Ultimately, the DNS enables human users to keep track of more web pages and to access them as required, and DNS caching expedites the DNS lookup process to more quickly resolve a domain name to an IP address when the OS has visited a web page before.
How does DNS caching affect the network how do I check my DNS cache How do I clear the DNS cache?
In Microsoft Windows, you can flush the local DNS cache using the ipconfig /flushdns command in a Command Prompt. You know it works when you see the Windows IP configuration successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache or Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache message.
Does clearing DNS cache help?
Flushing DNS will clear any IP addresses or other DNS records from your cache. This can help resolve security, internet connectivity, and other issues. It’s important to understand that your DNS cache will clear itself out from time to time without your intervention.
What is meant by DNS cache?
(Domain Name System cache) The storage location of IP addresses of websites for faster retrieval of subsequent DNS queries (URL to IP). The caches are located in the user’s computer as well as in company and ISP servers.
Is DNS caching safe?
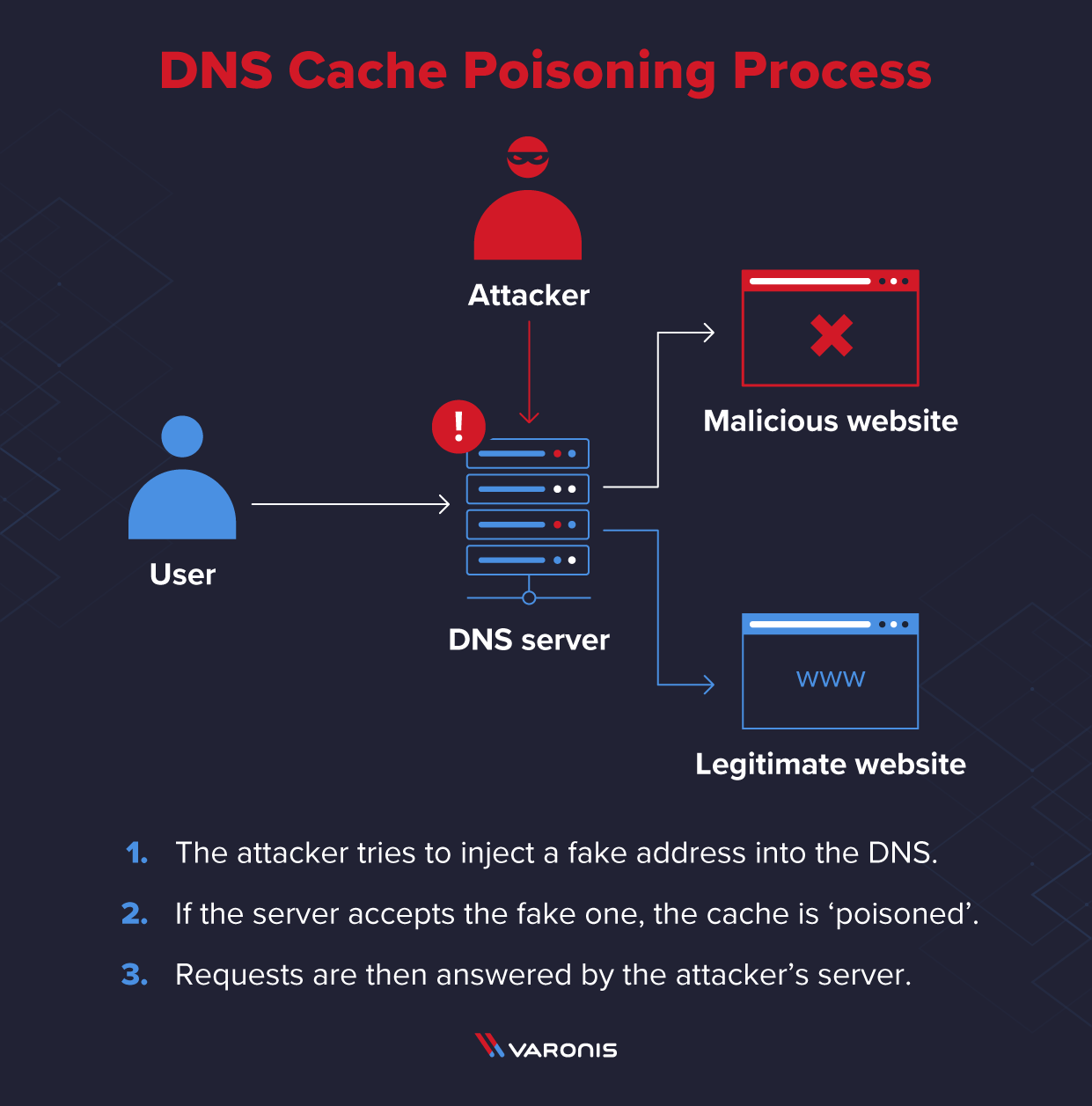
Attackers can poison a DNS cache by tricking DNS resolvers into caching false information, with the result that the resolver sends the wrong IP address to clients, and users attempting to navigate to a website will be directed to the wrong place.
How does DNS caching affect the network how do I check my DNS cache How do I clear the DNS cache?
In Microsoft Windows, you can flush the local DNS cache using the ipconfig /flushdns command in a Command Prompt. You know it works when you see the Windows IP configuration successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache or Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache message.
Is DNS caching safe?
Attackers can poison a DNS cache by tricking DNS resolvers into caching false information, with the result that the resolver sends the wrong IP address to clients, and users attempting to navigate to a website will be directed to the wrong place.
What is negative DNS caching?
A negative response indicates that information about a requested domain does not exist, or that the server cannot provide an answer for the query. The storage of this information is called negative caching. Negative caching helps speed up responses to queries about a domain.
Why would you implement a caching only DNS server on your network?
What is the primary advantage of a caching-only DNS server? It speeds DNS queries by building a DNS request cache.
How often should you flush DNS?
If you need clear DNS cache from client side for every 15 minutes, it is OK. After these caches were cleared, if needed, the client will re-query these records from DNS server. TTL times are always represented in seconds.
Does Flushing DNS help Ping?
What this does is clear out space or stored dns data like internet website addresses and sometimes that data gets corrupted it likely also stores dns data from servers too and having this cleared out will help with stability or even increases latency potential as this will allow for more Latency stability.
Where DNS cache is stored?
There is no “cache file” – the cache is kept in memory only. It is maintained by the “DNS Client” service (internally named Dnscache ), therefore the cache data would be somewhere inside one of the svchost.exe processes.
How long does a DNS cache last?
A. By default, Windows stores positive responses in the DNS cache for 86,400 seconds (i.e., 1 day) and stores negative responses for 300 seconds (5 minutes).
Where is the DNS cache?
To display the contents of the DNS resolver cache: Type ipconfig /displaydns and press Enter. Observe the contents of the DNS resolver cache. It is generally not necessary to view the contents of the DNS resolver cache, but this activity may be performed as a name resolution troubleshooting method.
What is DNS cache poisoning in cyber security?
Domain Name Server (DNS) spoofing (a.k.a. DNS cache poisoning) is an attack in which altered DNS records are used to redirect online traffic to a fraudulent website that resembles its intended destination.
Does DNS cache flush on reboot?
A DNS Server’s cache is cleared at reboot. Other than that you can manually clear the cache at any time by using the DNS Admin console.
How do I clear DNS cache on router?
This is the procedure to use: Turn off both your router & ONT. While they are off, clear your internet cache from all browsers, and close all browsers. Go to command prompt (cmd) run ipconfig /flushdns.
How do I clear my local DNS cache?
Open the Start Menu and start typing command prompt until you see it in the results. 2. Type ipconfig /flushdns when the prompt loads and hit Enter on the keyboard. The DNS Cache database on your computer is now clear.
How does DNS caching affect the network how do I check my DNS cache How do I clear the DNS cache?
In Microsoft Windows, you can flush the local DNS cache using the ipconfig /flushdns command in a Command Prompt. You know it works when you see the Windows IP configuration successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache or Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache message.
Is DNS caching safe?
Attackers can poison a DNS cache by tricking DNS resolvers into caching false information, with the result that the resolver sends the wrong IP address to clients, and users attempting to navigate to a website will be directed to the wrong place.
What is SOA record in DNS?
The DNS ‘start of authority’ (SOA) record stores important information about a domain or zone such as the email address of the administrator, when the domain was last updated, and how long the server should wait between refreshes. All DNS zones need an SOA record in order to conform to IETF standards.
Is Nxdomain cached?
The NXDOMAIN Value is how long the system will provide a non-existent domain name response via caching in the event something such as a domain name registration expiration. This value is also helpful in preventing problems such as DNS hijacking of our domain controls.