Everyone knows how a bike stays upright — the gyroscopic forces induced by the spinning wheels, and the “castor effect” created by trail. Or do they? A team of engineers says it’s proven that bikes can stay upright even without these things.
What force keeps a motorcycle upright?
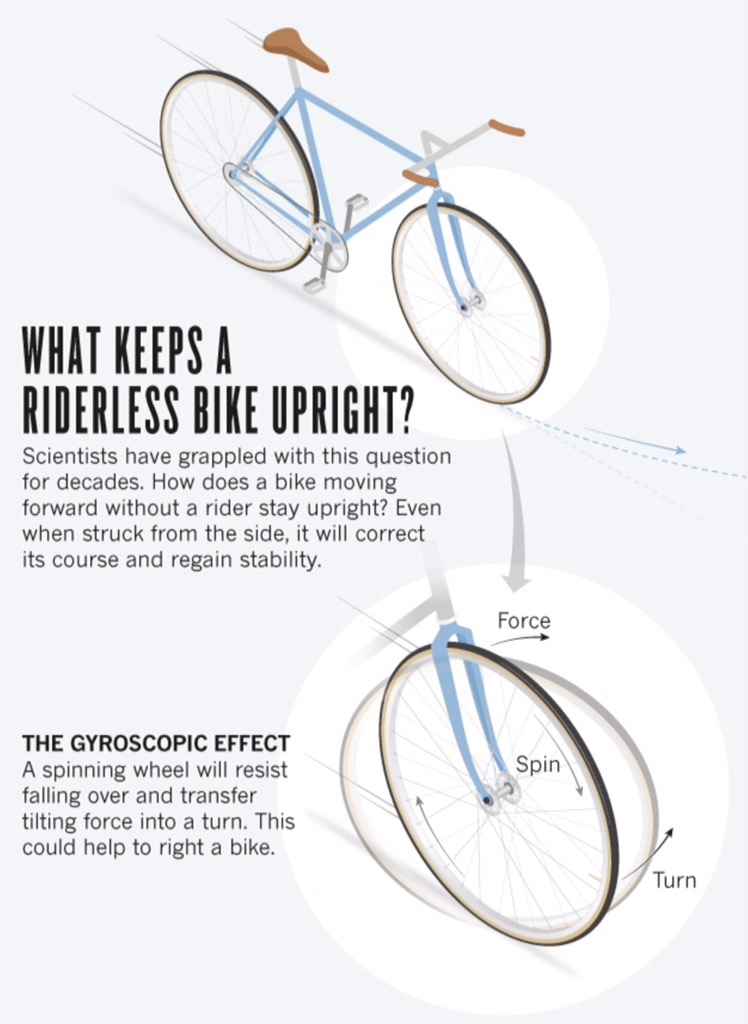
The gyroscopic forces created by a moving wheel give it stability and help keep it upright.
What forces does a bike use?
The forces resisting motion of a bicycle include rolling resistance and aerodynamic drag, together with inertia forces during acceleration and gravity forces when climbing an incline. The rider overcomes these resistances by applying forces to the pedals which are transmitted by the mechanical drive to the rear wheel.
How do bicycles work physics?
The force used by pedaling enables the gears of a bike to spin the back wheel. As the back wheel rotates, the tire uses friction to grip the area and move the bike in the desired direction.
What effect does the force have on the bicycle?
When biking on a level road, your forward force comes from pushing and pulling on the pedals to make the back tyre push backwards against the road. The two main forces that oppose your motion are aerodynamic drag (air resistance) and rolling resistance of the tyres against the road caused as the tyre is compressed.
What is centrifugal force in bike?
The centrifugal force acts on the center of mass of the bike, which creates a torque that rotates the bike with the tires acting as the pivot point – or hinges if you will.
How do motorcycles not fall over?
In short, leaning the bike allows there to be a gravitational torque to balance the torque from the fake force. Leaning prevents you from falling over.
Why do we not fall over on a bike?
The most common explanation is that the wheels on a bike act as a gyroscope, preventing the bike from falling over. A bike was constructed with counter-rotating wheels to test this. The bike had two front wheels, one on the ground and rotating forward, and one off the ground rotating backward.
What are two forces you exert when riding a bicycle?
it can be summarized as the following forces: compression. tension. friction.
How much force is required to move a bike?
What force causes bike acceleration?
The wheel pushes on the road and, provided that there is enough friction to prevent the wheel from slipping, the push of the road on the wheel accelerates the cycle forwards. The force that pushes a cycle or other vehicle forwards is called the driving force, or motive force.
Why does a spinning wheel stay upright?
Put simply, the gyroscopic effect occurs because a spinning wheel wants to stay spinning about its axis, just as a spinning top or even planet Earth stay aligned to their spin axes.
How does a bicycle stop moving?
When we apply the brake then there is a frictional force between the brake and the rim of the cycle. This force opposes the forward motion of the body and hence bicycle stops.
When a bicycle is in motion the force?
When a bicycle is in motion, the force of friction exerted by the ground on the two wheels is such that it acts. (A) In the backward direction on the front wheel and in the forward direction on the rear wheel.
How does frictional force help us ride a bicycle?
The brake pads and the wheel rims have friction when we brake. There is friction between the handlebar and the hands that allows for a successful gripping. The bike tire and the road have some friction so that we can actually roll the bike wheels safely without sliding.
What law of motion is riding a bike?
Newton’s Second Law of Motion says that acceleration (gaining speed) happens when a force acts on a mass (object). Riding your bicycle is a good example of this law of motion at work.
Why do Superbike riders put their leg out?
Dangling your leg into this high-speed airstream results in a significant force on the rider’s leg as it acts like a small parachute, creating a turning moment by pulling the riders leg around his core. This in turn encourages a pull on the outside handlebar, further helping to turn the bike through counter-steering.
At what speed will a motorcycle not fall over?
When you are moving at a speed in excess of about 10 MPH on your motorcycle, so long as you keep your tires on the ground (without losing traction), you CANNOT FALL DOWN. It is IMPOSSIBLE!
Do motorcycle balance themselves?
When the bike slows down to a stop, or when it’s traveling slower than 4 kph, the angle of the fork changes and brings the front wheel forward. This action activates the self-balancing system that makes small left and right adjustments to the wheel in order to balance the bike.
What keeps a riderless bike upright?
The front wheel of the bicycle is spinning forward quickly, acting like a gyroscope. Then when you tip the bike to the right, the gyroscope applies the torque, which turns the handlebars to the right and causes the steering, bringing the wheels back under the bicycle and holding it up.
What are the action force and the reaction that enable the bicycle to move?
When you pedal a bicycle, it causes the wheels to spin. As they pass along the ground, the wheels “grip” it, and push it backwards. Every force has an equal and opposite reaction, and the reaction to this force is a “push” from the ground which propels the bicycle.
Which forces are responsible for the motorcycle to move?
As with all masses, gravity pulls the rider and all the bike components toward the earth. At each tire contact patch there are ground reaction forces with both horizontal and vertical components. The vertical components mostly counteract the force of gravity, but also vary with braking and accelerating.