For example, after a DHCP server has assigned an IP to a requesting client, it can communicate this information to a DNS server which then automatically updates the DNS information.
How is DHCP related to DNS?
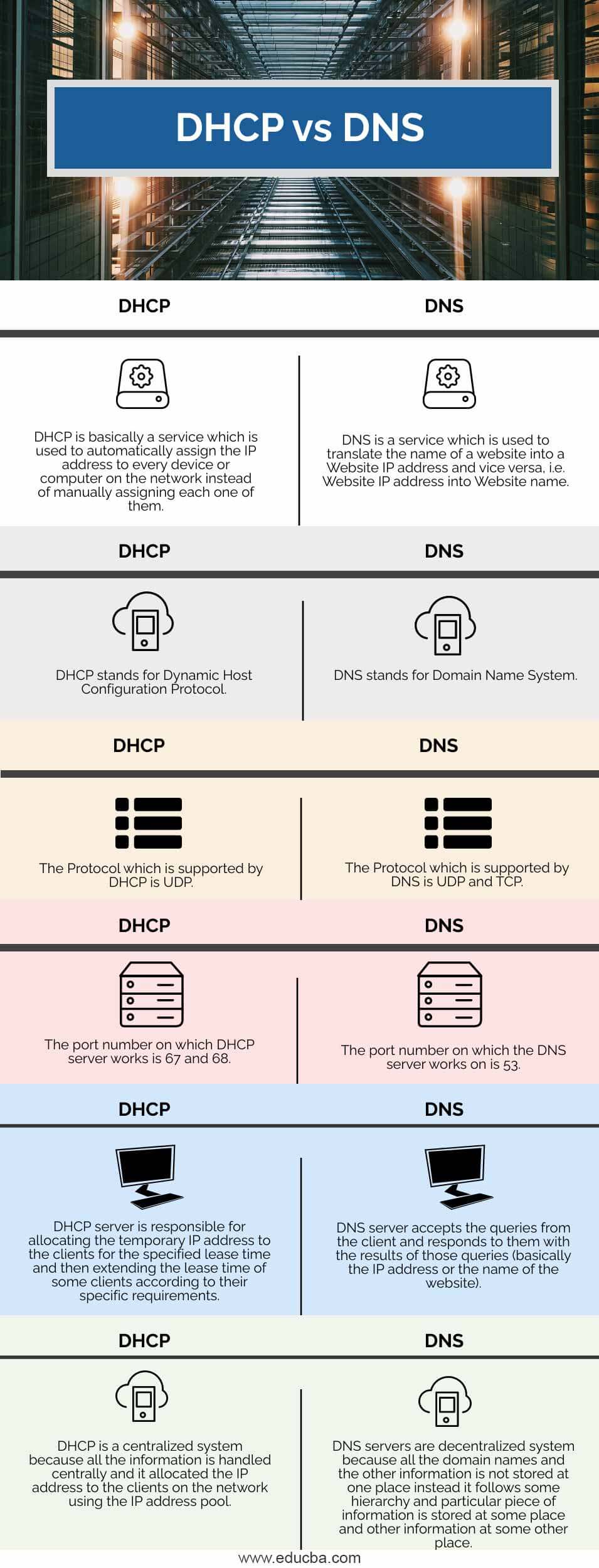
Domain Name System (DNS) is an Internet service that translates domain names (e.g., its.umich.edu) into IP addresses. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a protocol for automatically assigning IP addresses and other configurations to devices when they connect to a network.
What layer is DHCP and DNS?
DHCP runs at the application layer of the Transmission Control Protocol/IP (TCP/IP) stack to dynamically assign IP addresses to DHCP clients and to allocate TCP/IP configuration information to DHCP clients. This includes subnet mask information, default gateway IP addresses and domain name system (DNS) addresses.
Should DHCP and DNS be on the same server?
DNS should be installed on every domain controller – there is no reason not to these days. DHCP can sit where ever you want it to, either on a DC or on it’s own server, the latter should be considered for large companies.
Does DHCP update DNS?
The DHCP server always registers and updates client information with its configured DNS servers. This is a modified configuration supported for Windows Server DHCP servers and clients that are running Windows.
Is DHCP part of DNS?
DHCP and DNS are two essential services in IT networks. While a DHCP server sends out information that clients need to communicate with other machines and services, DNS ensures that servers, clients, and services can be found by their names.
What is the main difference between DNS and DHCP?
To summarize, DHCP server assigns the IP addresses to client computers, while DNS server resolves them. They are two essential technology developed for us to use the network or Internet conveniently.
What layer is DNS?
At a high level, the DNS protocol operates (using OSI model terminology) at the application level, also known as Layer 7. This layer is shared by HTTP, POP3, SMTP, and a host of other protocols used to communicate across an IP network.
What Layer 4 protocol is used for DNS?
Just like every application layer protocol, DNS uses the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) on the Transport layer of the TCP/IP model to transport data. UDP is preferred over TCP for DNS because of its speed and lightweight packets.
Should DNS and DHCP be on the domain controller?
Domain controllers do not require the DHCP Server service to operate and for higher security and server hardening it is recommended not to install the DHCP Server role on domain controllers.
Should DNS be on domain controller?
In a small environment, at least one domain controller (DC) should be a DNS server. It is possible to install DNS on servers which are not DCs, including non-Windows servers, but installing DNS on DCs allows the use of AD-integrated lookup zones (see below), which improve security and simplify zone replication.
Is DHCP required for Active Directory?
If you are configuring a DHCP server, authorization must occur as part of an Active Directory domain. If you do not authorize the DHCP server in the Active Directory domain, the DHCP service will fail to start properly, and then the DHCP server will not be able to support requests from DHCP clients.
How do I enable DHCP server to update DNS?
Click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click DHCP. Right-click the appropriate DHCP server or scope, and then click Properties. Click DNS. Click to select the Enable DNS dynamic updates according to the settings below check box to enable DNS dynamic update for clients that support dynamic update.
How long does it take DHCP to update?
How to change DHCP lease time? The standard DHCP lease time is 24 hours, but you can change it to meet your network’s needs. For example, if you’re setting up a lease time on your restaurant’s WiFi network, you can restrict it to an hour or two while a guest office network could have about 12 hours.
How do DNS servers get updated?
In order to synchronize the DNS information, the Secondary servers will periodically check with the Primary server to see if there have been any changes in the data hosted there. If they detect a change, they will pull down the update. (More on how that happens in the troubleshooting section below).
What does DNS and DHCP have in common?
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) and DNS (Domain Name System) both work across the client-server architecture though they are different terms. While DNS maps the name of the domain to the IP address, DHCP is a protocol that assigns the IP address to the host in a network either dynamically or statically.
What is the main use of DHCP?
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network protocol that is used to configure network devices to communicate on an IP network. A DHCP client uses the DHCP protocol to acquire configuration information, such as an IP address, a default route, and one or more DNS server addresses from a DHCP server.
What is the role of DHCP in the network?
A DHCP Server is a network server that automatically provides and assigns IP addresses, default gateways and other network parameters to client devices. It relies on the standard protocol known as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol or DHCP to respond to broadcast queries by clients.
What is the role of DHCP?
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a client/server protocol that automatically provides an Internet Protocol (IP) host with its IP address and other related configuration information such as the subnet mask and default gateway.
What port is DHCP?
DHCP is a network protocol to used to configure IP networks. A DHCP server listens to UDP port 67 and dynamically assigns IP addresses and other network parameters to DHCP clients. These clients will listen for responses on UDP port 68.
What does a DNS do?
DNS, or the Domain Name System, translates human readable domain names (for example, www.amazon.com) to machine readable IP addresses (for example, 192.0. 2.44).
What is the difference between DNS and IP address?
A system called the Domain Name System, or DNS, associates names, like www.example.com, with the corresponding addresses. Your computer uses the DNS to look up domain names and get the associated IP address, which is used to connect your computer to the destination on the internet.