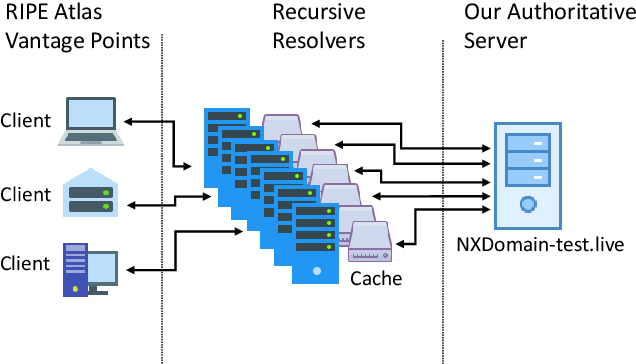
A negative response indicates that information about a requested domain does not exist, or that the server cannot provide an answer for the query. The storage of this information is called negative caching. Negative caching helps speed up responses to queries about a domain.
What is negative DNS cache?
Negative caching was an optional part of the DNS specification and deals with the caching of the non-existence of an RRset [RFC2181] or domain name. Negative caching is useful as it reduces the response time for negative answers.
What is the purpose of DNS caching?
DNS caching allows any DNS server or client to locally store the DNS records and re-use them in the future – eliminating the need for new DNS queries. The Domain Name System implements a time-to-live (TTL) on every DNS record. TTL specifies the number of seconds the record can be cached by a DNS client or server.
Is clearing DNS cache good?
There’s a lot of reasons to regularly flush your DNS cache. It can help prevent phishing schemes or other attacks on your computer, direct you to the most up-to-date versions of your most frequently visited sites, restore your internet connection, and keep your data private.
Should I use DNS caching?
DNS cache is a very efficient way to avoid having to complete an entire DNS lookup each time you visit a site. Instead, this process will only need to occur the first time you visit the site and upon subsequent requests, your machine will use the OS’s and browser’s cached DNS information until it expires or is flushed.
What is negative DNS cache?
Negative caching was an optional part of the DNS specification and deals with the caching of the non-existence of an RRset [RFC2181] or domain name. Negative caching is useful as it reduces the response time for negative answers.
Is cache positive or negative?
A positive cache is useful if success – retrieving an object or resource – is more expensive than storing information about what you want. In contrast, a negative cache is useful if failure – determining that something does not exist – is very expensive.
How long does a DNS cache last?
A. By default, Windows stores positive responses in the DNS cache for 86,400 seconds (i.e., 1 day) and stores negative responses for 300 seconds (5 minutes). To modify these values, perform the following steps: Start a registry editor (e.g., regedit.exe).
How does DNS caching affect the network?
Ultimately, the DNS enables human users to keep track of more web pages and to access them as required, and DNS caching expedites the DNS lookup process to more quickly resolve a domain name to an IP address when the OS has visited a web page before.
How do I know if my DNS is poisoned?
The main symptom of a DNS poisoning attack is a sudden, unexplained drop in web traffic. Though web traffic is always volatile, if you see a sudden reduction in the number of visitors to your site, it’s always worth investigating why.
How DNS cache poisoning attacks work?
DNS cache poisoning occurs when a threat actor feeds false information into the DNS cache, thereby making a user’s web browser return an incorrect response. This response usually redirects users to a website other than the one they intended to view.
How often should you flush DNS?
If you need clear DNS cache from client side for every 15 minutes, it is OK. After these caches were cleared, if needed, the client will re-query these records from DNS server.
How do I clean my DNS?
Navigate to All Programs > Accessories and select Command Prompt. In the command line interface, run ipconfig /flushdns . You should receive a confirmation message once the DNS cache is flushed.
What happens when you clear DNS cache?
Since clearing the DNS cache removes all the entries, it deletes any invalid records too and forces your computer to repopulate those addresses the next time you try accessing those websites. These new addresses are taken from the DNS server your network is set up to use.
Does DNS cache flush on reboot?
Answers. A DNS Server’s cache is cleared at reboot. Other than that you can manually clear the cache at any time by using the DNS Admin console. If you leave the cache alone, the individual records are removed from the DNS cache as the TTL (time-to-live) expires.
Does chrome have DNS cache?
Yes, Google Chrome browser has inbuilt DNS and proxy caching server to improve performance. You can quickly clean out or flush out DNS entries manually on Google Chrome browser.
What is DNS record TTL?
Time to Live (TTL) is a field on DNS records that controls how long each record is valid and — as a result — how long it takes for record updates to reach your end users.
What is SOA record in DNS?
The DNS ‘start of authority’ (SOA) record stores important information about a domain or zone such as the email address of the administrator, when the domain was last updated, and how long the server should wait between refreshes. All DNS zones need an SOA record in order to conform to IETF standards.
What is SOA record type?
A start of authority record (abbreviated as SOA record) is a type of resource record in the Domain Name System (DNS) containing administrative information about the zone, especially regarding zone transfers. The SOA record format is specified in RFC 1035.
What is Nxdomain error?
The NXDOMAIN is a DNS message type received by the DNS resolver (i.e. client) when a request to resolve a domain is sent to the DNS and cannot be resolved to an IP address. An NXDOMAIN error message means that the domain does not exist.
What is negative DNS cache?
Negative caching was an optional part of the DNS specification and deals with the caching of the non-existence of an RRset [RFC2181] or domain name. Negative caching is useful as it reduces the response time for negative answers.
What is cache in simple terms?
Cache primarily refers to a thing that is hidden or stored somewhere, or to the place where it is hidden. It has recently taken on another common meaning, “short-term computer memory where information is stored for easy retrieval.” Cash, on the other hand, is most often used in the sense “ready money.”