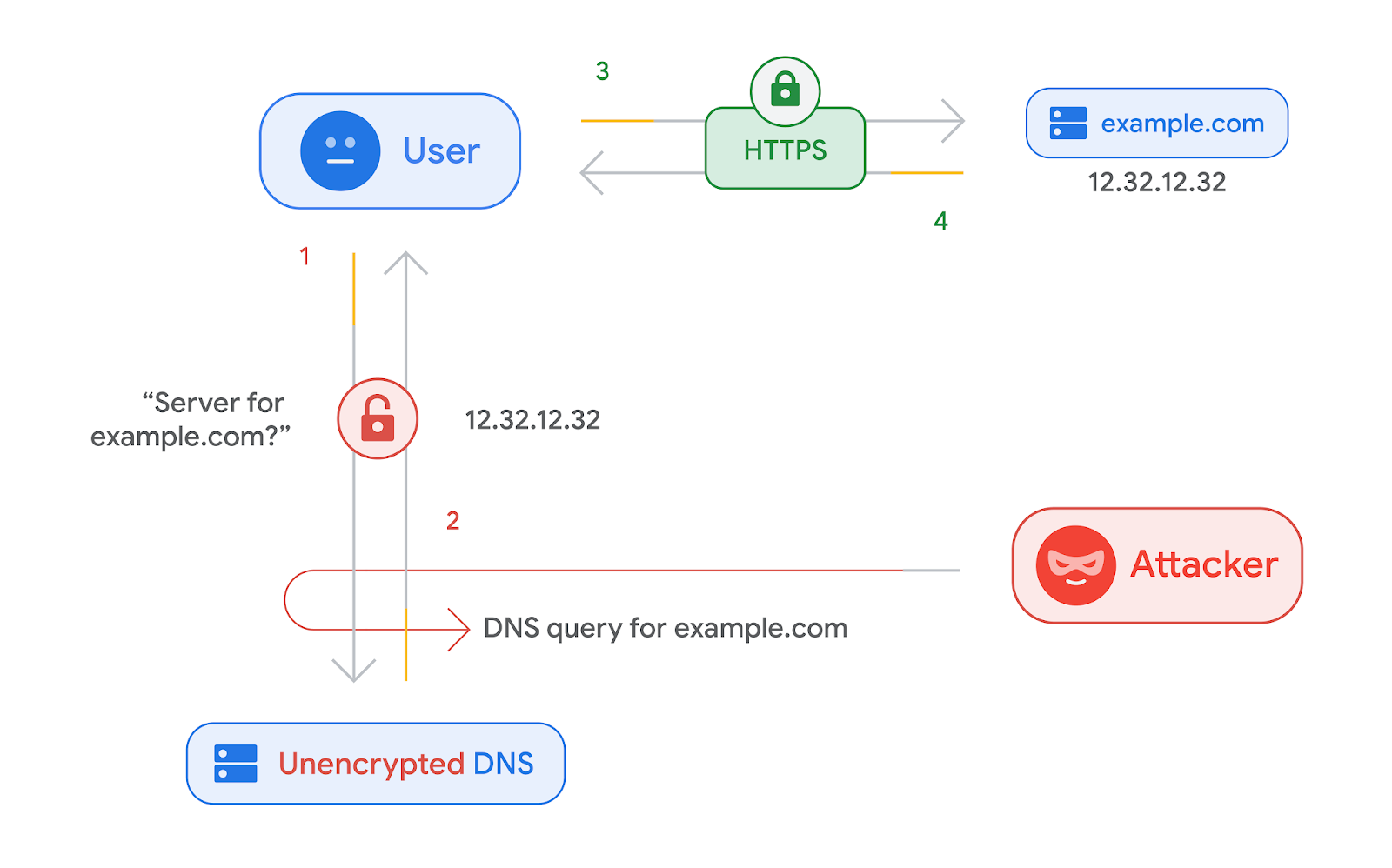
Security depends entirely on the server you’re using. Your Internet Service Provider sets you up on a DNS server, and if you feel it’s not secure, third party DNS servers like Google Public DNS, OpenDNS and Cloudfare have top-notch security features and connection speeds.
Is DNS a security risk?
However, the DNS data cached on these servers may be vulnerable to “poisoning” attacks. Hackers exploit poor configuration of DNS servers to inject fraudulent address information that can reroute users to a fake website under their control. Even the user’s browser would not know the site was not legitimate.
Is the 8.8 8.8 DNS safe?
8.8 and 8.8. 4.4. Google promises a secure DNS connection, hardened against attacks, as well as speed benefits.
Is using Google’s DNS safe?
Google Public DNS complies with Google’s main privacy policy, available at our Privacy Center. Your client IP address is only logged temporarily (erased within a day or two), but information about ISPs and city/metro-level locations are kept longer for the purpose of making our service faster, better, and more secure.
Can a DNS server track you?
They can glean a lot of information about your browsing habits this way. Changing DNS servers won’t stop your ISP from tracking, but it will make it a little harder. Using a virtual private network (VPN) for your daily browsing is the only real way to prevent your ISP from seeing what you’re connecting to online.
Is the 8.8 8.8 DNS safe?
8.8 and 8.8. 4.4. Google promises a secure DNS connection, hardened against attacks, as well as speed benefits.
Is using Google’s DNS safe?
Google Public DNS complies with Google’s main privacy policy, available at our Privacy Center. Your client IP address is only logged temporarily (erased within a day or two), but information about ISPs and city/metro-level locations are kept longer for the purpose of making our service faster, better, and more secure.
Do hackers use DNS?
Attackers can take over a router and overwrite DNS settings, affecting all users connected to that router. Man in the middle DNS attacks — attackers intercept communication between a user and a DNS server, and provide different destination IP addresses pointing to malicious sites.
Can DNS steal your data?
Theft. Hackers get an easy way through DNS poisoning to steal personal data from a device. They can steal data like financial credentials, login credentials, security numbers, and other sensitive data. Blocks Device Security Updates.
Does 1.1 1.1 Make your internet faster?
1.1. 1.1 is a free, public DNS resolver from Cloudflare and Asia Pacific Network Information CentreAsia Pacific Network Information CentreAPNIC (the Asia Pacific Network Information Centre) is the regional Internet address registry (RIR) for the Asia-Pacific region. It is one of the world’s five RIRs and is part of the Number Resource Organization (NRO).https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › APNICAPNIC – Wikipedia (APNIC) that could make your searches faster and more secure. But the product won’t work for everyone, and some have concerns about how it will use their data.
Has Google DNS Been Hacked?
Is 1.1.1.1 still the fastest DNS?
The independent DNS monitor DNSPerf ranks 1.1.1.1 the fastest DNS service in the world. Since nearly everything you do on the Internet starts with a DNS request, choosing the fastest DNS directory across all your devices will accelerate almost everything you do online.
Why do we use 8.8 8.8 DNS?
Which DNS server is best?
Is DNS legal?
Yes, changing the DNS is legal. The service is mostly there to provide basic internet functionality. You are not forced to use your ISP’s DNS. That’s why high-profile alternative DNS services like OpenDNS and Google’s Public DNS exist.
Are DNS attacks common?
#3 DNS Hijacking This is also known as DNS poisoning or DNS redirection. Unfortunately, DNS hijacking attacks are also very common in the realm of cybercrime.
What can a DNS see?
Your DNS server will always know which websites you visit. It does not matter if you use one from google or the one from your ISP. This is because everytime you visit a webpage that your computer does not know the IP of, it will send a DNS lookup to find the IP which maps to the webpages domain (=URL) you visit.
What are DNS risks?
The most common DNS risks include denial-of-service (DoS), distributed denial-of-service (DDoS), DNS hijacking, DNS spoofing, DNS tunneling, DNS amplification, DNS typosquating.
What is DNS direct risk?
DNS is vulnerable to a variety of trust-based attacks. These attacks include unauthenticated responses, cache poisoning, and blind ID attacks. In addition, some DNS implementations are vulnerable to corrupt DNS packets.
What are DNS threats?
A DNS attack is an exploit in which an attacker takes advantage of vulnerabilities in the domain name system (DNS).
What are DNS vulnerabilities?
A DNS Exploit is a vulnerability in the domain name system (DNS) through which an attacker an infiltrate a network.
Is the 8.8 8.8 DNS safe?
8.8 and 8.8. 4.4. Google promises a secure DNS connection, hardened against attacks, as well as speed benefits.