When you boot a computer, your processor looks for instructions in system ROM (the BIOS) and executes them. They normally ‘wake up’ peripheral equipment and search for the boot device. The boot device either loads the operating system or gets it from someplace else.
Does rebooting laptop delete everything?
Rebooting the device will just turn it off and on, and won’t actually reset/restore the software like you really want, which in this case would erase all your custom apps and delete any lingering personal information.
What does booting a laptop mean?
In computing, booting is the process of starting a computer as initiated via hardware such as a button or by a software command. After it is switched on, a computer’s central processing unit (CPU) has no software in its main memory, so some process must load software into memory before it can be executed.
Does booting erase data?
No, booting from a USB or DVD is only temporary. If you change the boot order back to the hard drive everything will be there. However if you run Startup Repair or perform other changes while using the USB then Windows might be changed (hopefully for the better). Though the data should still be as it was.
What happen after booting?
Booting is basically the process of starting the computer. When the CPU is first switched on it has nothing inside the Memory. In order to start the Computer, load the Operating System into the Main Memory and then Computer is ready to take commands from the User.
Is Rebooting laptop safe?
So, while you think you’re saving time by not completely turning off and restarting your computer, it can actually be slowing you down. Rebooting both keeps your computer healthy and can fix PC problems you may be having with memory or certain programs not functioning correctly.
Is reboot same as restart?
Reboot vs restart, is restart and reboot the same thing? You may be easily confused with reboot and restart. They are almost the same but have slight differences. The term restart means a reboot when computer OS turns off all programs and ends all pending input and output operations before conducting a soft reboot.
What happens in the boot process?
The boot process begins when you push the power button, which sends power to the bootloader in the cache memory. The bootloader program performs a POST, or Power On Self Test called, and if everything is okay, the Basic Input Output System, or BIOS, is activated and then finds and loads the operating system.
Why do we boot a computer?
A boot causes the computer to start executing instructions. PCs and Macs contain built-in instructions in a ROM or flash memory chip that are automatically executed on startup. These instructions search for the operating system, load it and pass control to it.
Why is it called booting?
The term “boot” comes from the word “bootstraps,” which people at one time used to get their boots on. Likewise, “booting” a computer gets it up and running. In simple terms, to boot a computer is to turn it on. Once the computer’s power is turned on, the “boot process” takes place.
Does boot mean reset?
Usually, rebooting to bootloader is a feature of Android smartphones. It means to restart the device to bootloader or download mode. Rebooting to bootloader implies that the default will not be started. Instead, it will be stalled so you can load alternate systems.
Is a clean boot safe?
Is a Clean Boot safe? Yes, it is safe. When you boot normally, it will launch all the programs that have registered with the startup. During Clean Boot, it filters out those programs and helps users to troubleshoot hardware or software problems.
What happens when boot from USB?
When you boot from a USB device, you’re running your computer with the operating system installed on the USB device. When you start your computer normally, you’re running it with the operating system installed on your internal hard drive—such as Windows, Linux, or macOS.
What are two types of booting?
There are two types of Booting available: Cold Booting/ Hard Booting: Cold booting is the process when our computer system moves from shut down state to the start by pressing the power button. The system reads the BIOS from ROM and will eventually load the Operating System.
What is the first step in the boot process?
Power Up. The first step of any boot process is applying power to the machine. When the user turns a computer on, a series of events begins that ends when the operating system gets control from the boot process and the user is free to work.
Which step happens first during the boot process?
In the first step of the boot process, the CPU activates the basic input/output system, or BIOS, a program that manages the exchange of data between the OS and the input and output devices attached to the system. The first job BIOS performs is to ensure that the computer’s peripheral devices are attached and working.
Does reboot Clear memory?
Selecting Restart to reboot the computer does not clear memory, but turning it off and on again guarantees that memory is cleared and the system is reset.
Does rebooting cause data loss?
A reboot shouldn’t cause the loss of data. A reboot is just turning off and back on.
What is the difference between booting and rebooting?
To reboot is to reload the operating system of a computer: to start it up again. Booting is starting a computer’s operating system, so rebooting is to start it for a second or third time. Rebooting is usually necessary after a computer crashes, meaning it stops working because of a malfunction.
How do I soft boot my laptop?
There are two ways to do soft reboot on Windows: Ctrl + Alt + Delete key combination and. Selecting “Shut Down” or “Restart” from the start menu.
What is a boot in computer?
Booting is a startup sequence that starts the operating system of a computer when it is turned on. A boot sequence is the initial set of operations that the computer performs when it is switched on. Every computer has a boot sequence.
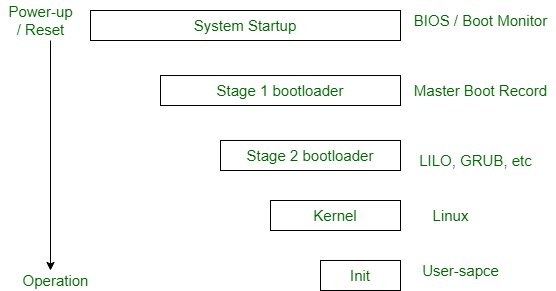
What are the 4 stages of the boot process?
Six steps of the booting process are BIOS and Setup Program, The Power- On-Self-Test (POST), The Operating system Loads, System Configuration, System Utility Loads and Users Authentication.