space. To make disk space available, you can move files to another disk or an external storage device, then delete files you no longer need on the startup disk.
Do Apple computers need defragging?
Should I shut down my Mac every night?
Yes, it is 100% beneficial. What’s more, restarting your Mac is the number one tip on any troubleshooting list. Shut Down mode can help fix many Mac issues, plus it will also flush your RAM and allow your device to cool down, protecting it from overheating.
What should you not do with a MacBook?
Do not place your MacBook on a pillow or other soft material when it’s powered on, as the material can block the airflow vents (in particular, the rear vents) and cause the computer to overheat. Never place anything over your keyboard when operating in closed-lid (clamshell) mode.
How long does a MacBook last?
We’d say five to eight years, but beware that you probably won’t be able to replace any faulty parts in a Mac when more than five years has passed since Apple last sold it. Before you buy a new Mac, read our article about the best time to buy a Mac or MacBook.
Does clearing cache delete passwords?
If you saved passwords in your browser so you could automatically log in to certain sites, clearing your cache can clear your passwords as well.
Why should I clear cache on Mac?
Cache is meant to help your Mac load sites faster, but sometimes it brings more harm than good. For example, if the website you’re about to visit has been updated ever since your Mac cached its data, your browser will still load the outdated cached version of the site.
Why is there so much other storage on my Mac?
We generate more and more content on our devices and use apps that are bursting with cache files. This is what creates the cryptic category of “Other” storage on Mac. On recent macOS versions, this storage category is labeled “other volumes in container.” Which, of course, doesn’t make it any less cryptic.