The Get-DnsClientCache cmdlet retrieves the contents of the local DNS client cache.
How do I check my local DNS cache?
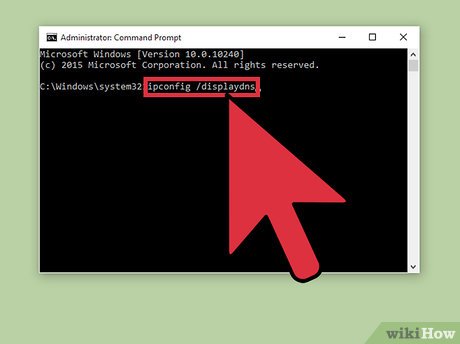
Checking your DNS cache Window – The process for viewing your DNS cache entries in Windows is pretty simple. Simply open your command prompt and enter the following command: ipconfig /displaydns .
What is local DNS caching?
DNS caching allows any DNS server or client to locally store the DNS records and re-use them in the future – eliminating the need for new DNS queries. The Domain Name System implements a time-to-live (TTL) on every DNS record. TTL specifies the number of seconds the record can be cached by a DNS client or server.
What is ipconfig Displaydns command?
/displaydns. Displays the contents of the DNS client resolver cache, which includes both entries preloaded from the local Hosts file and any recently obtained resource records for name queries resolved by the computer.
Where DNS cache is stored?
It is maintained by your computer, and it contains records of all the recently visited websites and their IP addresses. It serves as a database that keeps a copy of a DNS lookup, locally stored on your browser or operating system. Your computer can quickly refer to it whenever trying to load a website.
How do I see DNS cache on Linux?
In Debian/Ubuntu, that file is /var/cache/nscd/hosts for the hosts/DNS cache, so you can run strings /var/cache/nscd/hosts to see the hosts in cache.
Where is the local DNS file?
In Windows, the hosts file is located at C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts.
What is local DNS name server?
DNS server or Domain Name System is a directory of public IP (internet protocol) addresses and their affiliated host names. Often, DNS servers translate or resolve host names to IP addresses when requested. DNS servers operate exclusive software and connect using restricted protocols.
What is local DNS server windows?
How does a local DNS work?
The Internet’s DNS system works much like a phone book by managing the mapping between names and numbers. DNS servers translate requests for names into IP addresses, controlling which server an end user will reach when they type a domain name into their web browser. These requests are called queries.
What is DNS command?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical distributed naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participating entities.
How can I see DNS in CMD?
Go to Start and type cmd in the search field to open the command prompt. Alternatively, go to Start > Run > type cmd or command. Type nslookup and hit Enter. The displayed information will be your local DNS server and its IP address.
What commands clear DNS cache?
To Flush the DNS Cache: Type ‘ipconfig /flushdns’ in the Command Prompt, and press Enter. 3. The user has now flushed the DNS Cache and will receive a message that they have successfully done so. 4.
How do I view DNS records in Windows?
To check a specific DNS record, you need to specify the nslookup command, an optional record type (for example, A , MX , or TXT ), and the host name that you want to check. Note: If you omit the record type, it defaults to A . The first two lines of output specify the server to which the request was directed.
What is DNS cache manager?
The DNS Cache Manager caches the IP address and DNS hostname pairs and returns the cached value if the DNS hostname has a match in its internal cache. If this checkbox is ticked, the cache will be cleared at the start of the thread.
Are DNS records cached locally?
The DNS cache is a local storage of DNS records maintained by the operating system. The DNS cache contains the Resource Records (RR) of the domains you have previously visited and their IP address translations. When you access a web page, your computer’s OS initiates a DNS lookup for the domain.
How do I change my local DNS cache?
Flushing the DNS cache on Windows 10 is a very easy process. Ensure that you’re on the Windows 10 desktop. Right-click on the Start Menu and choose Command Prompt (Admin) from the menu. Type in the command ipconfig /flushdns and hit Enter.
How do I check my DNS records?
The most efficient way to check DNS records of the domain is to use a terminal with the command nslookup. This command will run on almost all operating systems (Windows, Linux, and macOS).
What is the DNS command in Linux?
Nslookup (stands for “Name Server Lookup”) is a useful command for getting information from the DNS server. It is a network administration tool for querying the Domain Name System (DNS) to obtain domain name or IP address mapping or any other specific DNS record. It is also used to troubleshoot DNS-related problems.
How do I check my DNS files?
The Check DNS Configuration (CHKDNSCFG) command checks the syntax (but not the semantics) of a Domain Name System (DNS) server’s named. conf configuration file. This may include files from the /QIBM/UserData/OS400/DNS/_DYN directory.
Where is DNS info in Linux?
On most Linux operating systems, the DNS servers that the system uses for name resolution are defined in the /etc/resolv. conf file. That file should contain at least one nameserver line. Each nameserver line defines a DNS server.
What are the 3 types of DNS?
There are three main kinds of DNS Servers — primary servers, secondary servers, and caching servers.