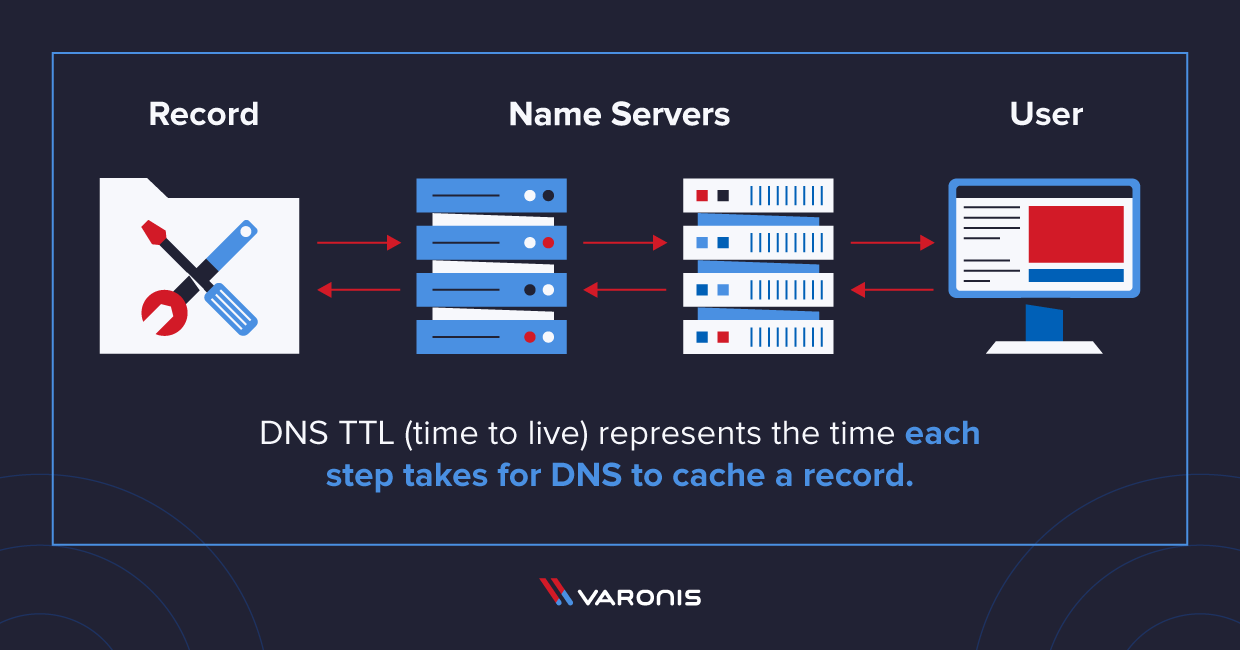
Once the TTL on a cached record expires, a recursive DNS resolver must begin the lookup process anew. It will have to resolve the DNS query via an authoritative nameserver. Separate from DNS caching, TTL is also used to ensure IP packets have a limited lifetime on a network.
Does TTL matter in DNS?
Time To Live, or TTL for short, is the sort of expiration date that is put on a DNS record. The TTL serves to tell the recursive server or local resolver how long it should keep said record in its cache. The longer the TTL, the longer the resolver holds that information in its cache.
How long should TTL be DNS?
Generally, we recommend a TTL of 24 hours (86,400 seconds). However, if you are planning to make DNS changes, you should lower the TTL to 5 minutes (300 seconds) at least 24 hours in advance of making the changes. After the changes are made, increase the TTL back to 24 hours.
Does TTL matter in DNS?
Time To Live, or TTL for short, is the sort of expiration date that is put on a DNS record. The TTL serves to tell the recursive server or local resolver how long it should keep said record in its cache. The longer the TTL, the longer the resolver holds that information in its cache.
Is low TTL good?
By having a lower TTL, you can ensure that you are receiving the most recent updates in a given timeframe. Your time to live is critical in controlling your resolver caching directly. For example, your DNS resolver will pull a DNS record from its authoritative server every hour.
Is higher TTL better?
Recommended High TTL Values High TTL values are typically used for records that rarely change, such as MX or TXT records. Longer TTLs reduce resolution times since every time an authoritative nameserver provides an answer to a query, it results in an additional lookup.
What is the best TTL in Ping?
The maximum TTL is 255, but it is not the default. The default value depends on the operating system as you can see here. So it seems that you’re getting replies from a machine whose default is 64.
What is default TTL value?
You could theoretically set a TTL as low as one second. However, most sites use a default TTL of 3600 (one hour). The maximum TTL that you can apply is 86,400 (24 hours).
How do I check my DNS cache TTL?
The best way to check DNS TTL is using nslookup command. Open the terminal and type nslookup -debug domain name. It will display the ttl value of this DNS record. This command is available on most systems.
Who sets TTL?
The time-to-live value can be thought of as an upper bound on the time that an IP datagram can exist in an Internet system. The TTL field is set by the sender of the datagram, and reduced by every router on the route to its destination.
What is TTL and how it works?
TTL is deployed as a counter or timestamp embedded in each packet. When the predefined timespan or event count expires, the packet is either discarded or revalidated. In networking, TTL prevents data packets from moving across the network indefinitely. In applications, TTL manages data caching and boosts performance.
What does TTL mean in a ping?
What is time-to-live (TTL) in networking? Time to live (TTL) refers to the amount of time or “hops” that a packet is set to exist inside a network before being discarded by a router.
What is TTL 128 ping?
By default, in Windows and many other OS’s, the TTL will be 128 — that means that after a packet passes through 128 routers, if it hasn’t reached it’s final destination yet, the packet will expire and will be removed from the network.
What is a good TTL Ping?
The current recommended default time to live (TTL) for the Internet Protocol (IP) is 64. if 64 as default.
What is TTL 255 in ping?
TTL stands for Time To Live, and this value tells the maximum number of hops this packet can cross. So, TTL 255 means the ping packet can cross a maximum of 255 hops in a network. On the 255th hop, this ping packet will expire.
What is TTL 64?
64 is the number of hops that the packet can travel before it is dropped. Hard to reach hosts that are across many hops of the Internet benefit from a larger TTL on packets. In multicast protocols 64 is used to restrict the packet to the same physical region.
What is default TTL value?
Most sites use a default TTL value of 3600 (one hour). Typically, the minimum available TTL value is 30 (seconds) although technically a TTL value could be as low as one second. 86,400 (24 hours) is the maximum TTL value. Technically, a TTL value can exist anywhere between the minimum and maximum parameters.
Does TTL matter in DNS?
Time To Live, or TTL for short, is the sort of expiration date that is put on a DNS record. The TTL serves to tell the recursive server or local resolver how long it should keep said record in its cache. The longer the TTL, the longer the resolver holds that information in its cache.
What is TTL 64?
64 is the number of hops that the packet can travel before it is dropped. Hard to reach hosts that are across many hops of the Internet benefit from a larger TTL on packets. In multicast protocols 64 is used to restrict the packet to the same physical region.
What is TTL Godaddy?
TTL: Time to live in seconds. This is the amount of time the record is allowed to be cached. A TTL of 3600 means the record will update every hour. A TTL of 86400 means it will take a day for changes to update.
How does TTL work in networking?
It is an 8-bit binary value set in the header of Internet Protocol (IP) by the sending host. The purpose of a TTL is to prevent data packets from being circulated forever in the network. The maximum TTL value is 255. The value of TTL can be set from 1 to 255 by the administrators.
How the choice of TTL value affects the performance of DNS cache performance?
Reasons for long or short TTLs Longer caching results in faster responses: a longer TTL enables caching for longer periods, and cache hits are far faster than retrieving answers from authoritative servers, as the . uy experience illustrates.