The DNS update functionality enables DNS client computers to register and to dynamically update their resource records with a DNS server whenever changes occur.
How do DNS servers get updated?
In order to synchronize the DNS information, the Secondary servers will periodically check with the Primary server to see if there have been any changes in the data hosted there. If they detect a change, they will pull down the update.
What happens when DNS changes?
Put simply: when you change your DNS preferences to OpenDNS, you are improving the capability of your computer and your network to navigate the Internet, send email and perform other Web functions.
What is DNS used for?
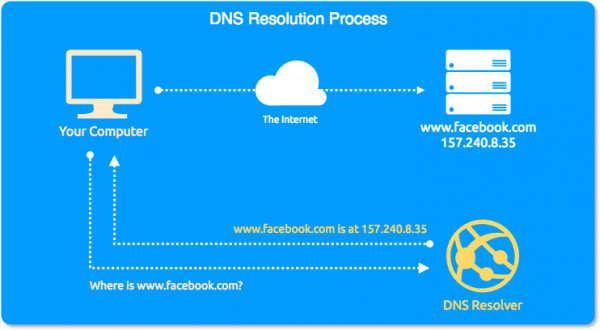
DNS, or the Domain Name System, translates human readable domain names (for example, www.amazon.com) to machine readable IP addresses (for example, 192.0. 2.44).
What is DNS and do I need it?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the phonebook of the Internet. Humans access information online through domain names, like nytimes.com or espn.com. Web browsers interact through Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. DNS translates domain names to IP addresses so browsers can load Internet resources.
How do DNS servers get updated?
In order to synchronize the DNS information, the Secondary servers will periodically check with the Primary server to see if there have been any changes in the data hosted there. If they detect a change, they will pull down the update.
How long do DNS updates take?
DNS propagation is the time frame it takes for DNS changes to be updated across the Internet. A change to a DNS record—for example, changing the IP address defined for a specific hostname—can take up to 72 hours to propagate worldwide, although it typically takes a few hours.
How do you check if DNS is updated?
The easiest way is to take a look at the domain’s Updated Date by doing a WHOIS Lookup. Another, more-detailed option is to look at the last time your website’s DNS was updated using an online DNS lookup tool, or by using the built-in nslookup command on Windows.
Is changing DNS safe?
Switching from your current DNS server to another one is very safe and will never harm your computer or device. However, ensure you are changing to a known and reliable server, such as Cloudflare or another third-party server that does not sell your data.
Is DNS safe?
DNS is widely trusted by organizations, and DNS traffic is typically allowed to pass freely through network firewalls. However, it is commonly attacked and abused by cybercriminals. As a result, the security of DNS is a critical component of network security.
Should I change my DNS?
The Domain Name System is an essential part of your internet communications. Upgrading to a better DNS server can make your surfing both faster and more secure, and we show you how.
How do I find out what my DNS is?
Open your Command Prompt from the Start menu (or type “Cmd” into the search in your Windows task bar). Next, type ipconfig/all into your command prompt and press Enter. Look for the field labeled “DNS Servers.” The first address is the primary DNS server, and the next address is the secondary DNS server.
Where do I find DNS settings?
DNS settings are specified in the TCP/IP Properties window for the selected network connection. Go to the Control Panel. Click Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Change adapter settings.
What are the 3 types of DNS?
There are three main kinds of DNS Servers — primary servers, secondary servers, and caching servers.
Should private DNS be on or off?
Important: By default, your phone uses Private DNS with all networks that can use Private DNS. We recommend keeping Private DNS turned on.
What is DNS in WIFI?
Domain Name Systems (DNS) are like the internet’s phone book. They maintain a directory of domain names (like “google.com”) and translate them to IP addresses. Google Nest Wifi and Google Wifi both operate as a DNS proxy.
Is Google DNS safe?
Google Public DNS complies with Google’s main privacy policy, available at our Privacy Center. Your client IP address is only logged temporarily (erased within a day or two), but information about ISPs and city/metro-level locations are kept longer for the purpose of making our service faster, better, and more secure.
What does changing the DNS to 8.8 8.8 do?
By changing your 8.8. 8.8 DNS, you are switching your operator from your ISP to Google Public DNS. It protects users from DDOS and malware attacks. However, by doing this, Google can see all your DNS queries and collect even more data.
What is the 8.8 4.4 DNS server?
8.8. 4.4 is the secondary DNS server for Google Public DNS. Google Public DNS is a global DNS service that is run by Google for the purpose of making the Internet and the DNS system faster, safer, secure, and more reliable for everyone online.
How often does a server register with DNS?
When a DNS client creates a record, it is assigned a timestamp. The DNS client attempts to refresh this record every 24 hours. Unless the record is changed (for example, the client receives a new IP address), the timestamp cannot be refreshed for a default period of seven days.
Should I use 8.8 8.8 DNS?
That is not recommended and may even be a violation of your security policies, depending on the level of security required in your organization or by any governing agency. DNS forwarders that only point to 8.8. 8.8 are using your ISP connection to hop to 8.8.
How do DNS servers get updated?
In order to synchronize the DNS information, the Secondary servers will periodically check with the Primary server to see if there have been any changes in the data hosted there. If they detect a change, they will pull down the update.