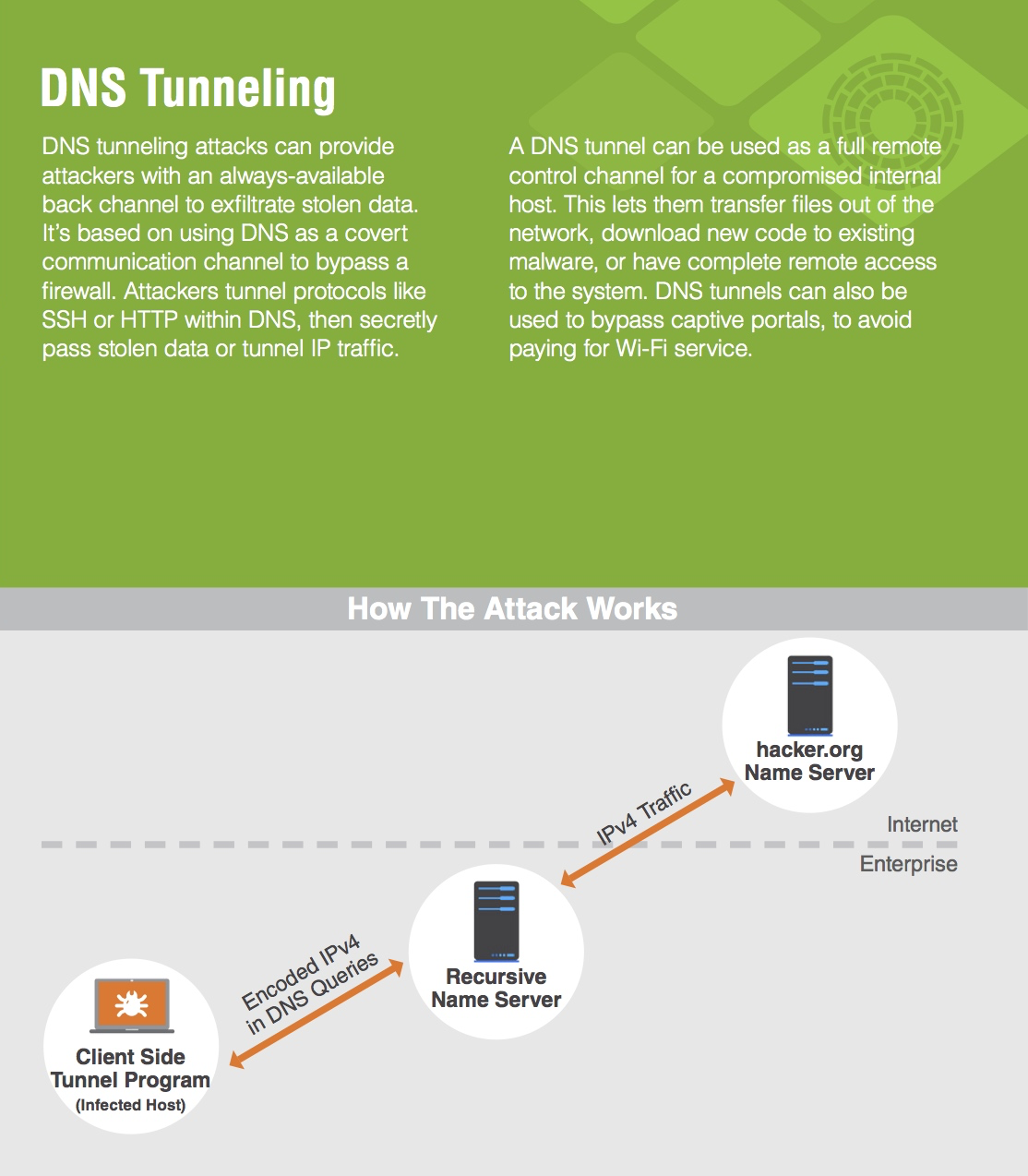
DNS tunneling exploits the DNS protocol to tunnel malware and other data through a client-server model. The attacker registers a domain, such as badsite.com. The domain’s name server points to the attacker’s server, where a tunneling malware program is installed.
What is DNS tunneling What is it used for and how can you detect it?
What Is DNS Tunneling? DNS tunneling is a difficult-to-detect attack that routes DNS requests to the attacker’s server, providing attackers a covert command and control channel, and data exfiltration path. DNS is like a phonebook for the internet, helping to translate between IP addresses and domain names.
How do I block DNS tunneling?
Use the protocol object to block the DNS tunnel protocol. Go to CONFIGURATION > Configuration Tree > Box > Assigned Services > Firewall > Forwarding Rules. In the left menu, click Application Rules. Click Lock.
Is DNS over https Tunnelling?
DNS is often used by attackers as a covert channel for data exfiltration, also known as DNS tunneling. Since the plaintext DNS lookup leads to privacy issues, DNS over HTTPS (DoH) has recently been standardized and deployed. DoH encapsulates DNS in HTTPS to encrypt DNS traffic between clients and recursive resolvers.
What is DNS tunneling Cisco?
DNS tunneling is a technique that encodes data of other programs and protocols in DNS queries, including data payloads that can be used to control a remote server and applications.
What is DNS tunneling What is it used for and how can you detect it?
What Is DNS Tunneling? DNS tunneling is a difficult-to-detect attack that routes DNS requests to the attacker’s server, providing attackers a covert command and control channel, and data exfiltration path. DNS is like a phonebook for the internet, helping to translate between IP addresses and domain names.
How do I check DNS tunneling?
DNS tunnels can be detected by analyzing a single DNS payload or by traffic analysis such as analyzing count and frequency of requests. Payload analysis is used to detect malicious activity based on a single request.
What is DNS TXT records tunneling?
DNS Tunneling is a method of cyber attack that encodes the data of other programs or protocols in DNS queries and responses. DNS tunneling often includes data payloads that can be added to an attacked DNS server and used to control a remote server and applications.
What is DNS Proxy?
A DNS proxy improves domain lookup performance by caching previous lookups. A typical DNS proxy processes DNS queries by issuing a new DNS resolution query to each name server that it has detected until the hostname is resolved.
What is a DNS firewall?
A DNS Firewall firewall is a network security solution that prevents network users and systems from connecting to known malicious Internet locations. DNS Firewall works by employing DNS Response Policy Zones (RPZs) and actionable threat intelligence to prevent data exfiltration.
What is DNS traffic?
DNS stands for Domain Name System. The pairing of the hostname and the IP address is called a namespace. Monitoring your DNS records helps you insure that the Domain Name System continues to route traffic properly to your websites, services, and electronic communications.
Is DNS better than HTTPS?
There are several possible benefits to using DNS over HTTPS. The primary benefit is that encrypting DNS name resolution traffic helps to hide your online activities. When users enters a URL into their browser, a DNS query is typically needed in order to resolve the domain portion of the URL into an IP address.
Which is better DNS over TLS or DNS over HTTPS?
DNS over TLS requests uses a distinct port, so anyone who’s on the network level can find and even block them. DNS over HTTPS requests can stay hidden in encrypted traffic. DNS over TLS is a good option when the user doesn’t want to deal with the clients, which are provided by DNS referrers/forwarders.
How does DNS exfiltration work?
DNS data exfiltration is a way to exchange data between two computers without any direct connection. The data is exchanged through DNS protocol on intermediate DNS servers. During the exfiltration phase, the client makes a DNS resolution request to an external DNS server address.
How does DNS exfiltration work?
DNS data exfiltration is a way to exchange data between two computers without any direct connection. The data is exchanged through DNS protocol on intermediate DNS servers. During the exfiltration phase, the client makes a DNS resolution request to an external DNS server address.
What are two methods used by cybercriminals to mask DNS attacks?
Answers Explanation & Hints: Fast flux, double IP flux, and domain generation algorithms are used by cybercrimals to attack DNS servers and affect DNS services. Fast flux is a technique used to hide phishing and malware delivery sites behind a quickly-changing network of compromised DNS hosts (bots within botnets).
What is a DNS firewall?
A DNS Firewall firewall is a network security solution that prevents network users and systems from connecting to known malicious Internet locations. DNS Firewall works by employing DNS Response Policy Zones (RPZs) and actionable threat intelligence to prevent data exfiltration.
What is DNS tunneling What is it used for and how can you detect it?
What Is DNS Tunneling? DNS tunneling is a difficult-to-detect attack that routes DNS requests to the attacker’s server, providing attackers a covert command and control channel, and data exfiltration path. DNS is like a phonebook for the internet, helping to translate between IP addresses and domain names.
What is the port no of DNS TCP?
DNS uses port 53.
What are two methods used by cybercriminals to mask DNS attacks?
Answers Explanation & Hints: Fast flux, double IP flux, and domain generation algorithms are used by cybercrimals to attack DNS servers and affect DNS services. Fast flux is a technique used to hide phishing and malware delivery sites behind a quickly-changing network of compromised DNS hosts (bots within botnets).
Why do attackers use DNS tunneling?
This tunnel can be used to exfiltrate data or for other malicious purposes. Because there is no direct connection between the attacker and victim, it is more difficult to trace the attacker’s computer.
Is DNS over TLS safe?
DNS over TLS, or DoT, is a standard for encrypting DNS queries to keep them secure and private. DoT uses the same security protocol, TLS, that HTTPS websites use to encrypt and authenticate communications.