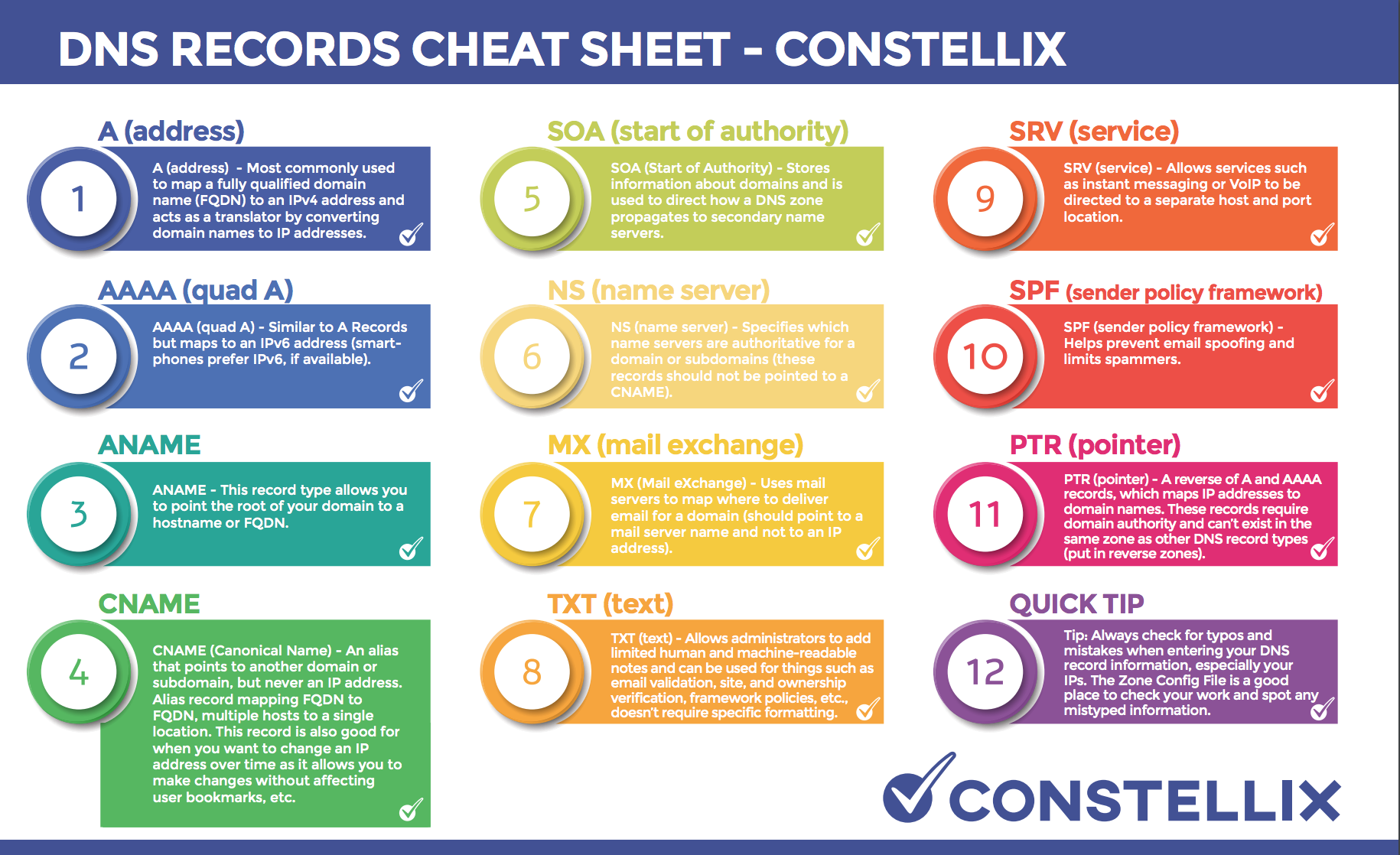
DNS servers store records. When a DNS query is sent by a device, that query gets a response from those records with the help of DNS servers and resolvers. There are eight records that you see again and again: A, AAAA, CNAME, PTR, NS, MX, SOA, and TXT.
What is DNS records and its types?
DNS records (aka zone files) are instructions that live in authoritative DNS servers and provide information about a domain including what IP address is associated with that domain and how to handle requests for that domain.
What are the three 3 types of DNS queries?
3 types of DNS queries—recursive, iterative, and non-recursive.
What is DNS records and its types?
DNS records (aka zone files) are instructions that live in authoritative DNS servers and provide information about a domain including what IP address is associated with that domain and how to handle requests for that domain.
What are the three 3 types of DNS queries?
3 types of DNS queries—recursive, iterative, and non-recursive.
What are AAAA records used for?
Like A records, AAAA records enable client devices to learn the IP address for a domain name. The client device can then connect with and load the website. AAAA records are only used when a domain has an IPv6 address in addition to an IPv4 address, and when the client device in question is configured to use IPv6.
What is a DNS A record example?
As an example, an A Record is used to point a logical domain name, such as “google.com”, to the IP address of Google’s hosting server, “74.125. 224.147”. These records point traffic from example.com (indicated by @) and ftp.example.com to the IP address 66.147. 224.236.
What is AAAA DNS record?
An AAAA record maps a domain name to the IP address (Version 6) of the computer hosting the domain. An AAAA record is used to find the IP address of a computer connected to the internet from a name.
Where are DNS records stored?
DNS records are stored in authoritative servers. These records provide information about a domain, including its associated IP address for each domain. It is mandatory for all domains to have a specific set of default records.
How many DNS servers are there?
Root name server overview In total, there are 13 main DNS root servers, each of which is named with the letters ‘A’ to ‘M’. They all have a IPv4 address and most have an IPv6 address. Managing the root server is ICANN’s responsibility (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers).
What is a cname record?
A Canonical Name or CNAME record is a type of DNS record that maps an alias name to a true or canonical domain name. CNAME records are typically used to map a subdomain such as www or mail to the domain hosting that subdomain’s content.
What is a primary DNS?
What is Primary DNS? A primary DNS server is the first point of contact for a browser, application or device that needs to translate a human-readable hostname into an IP address. The primary DNS server contains a DNS record that has the correct IP address for the hostname.
What is the most common type of record in a DNS zone?
A and AAAA DNS records Firstly, address (A) records are the most common record type by far. In brief, A records map domain names to IPv4 addresses. Secondly, as the internet gradually makes the transition to IPv6, there are AAAA records (spoken as “quad A”).
Which is type of DNS scopes?
The three DNS server types server are the following: DNS stub resolver server. DNS recursive resolver server. DNS authoritative server.
What is DNS AAAA record?
An AAAA record maps a domain name to the IP address (Version 6) of the computer hosting the domain. An AAAA record is used to find the IP address of a computer connected to the internet from a name.
What are the types of DNS zones?
There are two types of DNS zones – Primary (Master) DNS zone for control and Secondary (Slave) DNS zone for redundancy and better performance. The first contains all the original DNS records, and the second gets them from the Primary DNS zone. The process is called DNS zone transfer.
What are the two different types of DNS requests?
In general, there are two ways of resolving a host or a domain name to an IP address, using the domain name system – a Recursive query and a non-Recursive query.
What is A record vs Cname?
Difference Between A and CNAME An A Record maps a hostname to one or more IP addresses, while the CNAME record maps a hostname to another hostname.
What is DNS records and its types?
DNS records (aka zone files) are instructions that live in authoritative DNS servers and provide information about a domain including what IP address is associated with that domain and how to handle requests for that domain.
What are the three 3 types of DNS queries?
3 types of DNS queries—recursive, iterative, and non-recursive.
Is IPv6 faster than IPv4?
Network Security: Faster Speed and Lack of NAT IPv6 is faster than IPv4 in network devices because it lacks network-address translation (NAT). Using IPv6 is a better choice for people that require high speed for their network processing.
What is IPv6 DNS?
Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) is a new version of the Internet Protocol (IP), the transport mechanism used for most communication on the Internet. Devices use numeric IP addresses to connect to each other within and between networks.