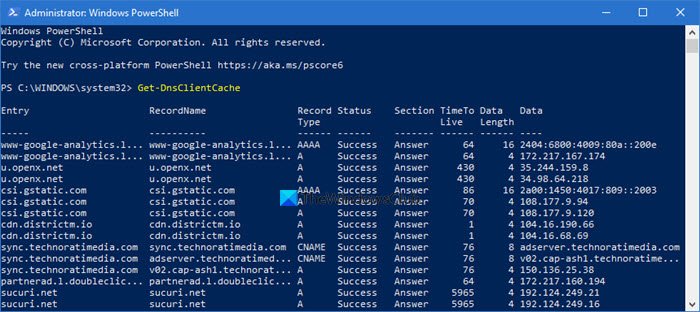
To improve the speed and performance of your internet connection, Microsoft Windows 10 stores vital domain name resolution information in a temporary file known as the DNS cache.
Does Windows 10 have a DNS cache?
To improve the speed and performance of your internet connection, Microsoft Windows 10 stores vital domain name resolution information in a temporary file known as the DNS cache.
How do I find my DNS records in Windows 10?
To see your current DNS settings, type ipconfig /displaydns and press Enter. To delete the entries, type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter. To see your DNS settings again, type ipconfig /displaydns and press Enter. You should see blank records or you might get the message “Could not display the DNS Resolver Cache.”
Where is the DNS cache file located?
Press the Win + R keys, type in “services. msc” (no quotes) and press Enter or click OK. Locate the DNS Client service (or Dnscache on some computers) and double-click it to open its Properties.
Should I clean my DNS cache?
That’s because the DNS cache is designed to act like a virtual address book, storing the information of the websites you visit regularly. To keep this information away from data collectors or bad actors on the web, it’s a good idea to regularly flush your DNS cache.
Where are Windows DNS records stored?
By default Windows DNS Servers storing File Based Zones look for database at the \Windows\System32\DNS Directory. This folder stores the data for the file-based DNS Zones.
Does Windows 10 restart flush DNS?
A DNS Server’s cache is cleared at reboot. Other than that you can manually clear the cache at any time by using the DNS Admin console.
How often should you flush your DNS cache?
If you need clear DNS cache from client side for every 15 minutes, it is OK.
Does Windows have a DNS cache?
Windows contains a client-side DNS cache. Microsoft doesn’t recommend disabling DNS client-side caching on DNS clients. A configuration in which DNS client-side caching is disabled isn’t supported.
How do I fix my DNS cache?
Navigate to All Programs > Accessories and select Command Prompt. In the command line interface, run ipconfig /flushdns . You should receive a confirmation message once the DNS cache is flushed.
Does Windows have a DNS cache?
Windows contains a client-side DNS cache. Microsoft doesn’t recommend disabling DNS client-side caching on DNS clients. A configuration in which DNS client-side caching is disabled isn’t supported.
Where are Windows DNS records stored?
By default Windows DNS Servers storing File Based Zones look for database at the \Windows\System32\DNS Directory. This folder stores the data for the file-based DNS Zones.
Where is the cache folder in Windows 10?
Replies (5) The internet files are located at
Where are DNS records stored on PC?
DNS records are stored in authoritative servers. These records provide information about a domain, including its associated IP address for each domain. It is mandatory for all domains to have a specific set of default records.
Does clearing DNS cache delete history?
If the domain name in the cache points to an old or incorrect IP address, the website won’t return the correct information. Even if you clear your browser history, the DNS cache will still have the old information, and the server needs to be flushed to get the updated results.
What happens if I delete all DNS records?
Delete a DNS record from your domain that’s no longer needed. Deleting records will completely remove them from your zone file. Changes to your DNS may interrupt how your domain works, such as your email and website.
Does clearing DNS cache speed up Internet?
If you’re looking for an easy way to speed up Web browsing and improve your browser’s performance, you should flush DNS cache in Windows 10 on a regular basis. This simple maintenance task could help to improve browsing speed quite a bit.
How do I check DNS logs in Windows?
In Event Viewer, navigate to Applications and Services Logs\Microsoft\Windows\DNS-Server. Right-click DNS-Server, point to View, and then click Show Analytic and Debug Logs. The Analytical log will be displayed.
What are main DNS records?
What is a DNS record? DNS records (aka zone files) are instructions that live in authoritative DNS servers and provide information about a domain including what IP address is associated with that domain and how to handle requests for that domain.
What are 3 types of DNS records?
The three DNS server types server are the following: DNS stub resolver server. DNS recursive resolver server. DNS authoritative server.
What is DNS cache history?
DNS cache refers to the temporary storage of information about previous DNS lookups on a machine’s OS or web browser. Keeping a local copy of a DNS lookup allows your OS or browser to quickly retrieve it and thus a website’s URL can be resolved to its corresponding IP much more efficiently.
Is DNS stored on the computer?
Root nameservers are designated servers around the world that are responsible for storing DNS data and keeping the system working smoothly. Once the DNS record is found on the root nameserver, it’s cached by your computer.