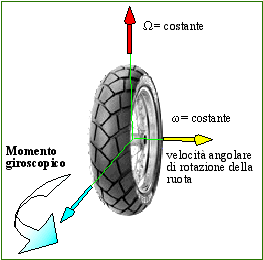
Gyroscopic effects The role of the gyroscopic effect in most bike designs is to help steer the front wheel into the direction of a lean. This phenomenon is called precession, and the rate at which an object precesses is inversely proportional to its rate of spin.
How does a gyroscope work on a motorcycle?
What is gyroscopic in bike?
A bicycle wheel acts like a giant gyroscope. A spinning bicycle wheel resists efforts to tilt it and point the axle in a new direction. Any rapidly spinning wheel exhibits this gyroscopic property—and you can use this tendency to take yourself for a spin.
What is the gyroscopic effect?
Gyroscopic effect: To change the direction of the axis of spin the only remaining possibility is to apply a couple at right angles to the spinning axis. 10. The axis of spin will deviate so as to direct its spin in the direction of the applied couple. This is called Gyroscopic Precession”.
Is there a self balancing motorcycle?
Honda’s Self-Balancing Motorcycles One of the popular self-balancing bikes is Honda’s Riding Assist concept. The automaker unveiled this bike almost five years ago in Las Vegas at a Consumer Electronics Show. You might be wondering about the secret behind these self-balancing motorcycles.
What is the effect of gyroscopic couple on the stability of an automobile which is negotiating a curve?
The gyroscopic couple will act over the vehicle outwards i.e., in the anticlockwise direction when seen from the front of the two wheeler. This couple tends to overturn/topple the vehicle in the outward direction as shown in Fig…
Do motorcycles have gyroscopes?
The motorcycle’s wheels act like gyroscopes and create gyroscopic forces when moving at speeds above five miles an hour. One of the most interesting effects related to a gyroscope is a phenomenon known as precession.
What is gyroscopic stability?
A Gyroscopic stabilizer is a control system that reduces tilting movement of a ship or aircraft. It senses orientation using a small gyroscope, and counteracts rotation by adjusting control surfaces or by applying force to a large gyroscope.
What is the effect of reactive gyroscopic couple on two wheeler when bike takes left turn?
Since the reactive gyroscopic couple acts in clockwise direction when seen from the front, therefore its effect is to increase the reaction on the left hand side bearing (i.e. A) and to decrease the reaction on the right hand side bearing (i.e. B).
When a vehicle is taking a turn the inner wheel rotate?
Explanation: When a four-wheeler takes a turn, the axis of rotating parts (i.e. wheels and engine) undergoes precession and the gyroscopic couple will be acting on these rotating parts. Also as the vehicle is moving along a curved path, the centrifugal force will also be acting on the vehicle.
What is gyroscopic effect on aeroplane?
When a single-engined aeroplane turns to the left, the nose tends to dip; when the turn is to the right, the gyroscopic effect tends to raise the nose.
What is an example of a gyroscope?
The classic type gyroscope finds application in gyro-compasses, but there are many more common examples of gyroscopic motion and stability. Spinning tops, the wheels of bicycles and motorcycles, the spin of the Earth in space, even the behavior of a boomerang are examples of gyroscopic motion.
What are gyroscopic vehicles?
A gyrocar is a two-wheeled automobile. The difference between a bicycle or motorcycle and a gyrocar is that in a bike, dynamic balance is provided by the rider, and in some cases by the geometry and mass distribution of the bike itself, and the gyroscopic effects from the wheels.
Do motorcycles have gyroscopes?
The motorcycle’s wheels act like gyroscopes and create gyroscopic forces when moving at speeds above five miles an hour. One of the most interesting effects related to a gyroscope is a phenomenon known as precession.
What is gyroscopic torque?
What is gyroscopic torque? The gyroscopic torque is the torque applied to the rotating body such that there is a change in the axis of rotation of the rotating body.
What is gyroscopic inertia?
1. Gyroscopic inertia: the gyro’s conservation of angular momentum (i.e., natural resistance to change in orientation with regard to its inertial frame of reference)
What is precession motion?
precession, phenomenon associated with the action of a gyroscope or a spinning top and consisting of a comparatively slow rotation of the axis of rotation of a spinning body about a line intersecting the spin axis. The smooth, slow circling of a spinning top is precession, the uneven wobbling is nutation. precession.
What is a self-balancing bike?
Self-balancing bike specs As well as the accelerometer and gyroscope, the bicycle is equipped with two brushless motors and a steering gear, as well as an RGBD depth camera, and a LiDAR sensor — as used by driverless cars to detect their surroundings.
How does self balance work?
The secret of the self-balancing system lies in the front fork, which connects the handlebars to the front wheel. When the bike slows to less than 4kph, the angle of the fork changes automatically, moving the wheel slightly forward.
How gyroscopic effects are set up in machines or automotive vehicles?
1 – place of the shaft support (left bearing A); 2 – rotating cutting drum; 3 – shaft; 4 – place of the shaft support (right bearing B) The gyroscope is created by the drum rotating at an angular speed ωx around the axis x. The axis y follows the direction of a vehicle rotation at the speed v.
How does a four wheeled car affect gyroscopic couple?
Explanation: When a four-wheeler takes a turn, the axis of rotating parts (i.e. wheels and engine) undergoes precession and the gyroscopic couple will be acting on these rotating parts. Also as the vehicle is moving along a curved path, the centrifugal force will also be acting on the vehicle.
What is the effect of gyroscopic couple on rolling of ship?
In case of rolling of a ship the axis of precession is always parallel to the axis of spin for all positions. Hence there is no effect of the gyroscopic couple acting on the body of the ship during rolling.