For example, DNS tunneling techniques enable threat actors to compromise network connectivity and gain remote access to a targeted server. Other forms of DNS attacks can enable threat actors to take down servers, steal data, lead users to fraudulent sites, and perform Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
Can you get hacked through DNS?
A DNS name server is a highly sensitive infrastructure which requires strong security measures, as it can be hijacked and used by hackers to mount DDoS attacks on others: Watch for resolvers on your network — unneeded DNS resolvers should be shut down.
What are the possible attacks on DNS?
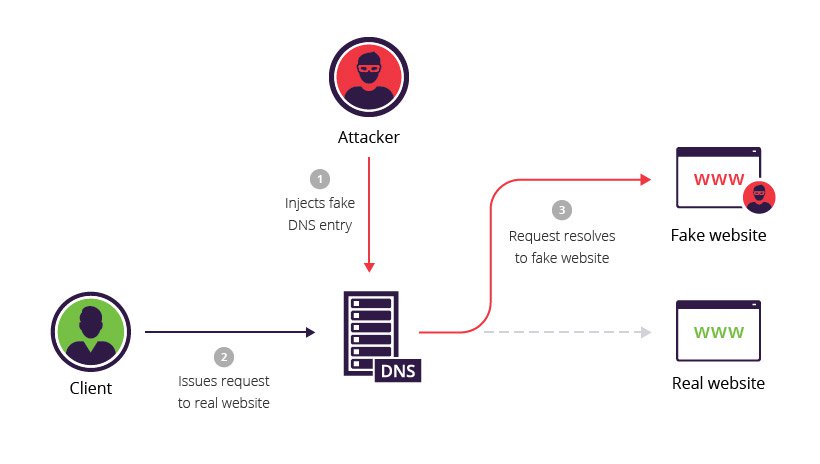
DNS poisoning and cache poisoning DNS poisoning (also known as DNS spoofing) and its cousin, DNS cache poisoning, use security gaps in the DNS protocol to redirect internet traffic to malicious websites. These are sometimes called man-in-the-middle attacks.
How do I know if my DNS is poisoned?
The main symptom of a DNS poisoning attack is a sudden, unexplained drop in web traffic. Though web traffic is always volatile, if you see a sudden reduction in the number of visitors to your site, it’s always worth investigating why.
What are DNS risks?
DNS as a security vulnerability The most common DNS risks include denial-of-service (DoS), distributed denial-of-service (DDoS), DNS hijacking, DNS spoofing, DNS tunneling, DNS amplification, DNS typosquating.
What are the possible attacks on DNS?
DNS poisoning and cache poisoning DNS poisoning (also known as DNS spoofing) and its cousin, DNS cache poisoning, use security gaps in the DNS protocol to redirect internet traffic to malicious websites. These are sometimes called man-in-the-middle attacks.
Does VPN prevent DNS hijacking?
Yes. A VPN helps prevent DNS hijacking. Most VPN services run their own DNS servers, preventing your DNS queries from being intercepted. ExpressVPN runs its own encrypted DNS on every VPN server, keeping your internet traffic protected.vor 7 Tagen
Is changing DNS settings safe?
to my computer? Changing your current DNS settings to the OpenDNS servers is a safe, reversible, and beneficial configuration adjustment that will not harm your computer or your network.
How do DNS attacks happen?
The attacker corrupts a DNS server by replacing a legitimate IP address in the server’s cache with that of a rogue address to redirect traffic to a malicious website, collect information or initiate another attack. Cache poisoning are also referred to as DNS poisoning.
What is a DNS virus?
By controlling DNS, a criminal can get an unsuspecting user to connect to a fraudulent website or to interfere with that user’s online web browsing. One way criminals do this is by infecting computers with a class of malicious software (malware) called DNSChanger.
How could DNS be abused by attackers?
Abuse of DNS to transfer data; this may be performed by tunneling other protocols like FTP, SSH through DNS queries and responses. Attackers make multiple DNS queries from a compromised computer to a domain owned by the adversary.
How common is DNS spoofing?
Through their research they discovered that DNS spoofing is still rare (occurring only in about 1.7% of observations) but has been increasing during the observed period, and that proxying is the most common DNS spoofing mechanism.
How do I clear my DNS cache?
Android (version 12) In the URL bar type in chrome://net-internals/#dns: In the left pane select DNS. In the right pane tap the Clear host cache button.
What are two symptoms that indicate that a computer system may be a victim of DNS spoofing?
Two of the biggest warning signs are (1) an increase in DNS activity from a single source about a single domain, which can indicate a Birthday attack and (2) an increase in DNS activity from a single source about multiple domain names, which can indicate attempts to find an entry point for DNS poisoning.
Is Google DNS safe?
Google Public DNS complies with Google’s main privacy policy, available at our Privacy Center. Your client IP address is only logged temporarily (erased within a day or two), but information about ISPs and city/metro-level locations are kept longer for the purpose of making our service faster, better, and more secure.
What is DNS protection on my phone?
Is DNS secure?
DNS is widely trusted by organizations, and DNS traffic is typically allowed to pass freely through network firewalls. However, it is commonly attacked and abused by cybercriminals. As a result, the security of DNS is a critical component of network security.
Is using Google DNS safe?
Google Public DNS complies with Google’s main privacy policy, available at our Privacy Center. Your client IP address is only logged temporarily (erased within a day or two), but information about ISPs and city/metro-level locations are kept longer for the purpose of making our service faster, better, and more secure.
Are Google DNS secure?
Google Public DNS offers support for encrypted transport protocols, DNS over HTTPS and DNS over TLS. These protocols prevent tampering, eavesdropping and spoofing, greatly enhancing privacy and security between a client and Google Public DNS. They complement DNSSEC to provide end-to-end authenticated DNS lookups.
Is Google a protective DNS service?
A “Protective DNS Service” is a security service and software/hardware that analyzes DNS queries and takes action to mitigate threats. The capture usually takes place on-prem (where the clients and resources are located). Google, AWS, etc. do not offer this type of service.
What are the possible attacks on DNS?
DNS poisoning and cache poisoning DNS poisoning (also known as DNS spoofing) and its cousin, DNS cache poisoning, use security gaps in the DNS protocol to redirect internet traffic to malicious websites. These are sometimes called man-in-the-middle attacks.
Why would an attacker want to hijack DNS service?
The hijacker may use it for pharming (displaying advertisements to users in order to generate revenue) or phishing (redirecting users to a bogus version of your website in order to steal data or login information). Domain redirection is also used by ISPs to control users’ DNS queries in order to collect user data.