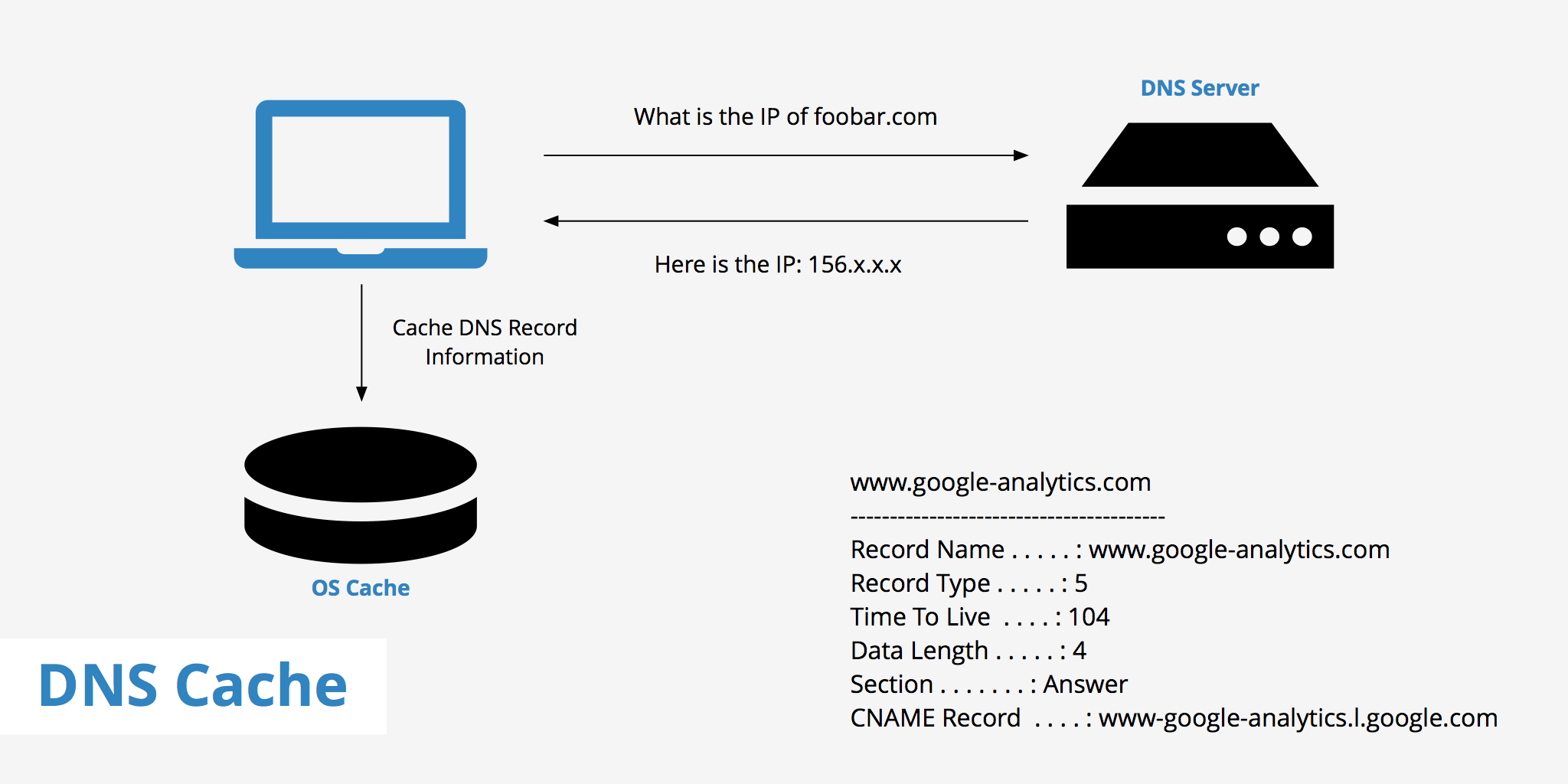
DNS caching allows any DNS server or client to locally store the DNS records and re-use them in the future – eliminating the need for new DNS queries. The Domain Name System implements a time-to-live (TTL) on every DNS record. TTL specifies the number of seconds the record can be cached by a DNS client or server.
Should I use DNS caching?
DNS cache is a very efficient way to avoid having to complete an entire DNS lookup each time you visit a site. Instead, this process will only need to occur the first time you visit the site and upon subsequent requests, your machine will use the OS’s and browser’s cached DNS information until it expires or is flushed.
What is the most useful reason for DNS?
DNS ensures the internet is not only user-friendly but also works smoothly, loading whatever content we ask for quickly and efficiently. It’s one of the cornerstones of how the internet operates. Without it, we’d be stuck memorizing long lists of numbers (IP addresses) to access the content we want.
Should I use DNS caching?
DNS cache is a very efficient way to avoid having to complete an entire DNS lookup each time you visit a site. Instead, this process will only need to occur the first time you visit the site and upon subsequent requests, your machine will use the OS’s and browser’s cached DNS information until it expires or is flushed.
Does DNS cache speed up?
Therefore, DNS caching will accelerate the DNS resolution speed of web browsers for any subsequent times they need to connect to your domain. You can use TTL or Time to Live to tell the recursive servers, operating systems and web browsers how long they should cache the IP address for your domain name.
What is DNS advantages and disadvantages?
No need for memorizing IP addresses -DNS servers provide a nifty solution of converting domain or sub domain names to IP addresses. Imagine how it would feel having to memorize the IP addresses of twitter, Facebook, Google or any other site that you normally frequent on a daily basis.
What are two uses of DNS?
DNS serves other purposes in addition to translating names to IP addresses. For instance, mail transfer agents use DNS to find the best mail server to deliver e-mail: An MX record provides a mapping between a domain and a mail exchanger; this can provide an additional layer of fault tolerance and load distribution.
Is it safe to clear cache on DNS server?
Clearing the DNS server will remove any invalid addresses, whether because they’re outdated or because they’ve been manipulated. It’s also important to note flushing the cache doesn’t have any negative side effects.
Should I use DNS for gaming?
DNS improves the gaming experience for users via its speed and high-security nature. It improves latency and reduces ping, allowing gamers to enjoy their activities and minimize lag issues. DNS also reduces packet loss, enables wider customizability with websites, and eliminates jitter.
What is turn off DNS caching?
To disable the caching completely on DNS Server, set the value of MaxCacheTtl to 0x0. The DNS Server saves the records in memory area so that it can respond quickly to the Client DNS Queries for the same name. Records are deleted from the cache as per the value defined in the MaxCacheTtl registry entry.
Should I use DNS caching?
DNS cache is a very efficient way to avoid having to complete an entire DNS lookup each time you visit a site. Instead, this process will only need to occur the first time you visit the site and upon subsequent requests, your machine will use the OS’s and browser’s cached DNS information until it expires or is flushed.
What are 2 advantages of cache memory?
Cache memory is faster than main memory. It consumes less access time as compared to main memory. It stores the program that can be executed within a short period of time. It stores data for temporary use.
Does cache improve performance?
Cache Memory and Performance Cache memory increases a computer’s performance. The cache memory is located very close to the CPU, either on the CPU chip itself or on the motherboard in the immediate vicinity of the CPU and connected by a dedicated data bus.
How does caching improve network performance?
Caching reduces the workload of the remote web server by spreading the data widely among the proxy caches over the WAN. In a scenario where the remote server is not available due to a crash or network partitioning, the client can obtain a cached copy at the proxy. Hence, the robustness of the Web service is enhanced.
Is clearing DNS cache good?
There’s a lot of reasons to regularly flush your DNS cache. It can help prevent phishing schemes or other attacks on your computer, direct you to the most up-to-date versions of your most frequently visited sites, restore your internet connection, and keep your data private.
How long is DNS cache stored?
By default, Windows stores positive responses in the DNS cache for 86,400 seconds (i.e., 1 day) and stores negative responses for 300 seconds (5 minutes). To modify these values, perform the following steps: Start a registry editor (e.g., regedit.exe).
How big should DNS cache be?
What are the 3 types of DNS?
There are three main kinds of DNS Servers — primary servers, secondary servers, and caching servers.
How often should I clear my DNS cache?
If you need clear DNS cache from client side for every 15 minutes, it is OK. After these caches were cleared, if needed, the client will re-query these records from DNS server.
What happens if I delete all DNS records?
Delete a DNS record from your domain that’s no longer needed. Deleting records will completely remove them from your zone file. Changes to your DNS may interrupt how your domain works, such as your email and website.
How often is DNS cache cleared?
By default, Windows stores positive responses in the DNS cache for 86,400 seconds (i.e., 1 day) and stores negative responses for 300 seconds (5 minutes).
Can DNS cause lag?
Can changing my DNS help reduce gaming lag ‘latency’? Although DNS is not directly related to your internet speed, it can influence the time it takes for your ISP to retrieve the website you are looking for. If you’re using the router supplied by your ISP, it will be pre-set with their DNS records.