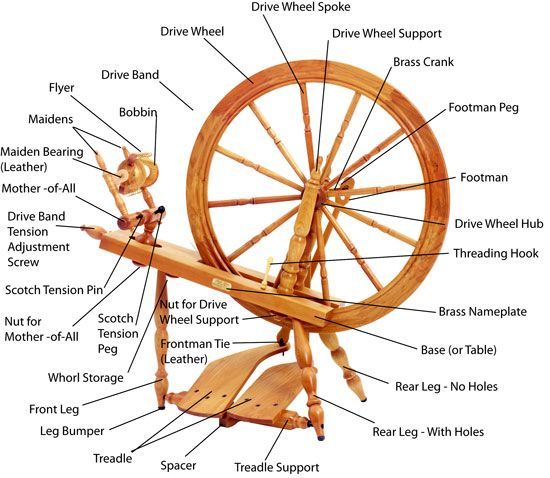
The working unit on all modern spinning wheels is the combination of the flyer (the ‘U’ shaped piece) and the bobbin on to which the yarn is wound as well as the whorl. The bobbin is mounted on the flyer shaft and rotates independently of the flyer. This winds on the yarn as it is spun.
What are the parts of a spinning wheel called?
The working unit on all modern spinning wheels is the combination of the flyer (the ‘U’ shaped piece) and the bobbin on to which the yarn is wound as well as the whorl. The bobbin is mounted on the flyer shaft and rotates independently of the flyer. This winds on the yarn as it is spun.
What is the mother of all on a spinning wheel?
The mother-of-all is the business end of the spinning wheel. This is the piece that holds the maidens, which in turn hold the flyer, bobbin and brake system. The flyer is a U-shaped piece with a metal shaft through the middle to hold the bobbin and whorls, if necessary.
What is the spinning wheel made of?
The raw materials for most modern spinning wheels are wood, wood glue, clear lacquer or urethane, and some bits and pieces of metal, primarily used as wire on the wheel. Some spinning wheels use a bit of brass as well. The wheels made on the North American continent are made of native hardwoods.
What is the mother of all on a spinning wheel?
The mother-of-all is the business end of the spinning wheel. This is the piece that holds the maidens, which in turn hold the flyer, bobbin and brake system. The flyer is a U-shaped piece with a metal shaft through the middle to hold the bobbin and whorls, if necessary.
What is the spindle of a spinning wheel?
A spindle is a straight spike usually made from wood used for spinning, twisting fibers such as wool, flax, hemp, cotton into yarn.
What is a distaff on a spinning wheel?
A distaff (/ˈdɪstɑːf/, /ˈdɪstæf/, also called a rock) is a tool used in spinning. It is designed to hold the unspun fibers, keeping them untangled and thus easing the spinning process. It is most commonly used to hold flax, and sometimes wool, but can be used for any type of fibre.
How many types of spinning wheels are there?
The common spinning (flyer) wheel styles are classified as; saxony wheel, castle wheel, Norwegian wheel or the modern wheel.
Does the bobbin spin on a spinning wheel?
When spinning, both the flyer and the bobbin are rotated by the drive band. The bobbin whorl is smaller in diameter than the flyer whorl, therefore, it will spin faster than the flyer if there is no brake being used.
How do spinner wheels work?
The modern spinner device is a decorative kinetic attachment to the wheel of an automobile. The spinner covers the center of a car’s wheel and is designed to independently rotate by using one or more roller bearings to isolate the spinner from the wheel, enabling it to turn while the wheel is at rest.
How much is a spinning wheel worth?
How big is a spinning wheel?
The most common modern wheels are multi-taskers, which do very well for a broad spectrum of types of spinning. They will commonly have drive wheels with diameters from 13″ to 24″, which translates to circumferences between 40″ and 75″ roughly speaking.
What is a distaff on a spinning wheel?
A distaff (/ˈdɪstɑːf/, /ˈdɪstæf/, also called a rock) is a tool used in spinning. It is designed to hold the unspun fibers, keeping them untangled and thus easing the spinning process. It is most commonly used to hold flax, and sometimes wool, but can be used for any type of fibre.
How many types of spinning wheels are there?
The common spinning (flyer) wheel styles are classified as; saxony wheel, castle wheel, Norwegian wheel or the modern wheel.
What is the mother of all on a spinning wheel?
The mother-of-all is the business end of the spinning wheel. This is the piece that holds the maidens, which in turn hold the flyer, bobbin and brake system. The flyer is a U-shaped piece with a metal shaft through the middle to hold the bobbin and whorls, if necessary.
What is spindle bearing?
Spindle bearings are single row angular contact ball bearings which support thrust loads in one direction. and are often used in machine tool spindles . At very high speeds, spindle bearings can simultaneously. absorb high radial forces and single direction axial forces . Spindle bearings have one open shoulder on.
What is spindle shaft?
Definition. A spindle is a rotating shaft with a fixture for holding a tool (in the case of a milling, grinding, or drilling spindle) or a workpiece (in the case of a turning spindle). The spindle shaft serves as a support, a positioner, and a rotary drive for the tool or workpiece.
Is there a needle on a spinning wheel?
This was the standard type of spinning wheel up until around 1500 when the bobbin and flyer assembly came into being, Crippen explains. As there is no place on a flyer wheel to conveniently prick one’s finger, it would stand to reason that Sleeping Beauty was using some type of spindle wheel, she believes.
What is a footman on a spinning wheel?
Footman – The bar the connects the treadle to the fly wheel and causes it to turn. K. Orifice – The opening at the end of the spindle where the yarn goes through to connect to the hooks of the flyer.
Who invented the first spinning wheel?
No one knows for certain who invented the first spinning wheel or when. Some evidence points to the invention of the spinning wheel in India between 500 and 1000 A.D. Other research indicates it was invented in China and then spread from China to Iran, Iran to India and then India to Europe.
Why is it important to make a spinning wheel in a circle shape?
The wheels of cars or automobiles are made circular for the purpose of reducing the frictional force. The rolling friction is lesser than sliding friction, therefore, wheels are made circular in shape.
What is the difference between a spindle and a distaff?
The basic tools used to spin the fibers were the spindle and the distaff. A distaff is designed to hold the unspun fibers, meanwhile a spindle is a straight spike, usually made from wood, onto which the fiber is being spun. The most commonly used fibers in Europe were wool and flax.