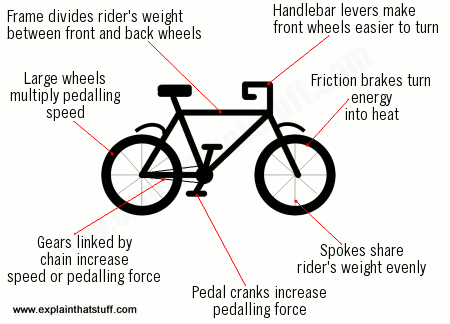
The pedals are connected by a chain to the back wheel. When the rider pushes on the pedals, the back wheel turns. This moves the bicycle forward. The rider steers by turning the handlebars or by leaning.
Can physics explain how a bicycle works?
If work, which transfers energy, is done on an object by applying a net force, the object speeds up and thereby gains kinetic energy. A bicycle can convert up to 90 percent of a person’s energy and movement into kinetic energy. This energy is then used to move the bike.
What is the physics of bicycle?
When the bicycle leans, the point of contact of the front tire moves to one side of the plane of the wheel, creating a frictional torque twisting the wheel into the lean and stabilizing the bicycle, as before, by centrifugal action. The contact point of the bicycle’s front tire is ahead of the steering axis.
What are the forces acting on a bicycle?
The primary external forces on the bike are gravity, ground, friction, rolling resistance, and air resistance.
Can physics explain how a bicycle works?
If work, which transfers energy, is done on an object by applying a net force, the object speeds up and thereby gains kinetic energy. A bicycle can convert up to 90 percent of a person’s energy and movement into kinetic energy. This energy is then used to move the bike.
How does a bicycle work step by step?
The pedals are connected by a chain to the back wheel. When the rider pushes on the pedals, the back wheel turns. This moves the bicycle forward. The rider steers by turning the handlebars or by leaning.
How does a bicycle stop moving?
When we apply the brake then there is a frictional force between the brake and the rim of the cycle. This force opposes the forward motion of the body and hence bicycle stops.
What type of energy transformation is a bicycle?
When you ride a bicycle, several things happen that require energy and it’s transformation. You pedaling the bike is transforming chemical energy, supplied by the breakdown of the food you eat, into mechanical energy to turn the pedals. The chemical energy is potential and the mechanical energy is kinetic.
What law of motion is riding a bike?
Newton’s Second Law of Motion says that acceleration (gaining speed) happens when a force acts on a mass (object). Riding your bicycle is a good example of this law of motion at work.
What energy transformation occurs in a bicycle?
The various energy transformations that occur when you are riding a bicycle are given below: The rider’s muscular energy is converted to heat energy and the bicycle’s kinetic energy while riding a bicycle. The rider’s body is heated by heat energy. The bicycle is propelled in a circular motion by kinetic energy.
Why is it easier to balance a bicycle in motion?
Solution : When a bicycle is in motion, it is easy to balance because the principle of conservation of angular momentum is involved.
How does a bicycle run on two wheels?
In a bicycle, the pair of gears is not driven directly but linked by a chain. At one end, the chain is permanently looped around the main gear wheel (between the pedals). At its other end, it shifts between a series of bigger or smaller toothed wheels when you change gear.
Do scientists not know how bicycles work?
Bike design has really just been a “guess and test” model — we know it works because we can ride it, we just don’t know why it works. Take the riderless bike, for example. You can push a bike along a path and it almost self-steers. It can recover from wobbles to stay upright.
What effect does the force have on the bicycle?
When biking on a level road, your forward force comes from pushing and pulling on the pedals to make the back tyre push backwards against the road. The two main forces that oppose your motion are aerodynamic drag (air resistance) and rolling resistance of the tyres against the road caused as the tyre is compressed.
What source of energy does a bicycle use to move?
The rider’s muscular energy is converted to heat energy and the bicycle’s kinetic energy while riding a bicycle. The rider’s body is heated by heat energy. The bicycle is propelled in a circular motion by kinetic energy.
Why can a bicycle be considered a device that can convert energy?
Suggested answer: Students should answer that a bicycle can be considered an energy conversion device because a bicycle takes one form of energy and turns it into another. What starts as the energy of a person’s feet pressing the pedals of the bicycle is converted into the energy that propels the bicycle forward.
Can physics explain how a bicycle works?
If work, which transfers energy, is done on an object by applying a net force, the object speeds up and thereby gains kinetic energy. A bicycle can convert up to 90 percent of a person’s energy and movement into kinetic energy. This energy is then used to move the bike.
Why is a bike a physical system?
Answer: In essence, a system is a set of parts which completes a task; parts which work together and it can be physical. A bicycle is a physical system because there are several parts which work together to perform a function.
Which simple machine is used in bicycle?
The wheel and axle is a simple machine consisting of a wheel attached to an axle. In order to move a bicycle, the force is applied to the axle which will exert larger force on the wheel.
How does the gears on a bicycle work?
Bicycle external drivetrains explained Gears are changed on the cassette (a set of sprockets on the rear wheel) by the rear derailleur. This shifts the chain up or down the cassette. As the derailleur moves to change gear it forces the chain against ramps or steps, moving it onto a bigger or smaller sprocket.
Why a moving bicycle does not fall?
The front wheel of the bicycle is spinning forward quickly, acting like a gyroscope. Then when you tip the bike to the right, the gyroscope applies the torque, which turns the handlebars to the right and causes the steering, bringing the wheels back under the bicycle and holding it up.
What effect does the force have on the bicycle?
When biking on a level road, your forward force comes from pushing and pulling on the pedals to make the back tyre push backwards against the road. The two main forces that oppose your motion are aerodynamic drag (air resistance) and rolling resistance of the tyres against the road caused as the tyre is compressed.