Local DNS hijack — attackers install Trojan malware on a user’s computer, and change the local DNS settings to redirect the user to malicious sites. Router DNS hijack — many routers have default passwords or firmware vulnerabilities.
Which of the following is a hacker attempts to redirect traffic from a legitimate website?
Pharming, a portmanteau of the words “phishing” and “farming”, is an online scam similar to phishing, where a website’s traffic is manipulated, and confidential information is stolen. In essence, it is the criminal act of producing a fake website and then redirecting users to it.
How are domains hijacked?
How are Domains Hijacked? Domain hijacking occurs from illegal access to or exploitation of a common cybersecurity vulnerability in a domain name registrar, or from acquiring access to the domain name owner’s email address and then changing the password to the owner’s domain name registrar.
Is DNS hijacking common?
DNS hijacking is a common cyberattack technique known as domain name server reconfiguration.
Is DNS hijacking common?
DNS hijacking is a common cyberattack technique known as domain name server reconfiguration.
What is a redirect hack?
“WordPress Malware Redirect” or “WordPress Redirect Hack” is a kind of 🔴 exploit where infected site redirects the visitors to malicious website, phishing page and malware websites. It is likely due to the code injected in your WordPress database, that gets your WordPress site redirects to another site.
What kind of tool could a hacker use to intercept traffic on your network?
Sniffers are used by network/system administrator to monitor and troubleshoot network traffic. Attackers use sniffers to capture data packets containing sensitive information such as password, account information etc. Sniffers can be hardware or software installed in the system.
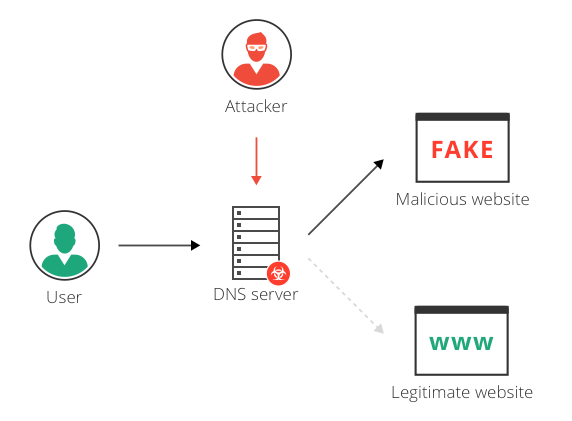
How do hackers hijack DNS?
DNS servers, routers and computers cache DNS records. Attackers can “poison” the DNS cache by inserting a forged DNS entry, containing an alternative IP destination for the same domain name. The DNS server resolves the domain to the spoofed website, until the cache is refreshed.
Can hackers spoof your domain?
In practice, domain spoofing is used by hackers in different ways. It could be, for example, by simply adding a letter to an email address or creating a fake website that has an address very similar to the legitimate one. In the day-to-day routine, these small changes end up being overlooked by many people.
Does VPN prevent DNS hijacking?
Yes. A VPN helps prevent DNS hijacking. Most VPN services run their own DNS servers, preventing your DNS queries from being intercepted. ExpressVPN runs its own encrypted DNS on every VPN server, keeping your internet traffic protected.
Why do hackers spoof DNS?
Domain name system (DNS) spoofing is a type of cyberattack that uses tampered DNS server data to redirect users to fake websites. These malicious sites often look legitimate but are actually designed to install malware onto users’ devices, steal sensitive data or redirect traffic.
What is an example of DNS spoofing?
For example, an attacker spoofs the IP address DNS entries for a target website on a given DNS server and replaces them with the IP address of a server under their control. The attacker then creates files on the server under their control with names matching those on the target server.
Is it legal to redirect a website?
Are there any legal issues with buying domain names of people who are competitors and redirecting traffic from those sites to my own business? Yes, you are risking a trademark infringement lawsuit. Operating under the domain name of your competitor is representing yourself (even if only momentarily) as your competitor.
Which code will redirect you?
To tell search engines and website visitors that your web page has permanently moved to a new location with an equivalent content use a 301 redirect. The code “301” is interpreted as “moved permanently”. (Learn more about HTTP Status Codes).
How many types of redirection are there?
A redirect is a way to send both users and search engines to a different URL from the one they originally requested. The three most commonly used redirects are 301, 302, and Meta Refresh.
What is an example of a redirect?
A redirect is when a web page is visited at a certain URL, it changes to a different URL. For instance, a person visits “website.com/page-a” in their browser and they are redirected to “website.com/page-b” instead.
What is URL hijacking or typosquatting?
Typosquatting, also known as URL hijacking, is a social engineering attack that purposely uses misspelled domains for malicious purposes.
What is redirect malware?
A browser hijacker is a malware program that modifies web browser settings without the user’s permission and redirects the user to websites the user had not intended to visit. It is often called a browser redirect virus because it redirects the browser to other, usually malicious, websites.
What redirect you to a phony website?
Website redirects are most commonly caused by adware and other types of malware present on your computer. The aim of these unwanted programs is to point you towards certain types of advertising or dangerous code that could further damage your system.
Is DNS hijacking common?
DNS hijacking is a common cyberattack technique known as domain name server reconfiguration.
How does a redirect work?
In HTTP, redirection is triggered by a server sending a special redirect response to a request. Redirect responses have status codes that start with 3 , and a Location header holding the URL to redirect to. When browsers receive a redirect, they immediately load the new URL provided in the Location header.
How do hackers intercept packets?
Packet sniffers, more generally known as sniffers, are almost like a dog sniffing information that’s crossing a network. They allow hackers to sniff out data packets from both public and private networks. The main goal of sniffing attacks is to steal data and personal information.