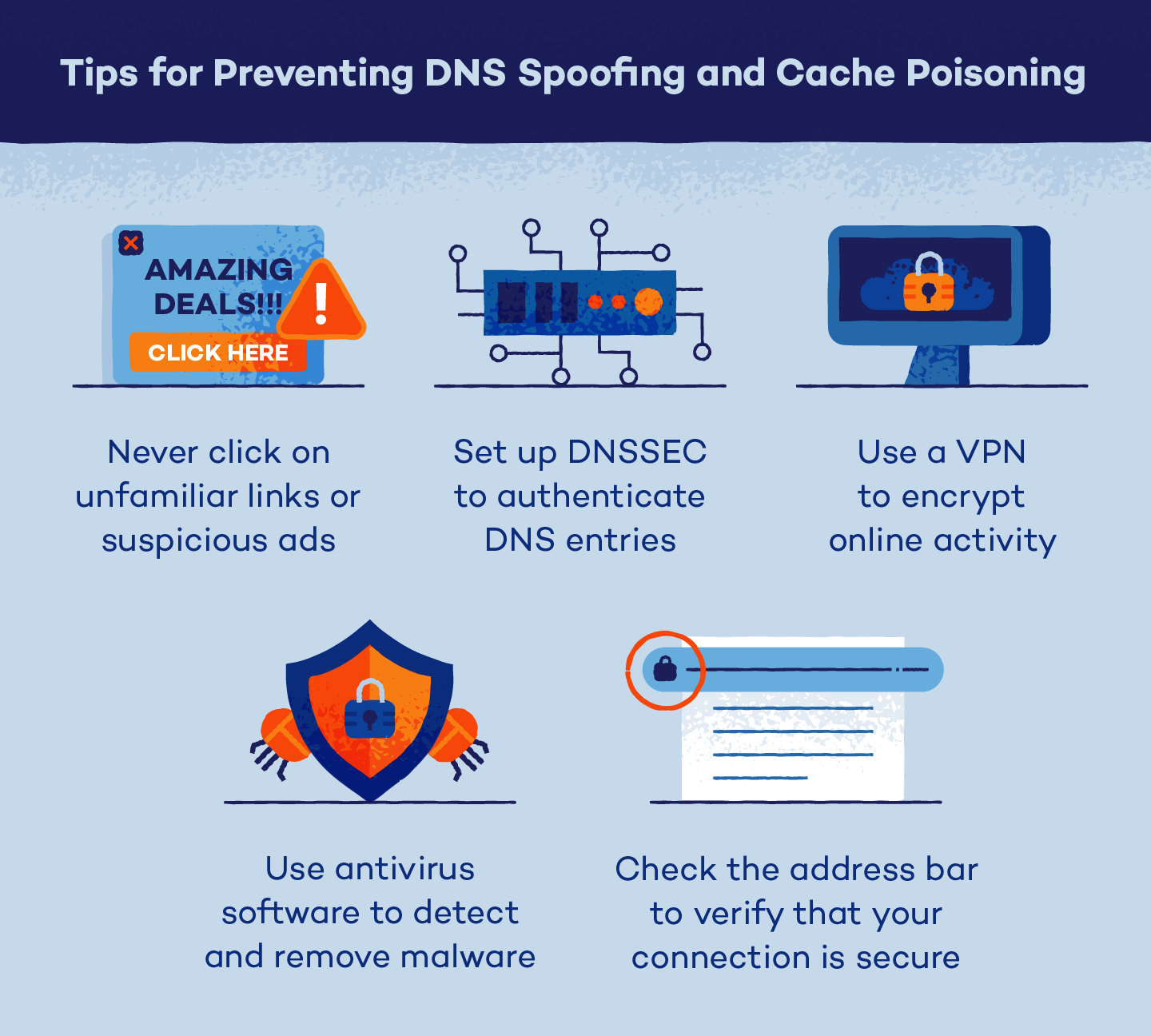
Use a virtual private network (VPN). These services give you an encrypted tunnel for all your web traffic and use of private DNS servers that exclusively use end-to-end encrypted requests. The result gives you servers that are far more resilient against DNS spoofing, and requests that can’t be interrupted.
What is DNS spoofing How do you prevent?
DNS spoofing is a cyber-attack in which fake data is introduced into the DNS resolver’s cache, which causes the name server to return an incorrect IP address. In other words, these types of attacks exploit vulnerabilities in domain name servers and redirect traffic towards illegitimate websites.
Does a VPN affect DNS?
Yes, because a smart DNS only changes your DNS address while a VPN encrypts data traffic, obfuscates it, and spoofs your location by changing your IP – effectively taking up more of your internet bandwidth.
Is it easy difficult to spoof DNS?
DNS is an unencrypted protocol, making it easy to intercept traffic with spoofing. What’s more, DNS servers do not validate the IP addresses to which they are redirecting traffic.
Can spoofing be stopped?
If you think you’ve been the victim of a spoofing scam, you can file a complaint with the FCC. You may not be able to tell right away if an incoming call is spoofed. Be extremely careful about responding to any request for personal identifying information. Don’t answer calls from unknown numbers.
How can I bypass anti-spoofing?
In the sidebar, under Security Settings, navigate to Malicious Content > Anti-Spoofing. Under the policy you want to bypass (Inbound DMARC, DKIM or SPF) click Manage Exceptions. This will open a drawer to the right; from here, select + Add Exception.
Can VPN override DNS?
Most VPN services use their own DNS servers, which will override any custom DNS or Smart DNS settings you have on your device. You can check which DNS servers your device is using with a DNS checker tool.
Does a VPN prevent DNS tracking?
Unfortunately, DNS is an unencrypted protocol, so your ISP can monitor your DNS traffic, even if you change your DNS provider to not use your ISP’s service. Tunneling your DNS traffic over the VPN is the only way to avoid this. Who are you hiding from? VPNs are often said to protect your privacy, and they do, in a way.
Can I use 1.1 1.1 DNS and VPN?
For example, if you’re on a public WiFi connection, hackers could still step in and see what you’re doing. A VPN could offer protection from that, but you can’t use one at the same time as 1.1. 1.1. You’ll have to choose between one product and the other.
How common is DNS spoofing?
Through their research they discovered that DNS spoofing is still rare (occurring only in about 1.7% of observations) but has been increasing during the observed period, and that proxying is the most common DNS spoofing mechanism.
Why do hackers spoof DNS?
Domain name system (DNS) spoofing is a type of cyberattack that uses tampered DNS server data to redirect users to fake websites. These malicious sites often look legitimate but are actually designed to install malware onto users’ devices, steal sensitive data or redirect traffic.
What is the main reason that DNS spoofing is possible?
Attackers can poison DNS caches by impersonating DNS nameservers, making a request to a DNS resolver, and then forging the reply when the DNS resolver queries a nameserver. This is possible because DNS servers use UDP instead of TCP, and because currently there is no verification for DNS information.
What is DNS spoofing explain?
DNS (Domain Name Service) spoofing is the process of poisoning entries on a DNS server to redirect a targeted user to a malicious website under attacker control.
What is DNS spoofing and how does it work?
Domain name system (DNS) spoofing is a type of cyberattack that uses tampered DNS server data to redirect users to fake websites. These malicious sites often look legitimate but are actually designed to install malware onto users’ devices, steal sensitive data or redirect traffic.
What is IP spoofing its concept and how can it be prevented?
Internet Protocol (IP) spoofing is a type of malicious attack where the threat actor hides the true source of IP packets to make it difficult to know where they came from. The attacker creates packets, changing the source IP address to impersonate a different computer system, disguise the sender’s identity or both.
What is an example of DNS spoofing?
For example, an attacker spoofs the IP address DNS entries for a target website on a given DNS server and replaces them with the IP address of a server under their control. The attacker then creates files on the server under their control with names matching those on the target server.
Can firewall stop IP spoofing?
A firewall will help protect your network by filtering traffic with spoofed IP addresses, verifying traffic, and blocking access by unauthorized outsiders.
Is spoofing traceable?
If you want to know how to trace a spoofed call, you usually need to get law enforcement involved. In other cases, tracing a spoofed phone number can be done using your telephone company. Telephone companies can sometimes trace spoof calls back to where they came from.
What are 4 types of spoofing attacks?
Spoofing is a technique through which a cybercriminal disguises themselves as a known or trusted source. Spoofing can take many forms, such as spoofed emails, IP spoofing, DNS Spoofing, GPS spoofing, website spoofing, and spoofed calls.
Which techniques can be used for Anti-Spoofing?
Some of the common anti-spoofing techniques used in this context are – Local Binary Pattern or LBP that uses texture image analysis; Eye blink detection is another method to differentiate between fake and live faces, and Convolutional Neural Network or CNN is a deep learning feature used for anti-spoofing.
What is Anti-Spoofing techniques?
Antispoofing is a technique for identifying and dropping packets that have a false source address. In a spoofing attack, the source address of an incoming packet is changed to make it appear as if it is coming from a known, trusted source.
Does VPN bypass DNS filtering?
Usually a VPN service first installs a VPN client, and for all future VPN traffic the path is fixed and encrypted – no DNS look up needed. Any web or other sessions you then engage that require DNS lookups are conducted within the protected VPN tunnel.