The main difference between domain and domain name server (DNS) is that the domain could be a piece of string that helps to spot a specific web site while the DNS (Domain Name System) could be a server that translates the domain to the corresponding ip address to supply the specified webpage.
Do I need DNS for my domain?
The DNS system provides a domain name to IP address mapping for devices connected to the Internet, and it is crucial to the working of the Internet. Usually you don’t need to worry about it as your are automatically assigned the address of the DNS server by your ISP and Home router.
What is the difference between AD domain and DNS domain?
While DNS domains and AD DS domains typically have the same name, they are two separate objects with different roles. DNS stores zones and zone data required by AD DS and responds to DNS queries from clients. AD DS stores object names and object records and uses LDAP queries to retrieve or modify data.
What are the different domains in DNS?
The domain name space is divided into three different sections: generic domains, country domains, and inverse domain.
Does every domain have a DNS?
Every domain has its own DNS records, which include the nameserver. These are generated when you register your domain name with a hosting provider or a domain registrar. Therefore, your nameserver points your domain name to the IP address of your host or registrar.
What is DNS Example?
DNS, or the Domain Name System, translates human readable domain names (for example, www.amazon.com) to machine readable IP addresses (for example, 192.0. 2.44).
Is GoDaddy a DNS provider?
GoDaddy’s Premium DNS offers you more for less – it’s as simple as that. Not only does it include Standard DNS options, it also includes advanced features for a higher level of support.
Is Active Directory A DNS?
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) uses Domain Name System (DNS) name resolution services to make it possible for clients to locate domain controllers and for the domain controllers that host the directory service to communicate with each other.
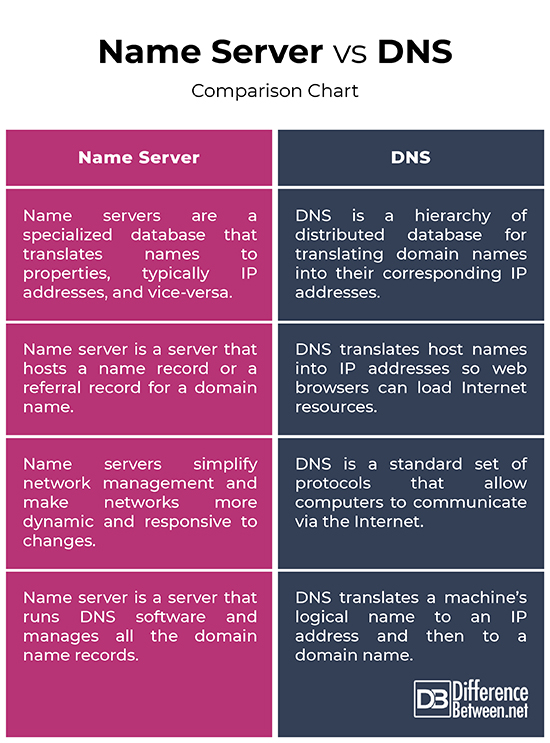
What is the difference between DNS and nameservers?
Are DNS and name servers the same thing? No, DNS and name servers aren’t the same thing. DNS is an overarching term for the system that connects computers and services across the internet. Name servers play a role in this system, holding the DNS records that connect a domain name to an IP address.
What does DNS do in a network?
The domain name system (i.e., “DNS”) is responsible for translating domain names into a specific IP address so that the initiating client can load the requested Internet resources. The domain name system works much like a phone book where users can search for a requested person and retrieve their phone number.
What are the 3 types of DNS?
There are three main kinds of DNS Servers — primary servers, secondary servers, and caching servers.
What is my DNS name?
Open your Command Prompt from the Start menu (or type “Cmd” into the search in your Windows task bar). Next, type ipconfig/all into your command prompt and press Enter. Look for the field labeled “DNS Servers.” The first address is the primary DNS server, and the next address is the secondary DNS server.
Where is DNS located?
These servers reside in your ISP’s data centers, and they handle requests as follows: If it has the domain name and IP address in its database, it resolves the name itself. If it doesn’t have the domain name and IP address in its database, it contacts another DNS server on the internet.
What happens if there is no DNS?
The DNS server returns the IP address, and the browser connects to the webpage that then appears on your screen. End users are unaware of the background tasks required to make the system work. If the DNS server is unavailable, the browser has no way of acquiring the website’s IP address, so it returns an error.
What happens if you dont have a DNS server?
The web would not work at all without DNS servers. They are responsible for translating domain names into IP addresses. Then computers use those IP addresses to locate and connect to web servers, and send users to the right websites.
What happens if we didn’t have DNS?
In other words, the DNS translates your web domain name into an IP address and vice versa. Without DNS, if you entered “www.google.com” into your browser, the servers would have no idea what that means and would not know where to direct you. DNS is a hierarchical tree data structure.
What would happen if there was no DNS?
It’s one of the cornerstones of how the internet operates. Without it, we’d be stuck memorizing long lists of numbers (IP addresses) to access the content we want. If a DNS cannot translate the domain name with the right IP address, you won’t be able to access the website you’re looking for.
What is DHCP and how it works?
A DHCP Server is a network server that automatically provides and assigns IP addresses, default gateways and other network parameters to client devices. It relies on the standard protocol known as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol or DHCP to respond to broadcast queries by clients.
What do you understand by domain name and DNS explain?
The Domain Name System (DNS) turns domain names into IP addresses, which browsers use to load internet pages. Every device connected to the internet has its own IP address, which is used by other devices to locate the device.
Who is the best DNS provider?
#1) Google Public DNS Safe and reliable internet access in mobile, desktop, and IoT devices for free. Google DNS is one of the best DNS lookup service providers. It offers a fast and reliable internet connection. The DNS service supports a lot of advanced features, such as DNS over UDP and TLS support.
Can I host my own DNS server?
There are 2 main types of DNS servers you can run: if you own a domain, you can run an authoritative nameserver for that domain. if you have a computer (or a company with lots of computers), you can run a resolver that’s resolves DNS for those computers.
What is DHCP in Active Directory?
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) allows a client to receive an IP address automatically from the DHCP server.