ICANN is the global non-profit organization responsible for coordinating the Internet’s core systems of unique identifiers, most notably the Domain Name System (DNS).
Where do DNS servers come from?
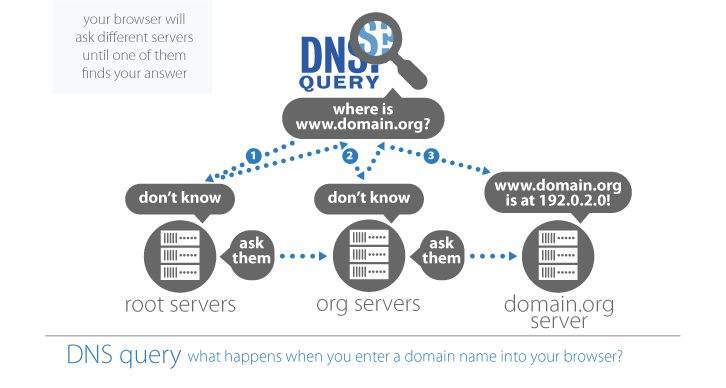
As mentioned earlier, the ISP’s DNS server is part of the network configuration you get from DHCP as soon as you go online. These servers reside in your ISP’s data centers, and they handle requests as follows: If it has the domain name and IP address in its database, it resolves the name itself.
Who is responsible for domain name system?
Today, the standards for DNS are maintained by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in RFC 1035.
How are DNS servers assigned?
The DNS system provides a domain name to IP address mapping for devices connected to the Internet, and it is crucial to the working of the Internet. Usually you don’t need to worry about it as your are automatically assigned the address of the DNS server by your ISP and Home router.
Where do DNS servers come from?
As mentioned earlier, the ISP’s DNS server is part of the network configuration you get from DHCP as soon as you go online. These servers reside in your ISP’s data centers, and they handle requests as follows: If it has the domain name and IP address in its database, it resolves the name itself.
Who is responsible for domain name system?
Today, the standards for DNS are maintained by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in RFC 1035.
Do routers have their own DNS?
The router has its own DNS that forwards requests to the ISP’s server (or whatever you configured). When your computer connects to the router, the router will tell the computer via DHCP which DNS server to use, and that will be the router’s internal DNS server.
Does router store DNS?
The router has a DNS server address stored, so it asks the DNS server for the IP address of that hostname. The DNS server finds the IP address that belongs to lifewire.com and then is able to understand what website you’re asking for, after which your browser can then load the appropriate page.
Who will configure DNS and where is situated?
In most cases, a primary and a secondary DNS server are configured on your router or computer when you connect to your internet service provider. There are two DNS servers in case one of them happens to fail, in which case the second is used to resolve hostnames you enter.
Who owns domain server?
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) is the non-profit organization that oversees the assignment of both IP addresses and domain names.
What if the DNS server is not responding?
DNS Server Not Responding error means that your browser was unable to connect to the internet or the DNS of the domain you’re trying to reach are unavailable. In order to resolve it, restart your router or modem, check for network issues and update your browser.
Does the Registrar own the domain name?
Although people often speak of buying and owning domain names, the truth is that registries own all of their domain names and registrars simply offer customers the opportunity to reserve those domain names for a limited amount of time.
What are the 3 types of DNS?
There are three main kinds of DNS Servers — primary servers, secondary servers, and caching servers.
Does DHCP give DNS?
Knowledgeable network administrators take full advantage of available network services to manage their network. DHCP can be used to assign IP addresses and DNS servers. DNS servers are used to translate hostnames and domain names on both locally and on the internet.
Why do companies have their own DNS server?
A local DNS is vital for enterprise level and larger companies. A DNS server keeps IP addresses inside a company network private. They are invisible to the outside world. It also helps to add zest to your network speeds.
Does DHCP update DNS?
The DHCP server always registers and updates client information with its configured DNS servers. This is a modified configuration supported for Windows Server DHCP servers and clients that are running Windows.
Does computer DNS Override router DNS?
No. The DNS server that is used is determined by the OS. If you tell the OS “manually” that it has to use 8.8. 8.8 as nameserver, then it will do so.
Where is the DNS server located on my router?
The easiest way to find out your dns server IP address is to go through the router’s admin interface status page. All routers have a built-in web-based setup page that allows the user to customize settings and set view properties such as IP address and dns settings.
Should DNS and IP address be the same?
If your DNS and DHCP services are on the same server, that is not a problem. If these are on different machines, it could be that you have an IP address conflict in which case you must change the IP of one of your servers.
What should your router DNS BE?
If you’re using a router for your office network DNS settings—and you probably are—log into it and find your DNS server settings. Once there, note down your existing DNS records and replace them with the following: For IPv4: 1.1. 1.1 and 1.0.
Where do DNS servers come from?
As mentioned earlier, the ISP’s DNS server is part of the network configuration you get from DHCP as soon as you go online. These servers reside in your ISP’s data centers, and they handle requests as follows: If it has the domain name and IP address in its database, it resolves the name itself.
Who is responsible for domain name system?
Today, the standards for DNS are maintained by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in RFC 1035.