What is spoofing attack example?
Spoofing techniques vary based on the type of attack. For example, in email spoofing, the adversary can hack an unsecured mail server in order to hide their true identity. In a MitM attack, an adversary can create a Wi-Fi access point in order to intercept any web activity and gather personal information.
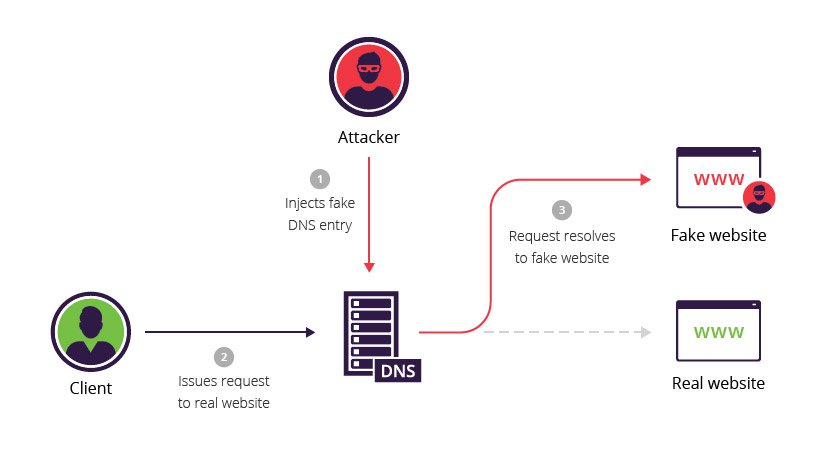
What causes DNS spoofing?
Specifically, hackers gain access to a DNS server so that they can adjust its directory to point the domain name users enter to a different, incorrect IP address. Once someone gains access to a DNS server and begins redirecting traffic, they are engaging in DNS spoofing.
How common is DNS spoofing?
Through their research they discovered that DNS spoofing is still rare (occurring only in about 1.7% of observations) but has been increasing during the observed period, and that proxying is the most common DNS spoofing mechanism.
Which tool is used to spoof the DNS of site?
DNS Spoofing Tool Dnsspoof – The function of this tool is to navigate all the DNS requests to the fake local computer’s host file once it is created in the name of the phony website’s IP address.
What causes DNS spoofing?
Specifically, hackers gain access to a DNS server so that they can adjust its directory to point the domain name users enter to a different, incorrect IP address. Once someone gains access to a DNS server and begins redirecting traffic, they are engaging in DNS spoofing.
What is spoofing in simple words?
Spoofing is when someone or something pretends to be something else in an attempt to gain a victim’s confidence, get access to a system, steal data, or spread malware.
What is spoofing and how do you prevent it?
Spoofing is a cybercrime that happens when someone impersonates a trusted contact or brand, pretending to be someone you trust in order to access sensitive personal information. Spoofing attacks copy and exploit the identity of your contacts, the look of well-known brands, or the addresses of trusted websites.
Is there a way to prevent spoofing?
Packet filtering can prevent an IP spoofing attack since it is able to filter out and block packets that contain conflicting source address information. Using cryptographic network protocols such as HTTP Secure (HTTPS) and Secure Shell (SSH) can add another layer of protection to your environment.
What is difference between DNS spoofing and DNS poisoning?
While the terms DNS poisoning and DNS spoofing are used interchangeably, there’s a difference between the two. DNS Poisoning is the method attackers use to compromise and replace DNS data with a malicious redirect. DNS Spoofing is the end result, where users are redirected to the malicious website via a poisoned cache.
Can someone hack you through DNS?
A DNS name server is a highly sensitive infrastructure which requires strong security measures, as it can be hijacked and used by hackers to mount DDoS attacks on others: Watch for resolvers on your network — unneeded DNS resolvers should be shut down.
Does spoofing change your IP?
Internet Protocol (IP) spoofing is a type of malicious attack where the threat actor hides the true source of IP packets to make it difficult to know where they came from. The attacker creates packets, changing the source IP address to impersonate a different computer system, disguise the sender’s identity or both.
Can you spoof a domain name?
Domain spoofing, a common form of phishing, occurs when an attacker appears to use a company’s domain to impersonate a company or one of its employees. This can be done by sending emails with false domain names which appear legitimate, or by setting up websites with slightly altered characters that read as correct.
Can you spoof a URL?
Website spoofing is when an attacker builds a website with a URL that closely resembles, or even copies, the URL of a legitimate website that a user knows and trusts. In addition to spoofing the URL, the attacker may copy the content and style of a website, complete with images and text.
Can hackers spoof your domain?
In practice, domain spoofing is used by hackers in different ways. It could be, for example, by simply adding a letter to an email address or creating a fake website that has an address very similar to the legitimate one. In the day-to-day routine, these small changes end up being overlooked by many people.
What are the examples of on Path attack?
You can think of an on-path attacker like a rogue postal worker who sits in a post office and intercepts letters written between two people. This postal worker can read private messages and even edit the contents of those letters before passing them along to their intended recipients.
How does spoofing attack occur?
Spoofing is a cybercrime that happens when someone impersonates a trusted contact or brand, pretending to be someone you trust in order to access sensitive personal information. Spoofing attacks copy and exploit the identity of your contacts, the look of well-known brands, or the addresses of trusted websites.
What is spoofing in cyber crime?
Spoofing involves faking one’s identity, and can be used for various attacks such as identity theft. Phishing is one such use of spoofing that attempts to steal somebody’s personal information or credentials by having them volunteer that information from a nefarious source that looks legit.
What causes DNS spoofing?
Specifically, hackers gain access to a DNS server so that they can adjust its directory to point the domain name users enter to a different, incorrect IP address. Once someone gains access to a DNS server and begins redirecting traffic, they are engaging in DNS spoofing.
What are spoofing tools?
In IP spoofing, a hacker uses tools to modify the source address in the packet header to make the receiving computer system think the packet is from a trusted source, such as another computer on a legitimate network, and accept it. This occurs at the network level, so there are no external signs of tampering.
What is spoofing used for?
In cybersecurity, ‘spoofing’ is when fraudsters pretend to be someone or something else to win a person’s trust. The motivation is usually to gain access to systems, steal data, steal money, or spread malware.
How does someone spoof an email address?
In spoofing attacks, the sender forges email headers so that client software displays the fraudulent sender address, which most users take at face value. Unless they inspect the header more closely, users see the forged sender in a message. If it’s a name they recognize, they’re more likely to trust it.