What is a DNS record? DNS records (aka zone files) are instructions that live in authoritative DNS servers and provide information about a domain including what IP address is associated with that domain and how to handle requests for that domain.
What are 3 types of DNS records?
The three DNS server types server are the following: DNS stub resolver server. DNS recursive resolver server. DNS authoritative server.
What is a DNS A record example?
The “A” stands for “address” and this is the most fundamental type of DNS record: it indicates the IP address of a given domain. For example, if you pull the DNS records of cloudflare.com, the A record currently returns an IP address of: 104.17. 210.9. A records only hold IPv4 addresses.
What are the records available in DNS?
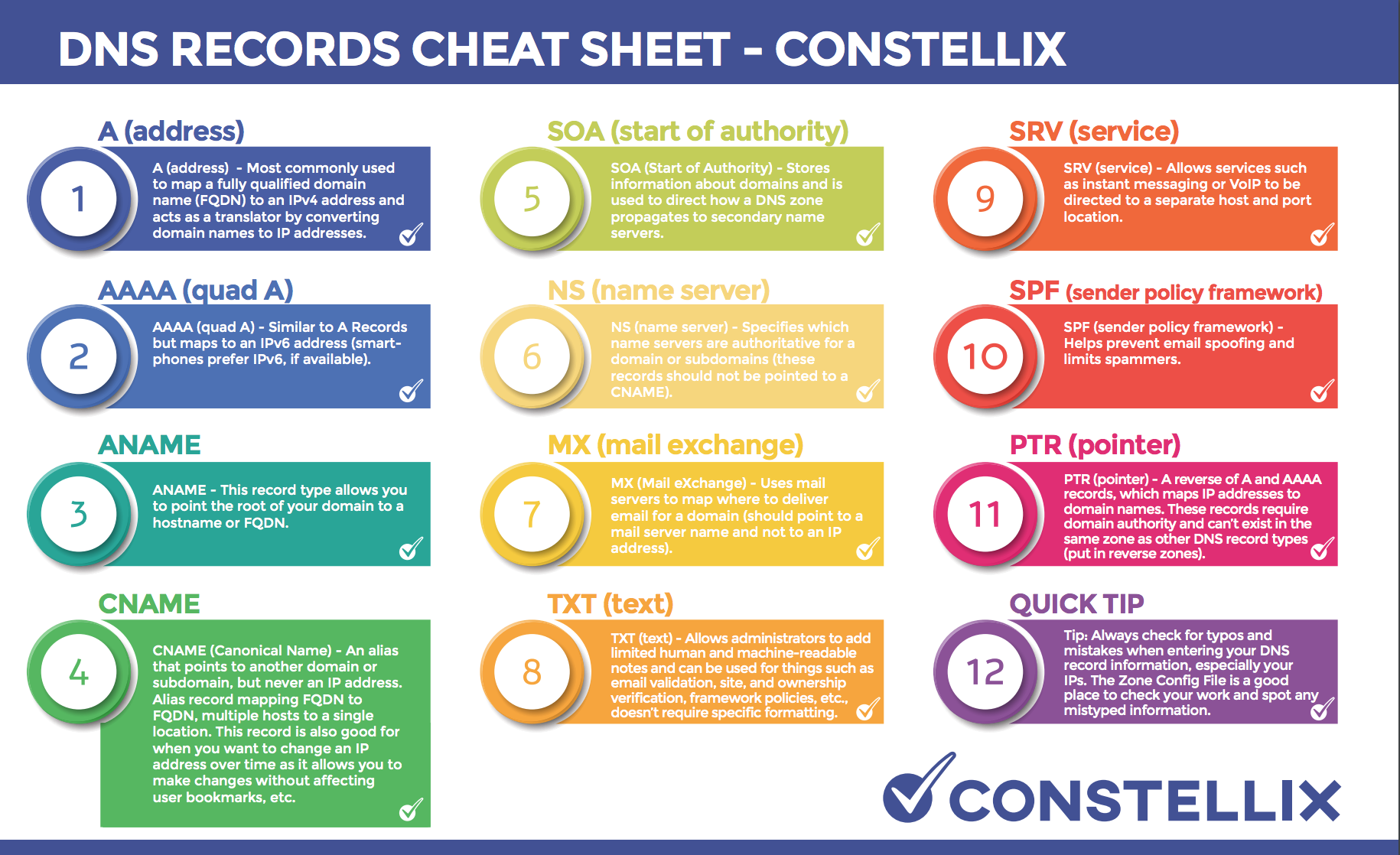
DNS servers store records. When a DNS query is sent by a device, that query gets a response from those records with the help of DNS servers and resolvers. There are eight records that you see again and again: A, AAAA, CNAME, PTR, NS, MX, SOA, and TXT.
What are MX and NS Records?
A DNS ‘mail exchange’ (MX) record directs email to a mail server. The MX record indicates how email messages should be routed in accordance with the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP, the standard protocol for all email). Like CNAME records, an MX record must always point to another domain.
What is the most commonly used DNS record?
The most common DNS record types are: Address Mapping record (A Record)—also known as a DNS host record, stores a hostname and its corresponding IPv4 address. IP Version 6 Address record (AAAA Record)—stores a hostname and its corresponding IPv6 address.
Where are DNS records stored?
DNS records are stored in authoritative servers. These records provide information about a domain, including its associated IP address for each domain. It is mandatory for all domains to have a specific set of default records.
What is AAAA DNS record?
An AAAA record is used to find the IP address of a computer connected to the internet from a name. The AAAA record is conceptually similar to the A record, but it allows you to specify the IPv6 address of the server, rather than the IPv4.
What are record examples?
Examples include documents, books, paper, electronic records, photographs, videos, sound recordings, databases, and other data compilations that are used for multiple purposes, or other material, regardless of physical form or characteristics.
Why do we need DNS records?
This allows you to change web hosts without changing domain names. Each website has a specific IP address, and the DNS records pair that IP address to the domain name so users don’t need to remember the numeric line. DNS records hold information about every single website on the internet.
What is DNS name example?
DNS, or the Domain Name System, translates human readable domain names (for example, www.amazon.com) to machine readable IP addresses (for example, 192.0. 2.44).
Is DNS a layer 3 or 4?
From a functionality perspective, DNS is pretty clearly part of the application layer (that’s layer 4). It’s invoked by the application layer and rides on top of the transport layer (UDP).
What is AAAA DNS record?
An AAAA record is used to find the IP address of a computer connected to the internet from a name. The AAAA record is conceptually similar to the A record, but it allows you to specify the IPv6 address of the server, rather than the IPv4.
What Layer 4 protocol is associated with DNS?
Just like every application layer protocol, DNS uses the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) on the Transport layer of the TCP/IP model to transport data. UDP is preferred over TCP for DNS because of its speed and lightweight packets.
What are 7 records?
7-inch records are often referred to as 45s due to their play speed being 45 RPM. These records are noticeably smaller than their LP counterparts, and they spin significantly faster. The higher RPM gives 45s superior sound quality, but it also means that only a few minutes of recorded sound can be stored on each side.
What is TXT and MX record?
TXT record: This is used to store text-based information of the outside domain for the configured domain. This is useful in identifying ownership of a domain. MX record: This is used in mail delivery based on the configured domain. This is useful in redirecting email requests to the mail servers for a specified domain.
What type of record is DKIM?
A DKIM record is really a DNS TXT (“text”) record. TXT records can be used to store any text that a domain administrator wants to associate with their domain. DKIM is one of many uses for this type of DNS record.
What is Cname and NS record?
The ‘canonical name’ (CNAME) record is used in lieu of an A record, when a domain or subdomain is an alias of another domain. All CNAME records must point to a domain, never to an IP address.
How many DNS servers are there?
Root name server overview In total, there are 13 main DNS root servers, each of which is named with the letters ‘A’ to ‘M’. They all have a IPv4 address and most have an IPv6 address. Managing the root server is ICANN’s responsibility (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers).
How are DNS records created?
A DNS record is simply a database that maps human-friendly URLs to IP addresses. When someone types in a URL such as google.com, that entry is sent to an internet service provider (ISP) where it’is forwarded to the DNS servers, and then directed to the proper web server using the corresponding IP address as a label.
What is DNS record not found?
The ‘Site Not Found’ error means the IP address your domain is using is not pointed to the correct IP. More technically, the ‘Site Not Found’ error means that the DNS records for your domain are resolving to the IP address of an Apache web server service that is not configured for your domain.
Are DNS records public?
Public DNS and Private DNS For a server to be accessible on the public internet, it needs a public DNS record, and its IP address needs to be reachable on the internet – that means it’s not blocked by a firewall. Public DNS servers are accessible to anyone that can connect to them and don’t require authentication.