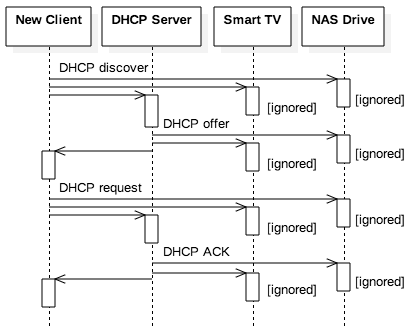
DHCP runs at the application layer of the Transmission Control Protocol/IP (TCP/IP) stack to dynamically assign IP addresses to DHCP clients and to allocate TCP/IP configuration information to DHCP clients. This includes subnet mask information, default gateway IP addresses and domain name system (DNS) addresses.
What layer is the DHCP?
DHCP runs at the application layer of the Transmission Control Protocol/IP (TCP/IP) stack to dynamically assign IP addresses to DHCP clients and to allocate TCP/IP configuration information to DHCP clients. This includes subnet mask information, default gateway IP addresses and domain name system (DNS) addresses.
Is DNS a Layer 2 or 3?
At a high level, the DNS protocol operates (using OSI model terminology) at the application level, also known as Layer 7. This layer is shared by HTTP, POP3, SMTP, and a host of other protocols used to communicate across an IP network.
What network layer is DNS?
DNS is an Application-layer protocol. The Application layer is the top-most layer on the TCP/IP Model. Just like every application layer protocol, DNS uses the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) on the Transport layer of the TCP/IP model to transport data.
Is DNS a layer 3 or 4?
DNS is a application layer protocol, because DNS query and answer is the application level communications. Application layer only understand the query and answer section in the DNS packet. so application layer DNS query/answer is encapsulated in layer 4 udp then layer 3 IP…..and so on.
Is DHCP a layer 2 or 3 protocol?
DHCP works on Layer 2 in the OSI model.
Is DHCP Layer 3 protocol?
DHCP is an application-layer protocol that allows a client machine on the network, to get an IP address and other configuration parameters from the server.
What is L2 and L3 layer in networking?
Commonly known as L2/L3 device or multi-layer switch (L2 = Ethernet, L3 = IP). To simply put it, an L3 switch is a combination of an Ethernet switch and IP router.
What are L2 and L3 protocols?
There are several sorts of network protocols. Layer 2 − The second layer is the data link layer. Data link layers 2 are best shown by Mac addresses and Ethernet. Layer 3 − Layer 3 is a network layer that identifies the best available communication channel in the network. Layer 3 is exemplified by an IP address.
What transport layer does DNS normally use?
What transport layer protocol does DNS normally use? UDP; While DNS over TCP does exist, UDP is the most common protocol.
Where does DNS fit in the OSI model?
In OSI stack terms, DNS runs in parallel to HTTP in the Application Layer (layer 7). DNS is in effect an application that is invoked to help out the HTTP application, and therefore does not sit “below” HTTP in the OSI stack. DNS itself also makes use of UDP and more rarely TCP, both of which in turn use IP.
What is DNS layer security?
DNS layer security solutions operate on the edge of your network—they are in essence the first line of defense for organizations. The way they do this is by monitoring communications between end users and the public internet at the DNS-layer level.
What is Layer 4 networking?
Layer 4 of the OSI model, also known as the transport layer, manages network traffic between hosts and end systems to ensure complete data transfers. Transport-layer protocols such as TCP, UDP, DCCP, and SCTP are used to control the volume of data, where it is sent, and at what rate.
What is L4 in networking?
L4 – the Transport Layer is for transmission of data between points on a network. Example protocols: TCP/UDP. L5 – the Session Layer is for managing the dialogues between computers. L5 establishes and manages connections between applications.
What is a layer 3 address?
Layer 3 is the network layer and its protocol is the Internet Protocol or IP. Devices in an IP network are identified by an IP address, which can be dynamically assigned and may change over time.
What is layer 2 of the OSI model?
The data link layer, or layer 2, is the protocol layer that transfers data between nodes on a network segment across the physical layer, or what is commonly known as a host’s physical address.
What layer is SMTP?
As with the other protocols and services discussed in this section, SMTP operates at the Application layer and relies on the services of the underlying layers of the TCP/IP suite to provide the actual data transfer services.
What layer is ARP?
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) The Address Resolution Protocol is a layer 2 protocol used to map MAC addresses to IP addresses. All hosts on a network are located by their IP address, but NICs do not have IP addresses, they have MAC addresses. ARP is the protocol used to associate the IP address to a MAC address.
Why DHCP and DNS works on application layer?
Why are DHCP and DNS essential application layer protocols for nearly every network? DHCP facilitates dynamic IP address assignment, and DNS provides domain name to IP address resolution.
Is DHCP a TCP or UDP?
The DHCP employs a connectionless service model, using the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). It is implemented with two UDP port numbers for its operations which are the same as for the bootstrap protocol (BOOTP). UDP port number 67 is the port used by the server, and UDP port number 68 is used by the client.
What is Layer 2 of the OSI model?
The data link layer, or layer 2, is the protocol layer that transfers data between nodes on a network segment across the physical layer, or what is commonly known as a host’s physical address.
What OSI layer is ARP protocol?
ARP works between Layers 2 and 3 of the Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model). The MAC address exists on Layer 2 of the OSI model, the data link layer. The IP address exists on Layer 3, the network layer.