An -Active Directory-integrated zone is a primary DNS zone that is stored in Active Directory and thus can, unlike all other zone types, use multi-master replication and Active Directory security features. It is an authoritative primary zone in which all of the zone data is stored in Active Directory.
What is an Active Directory DNS zone?
An -Active Directory-integrated zone is a primary DNS zone that is stored in Active Directory and thus can, unlike all other zone types, use multi-master replication and Active Directory security features. It is an authoritative primary zone in which all of the zone data is stored in Active Directory.
What are the two zones of DNS server required to add to the file?
DNS Zone files start with two mandatory records: Global Time to Live (TTL), which specifies for how records should be kept in local DNS cache. Start of Authority (SOA) record—specifies the primary authoritative name server for the DNS Zone.
What is primary zone and secondary zone in DNS?
Primary DNS servers contain all relevant resource records and handle DNS queries for a domain. By contrast, secondary DNS servers contain zone file copies that are read-only, meaning they cannot be modified.
What are the two zones of DNS server required to add to the file?
DNS Zone files start with two mandatory records: Global Time to Live (TTL), which specifies for how records should be kept in local DNS cache. Start of Authority (SOA) record—specifies the primary authoritative name server for the DNS Zone.
What are the 3 types of DNS zones?
The three DNS server types server are the following: DNS stub resolver server. DNS recursive resolver server. DNS authoritative server.
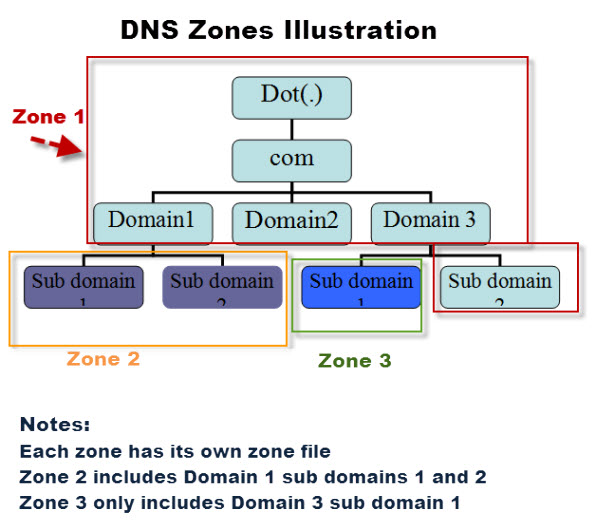
How many zones are there in Active Directory?
Broadly speaking, there are five types of DNS zones.
Which type of zone transfer works only for DNS update?
DNS zone transfers using the AXFR protocol are the simplest mechanism to replicate DNS records across DNS servers. To avoid the need to edit information on multiple DNS servers, you can edit information on one server and use AXFR to copy information to other servers.
Which is responsible for creating maintaining and updating the zone file?
A DNS creates, maintains and updates the zone file.
What is forward zone and reverse zone in DNS?
Forward lookup zones resolve names to IP addresses and Reverse lookup zones resolve IP addresses to names. ☑ Forwarders can be used on your DNS server to forward requests for which your DNS server does not have an authoritative answer.
What is the difference between secondary zone and stub zone?
Secondary zone and stub zone definitions are basically the same. Each definition lists the IP addresses of master name servers for a domain but does not include individual records for those servers. Those records are stored on the master name servers themselves.
Can you make any DNS changes in your secondary DNS for the zone?
Therefore, the secondary DNS servers cannot request changes to the DNS zone on their own but must be explicitly requested to do so by the hidden primary via a notify statement. A popular approach is to configure a computer in the local network as a DNS server and use it as the hidden primary.
What is secondary zone?
A secondary zone is a read-only copy of the primary zone that is stored on a different server. The secondary zone cannot process updates and can only retrieve updates from the primary zone. Secondary zones are organized within DNS views. For more information on DNS Zones, see Configuring DNS Zones.
What is a primary or master zone in DNS?
Primary (Master) DNS zone – holder of the original zone file (all the DNS records for the zone). You can manage a host through this zone. Secondary (Slave) DNS zone – holds a copy of the zone file. You can use them for better performance, for hiding your Primary, for backup and redundancy.
Where are DNS records stored in Active Directory?
DNS zone data is stored in an application directory partition. A forest-wide partition named ForestDnsZones is used for the zone data. For each AD DS domain, a domain partition is created named DomainDnsZones. Typically, DNS implementations are used with a contiguous namespace.
What is the use of the primary zone in DNS?
A primary DNS server is the first point of contact for a browser, application or device that needs to translate a human-readable hostname into an IP address. The primary DNS server contains a DNS record that has the correct IP address for the hostname.
What is the difference between DNS zone and domain?
A domain is a logical division of the DNS name space whereas a zone is physical, as the information is stored in a file called a zone file. In most cases you have a 1 to 1 relationship between a Domain and a DNS Zone i.e. the domain mydomain.com would be stored in a zone file called mydomain.com. txt.
What is a DNS zone file and its purpose?
A Domain Name System zone file (DNS zone file) is a simple text file which is automatically bundled with DNS records. The file contains all the necessary information of all resources records for the particular domain. Alternatively, it can also contain the complete Internet Protocol to domain mapping of the domain.
What are the two types of DNS zones?
There are two types of DNS zones – Primary (Master) DNS zone for control and Secondary (Slave) DNS zone for redundancy and better performance. The first contains all the original DNS records, and the second gets them from the Primary DNS zone. The process is called DNS zone transfer.
What are the two zones of DNS server required to add to the file?
DNS Zone files start with two mandatory records: Global Time to Live (TTL), which specifies for how records should be kept in local DNS cache. Start of Authority (SOA) record—specifies the primary authoritative name server for the DNS Zone.
What is reverse lookup zone in Active Directory?
Reverse Lookup Zones. As mentioned earlier, a reverse lookup zone is an authoritative DNS zone that is used primarily to resolve IP addresses to network resource names. This zone type can be primary, secondary, or Active Directory—integrated.
What is stub zone in Active Directory?
A stub zone is a copy of a Domain Name System (DNS) zone that contains only resource records that identify the DNS servers for that zone. You can add either a forward lookup zone or a reverse lookup zone. You can add either an Active Directory-integrated zone or a file-backed zone.