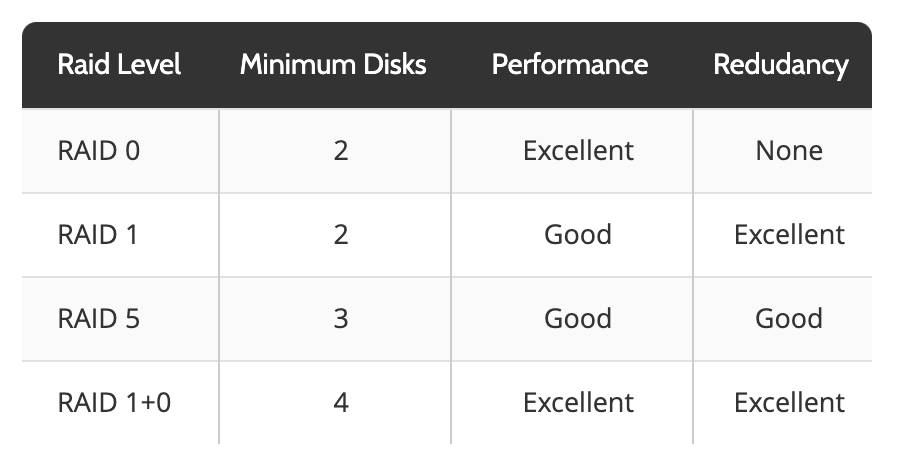
RAID 0RAID 0In computer data storage, data striping is the technique of segmenting logically sequential data, such as a file, so that consecutive segments are stored on different physical storage devices.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Data_stripingData striping – Wikipedia offers the best performance, both in read and write operations. There is no overhead caused by parity controls. All storage capacity is used, there is no overhead.
Which RAID levels offer the best performance?
RAID 10 is a combination of RAID 1 and 0 and is often denoted as RAID 1+0. It combines the mirroring of RAID 1 with the striping of RAID 0. It’s the RAID level that gives the best performance, but it is also costly, requiring twice as many disks as other RAID levels, for a minimum of four.
Which RAID type is fastest?
RAID 0 is the only RAID type without fault tolerance. It is also by far the fastest RAID type. RAID 0 works by using striping, which disperses system data blocks across several different disks.
Which RAID is best for performance and redundancy?
If you need solid performance but also need a level of redundancy, RAID 10 is the best way to go. Keep in mind that you will lose half your usable storage, so plan accordingly! Redundancy: If redundancy is most important to you, you will be safe choosing either a RAID 10 or a RAID 60.
Does RAID mode increase performance?
Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) is a virtual disk technology that combines multiple physical drives into one unit. RAID can create redundancy, improve performance, or do both.
Which RAID levels offer the best performance?
RAID 10 is a combination of RAID 1 and 0 and is often denoted as RAID 1+0. It combines the mirroring of RAID 1 with the striping of RAID 0. It’s the RAID level that gives the best performance, but it is also costly, requiring twice as many disks as other RAID levels, for a minimum of four.
Which RAID is best for performance and redundancy?
If you need solid performance but also need a level of redundancy, RAID 10 is the best way to go. Keep in mind that you will lose half your usable storage, so plan accordingly! Redundancy: If redundancy is most important to you, you will be safe choosing either a RAID 10 or a RAID 60.
Is RAID 6 or 10 better?
In general, RAID 10 rebuilds faster then RAID 6 or RAID 60: a single drive is read and written to recover the array instead of all the drives being read to recompute the missing data using parity. In practice, storage manufacturers might provide solutions that make this less of a trade-off.
Does RAID 0 increase speed?
RAID 0 is taking any number of disks and merging them into one large volume. This will greatly increase speeds, as you’re reading and writing from multiple disks at a time. An individual file can then use the speed and capacity of all the drives of the array. The downside to RAID 0 though is that it is NOT redundant.
What RAID is best for SSD?
In the aspect of performance, SSD RAID is absolutely superior to a single SSD. As we all know, an SSD RAID array configured by multiple SSDs can have an enormous impact on performance. Among these RAID levels, RAID 0 offers the best performance. SSD RAID 0 is also one of RAID levels that individual users may take.
Does RAID 5 improve performance?
RAID 5 uses at least three hard drives and strips data across multiple hard drives to improve performance through simultaneous access, but unlike RAID 0, RAID 5 includes correction codes (parity bits) between the data.
Why RAID 6 is better than RAID 5?
The primary difference between RAID 5 and RAID 6 is that a RAID 5 array can continue to function following a single disk failure, but a RAID 6 array can sustain two simultaneous disk failures and still continue to function. RAID 6 arrays are also less prone to errors during the disk rebuilding process.
Which RAID rebuilds fastest?
RAID 1: This is a mirrored pair and has a fast rebuild as data is copied block for block from the source to the target.
What type of RAID should I use?
RAID 6 is a good all-round system that combines efficient storage with excellent security and decent performance. It is preferable over RAID 5 in file and application servers that use many large drives for data storage.
Which RAID do I need?
RAID 5 is ideal when space and cost are more important than performance. RAID 6 is similar to RAID 5, except it provides another layer of striping and can sustain two drive failure. A minimum of four drives is required. The performance of RAID 6 is lower than that of RAID 5 due to this additional fault tolerance.
Is RAID 0 or 1 better?
RAID 0 offers the best performance and capacity but no fault tolerance. Conversely, RAID 1 offers fault tolerance but does not offer any capacity of performance benefits. While performance is an important factor, backup admins may prioritize fault tolerance to better protect data.
Is RAID faster than SSD?
Does RAID 0 increase SSD speed?
RAID 0 works far better with SSDs than it does with hard drives, because mechanical drives aren’t fast enough to take full advantage of the increased bandwidth. In most cases, running SSDs in tandem works really, really well. This tip is primarily for desktop PC owners, of course.
Which is faster RAID 0 or RAID 5?
RAID 0 gives you better performance than raid 5.
Does RAID 5 improve performance?
RAID 5 uses at least three hard drives and strips data across multiple hard drives to improve performance through simultaneous access, but unlike RAID 0, RAID 5 includes correction codes (parity bits) between the data.
Why RAID 6 is better than RAID 5?
The primary difference between RAID 5 and RAID 6 is that a RAID 5 array can continue to function following a single disk failure, but a RAID 6 array can sustain two simultaneous disk failures and still continue to function. RAID 6 arrays are also less prone to errors during the disk rebuilding process.
Is RAID 10 as fast as RAID 0?
RAID 10 Performance Because RAID 10 is a RAID 0 stripe of mirror sets, we have no overhead to worry about from the stripe, but each mirror has to write the same data twice to create the mirroring. This cuts our write performance in half compared to a RAID 0 array of the same number of drives.