The Internet’s DNS system works much like a phone book by managing the mapping between names and numbers. DNS servers translate requests for names into IP addresses, controlling which server an end user will reach when they type a domain name into their web browser. These requests are called queries.
What is DNS server simple explanation?
A DNS server is a computer with a database containing the public IP addresses associated with the names of the websites an IP address brings a user to. DNS acts like a phonebook for the internet.
What is DNS and its working principle?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the phonebook of the Internet. Humans access information online through domain names, like nytimes.com or espn.com. Web browsers interact through Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. DNS translates domain names to IP addresses so browsers can load Internet resources.
What is DNS server simple explanation?
A DNS server is a computer with a database containing the public IP addresses associated with the names of the websites an IP address brings a user to. DNS acts like a phonebook for the internet.
What are the 3 types of DNS queries?
3 types of DNS queries—recursive, iterative, and non-recursive.
What is the difference between DNS and IP address?
A system called the Domain Name System, or DNS, associates names, like www.example.com, with the corresponding addresses. Your computer uses the DNS to look up domain names and get the associated IP address, which is used to connect your computer to the destination on the internet.
What is the difference between DNS and DHCP server?
Domain Name System (DNS) is an Internet service that translates domain names (e.g., its.umich.edu) into IP addresses. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a protocol for automatically assigning IP addresses and other configurations to devices when they connect to a network.
What is the 8.8 8.8 DNS server?
8.8. 8.8 is the primary DNS server for Google DNS. Google DNS is a public DNS service that is provided by Google with the aim to make the Internet and the DNS system faster, safer, secure, and more reliable for all Internet users.
Where are DNS servers located?
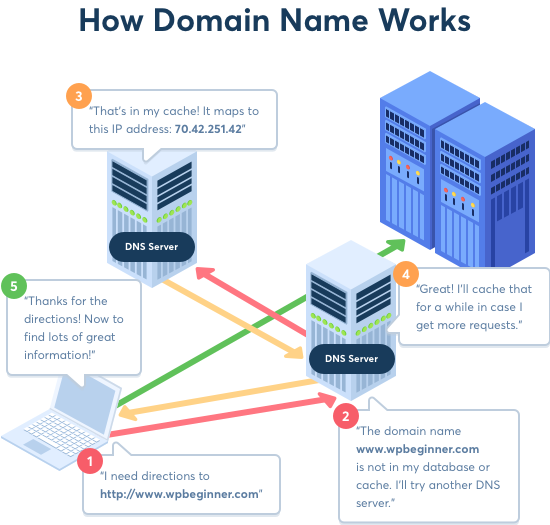
These servers reside in your ISP’s data centers, and they handle requests as follows: If it has the domain name and IP address in its database, it resolves the name itself. If it doesn’t have the domain name and IP address in its database, it contacts another DNS server on the internet.
How many DNS servers are there?
Root name server overview In total, there are 13 main DNS root servers, each of which is named with the letters ‘A’ to ‘M’. They all have a IPv4 address and most have an IPv6 address. Managing the root server is ICANN’s responsibility (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers).
What is DNS zone example?
DNS zones are not necessarily physically separated from one another, zones are strictly used for delegating control. For example, imagine a hypothetical zone for the cloudflare.com domain and three of its subdomains: support.cloudflare.com, community.cloudflare.com, and blog.cloudflare.com.
How do domain names work?
Domain names are just like a contact in your phone. Rather than typing a complicated set of numbers (the IP address) into your browser, you type in a domain name. That domain name is human-friendly and much easier to remember than an IP address. All domain names are connected to a unique IP address.
What is DNS diagram?
DNS stands for Domain Name System. DNS is a directory service that provides a mapping between the name of a host on the network and its numerical address. DNS is required for the functioning of the internet. Each node in a tree has a domain name, and a full domain name is a sequence of symbols specified by dots.
How do I configure DNS?
In Local Area Connection Properties, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties. Click Use the following DNS server addresses, and in Preferred DNS server and Alternate DNS server, type the IP addresses of the preferred and alternate DNS servers. To add more DNS servers, click the Advanced button.
What is the main process of the Domain Name System?
DNS keeps the record of all domain names and the associated IP addresses. When you type in a URL in your browser, DNS resolves the domain name into an IP address. In other words, DNS is a service that maps domain names to corresponding IP addresses.
What is DNS server simple explanation?
A DNS server is a computer with a database containing the public IP addresses associated with the names of the websites an IP address brings a user to. DNS acts like a phonebook for the internet.
What is DNS and its working principle?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the phonebook of the Internet. Humans access information online through domain names, like nytimes.com or espn.com. Web browsers interact through Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. DNS translates domain names to IP addresses so browsers can load Internet resources.
What problem does the DNS solve?
The Domain Name System resolves the names of internet sites with their underlying IP addresses adding efficiency and even security in the process.
Do DNS servers have their own IP address?
The DNS server contains a database of public IP addresses and their corresponding domain names. Every device connected to the internet has a unique IP address that helps to identify it, according to the IPv4 or IPV6 protocols.
Why do I have 2 DNS servers?
There are two main benefits of using a secondary DNS server: Redundancy and resiliency: Relying on just one DNS server creates a single point of failure. If the primary server fails or is compromised by an attack, prospective visitors can no longer access the desired domain.
Is DHCP part of DNS?
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) and DNS (Domain Name System) both work across the client-server architecture though they are different terms. While DNS maps the name of the domain to the IP address, DHCP is a protocol that assigns the IP address to the host in a network either dynamically or statically.
What is the difference between domain and DNS?
The main difference between domain and domain name server (DNS) is that the domain could be a piece of string that helps to spot a specific web site while the DNS (Domain Name System) could be a server that translates the domain to the corresponding ip address to supply the specified webpage.