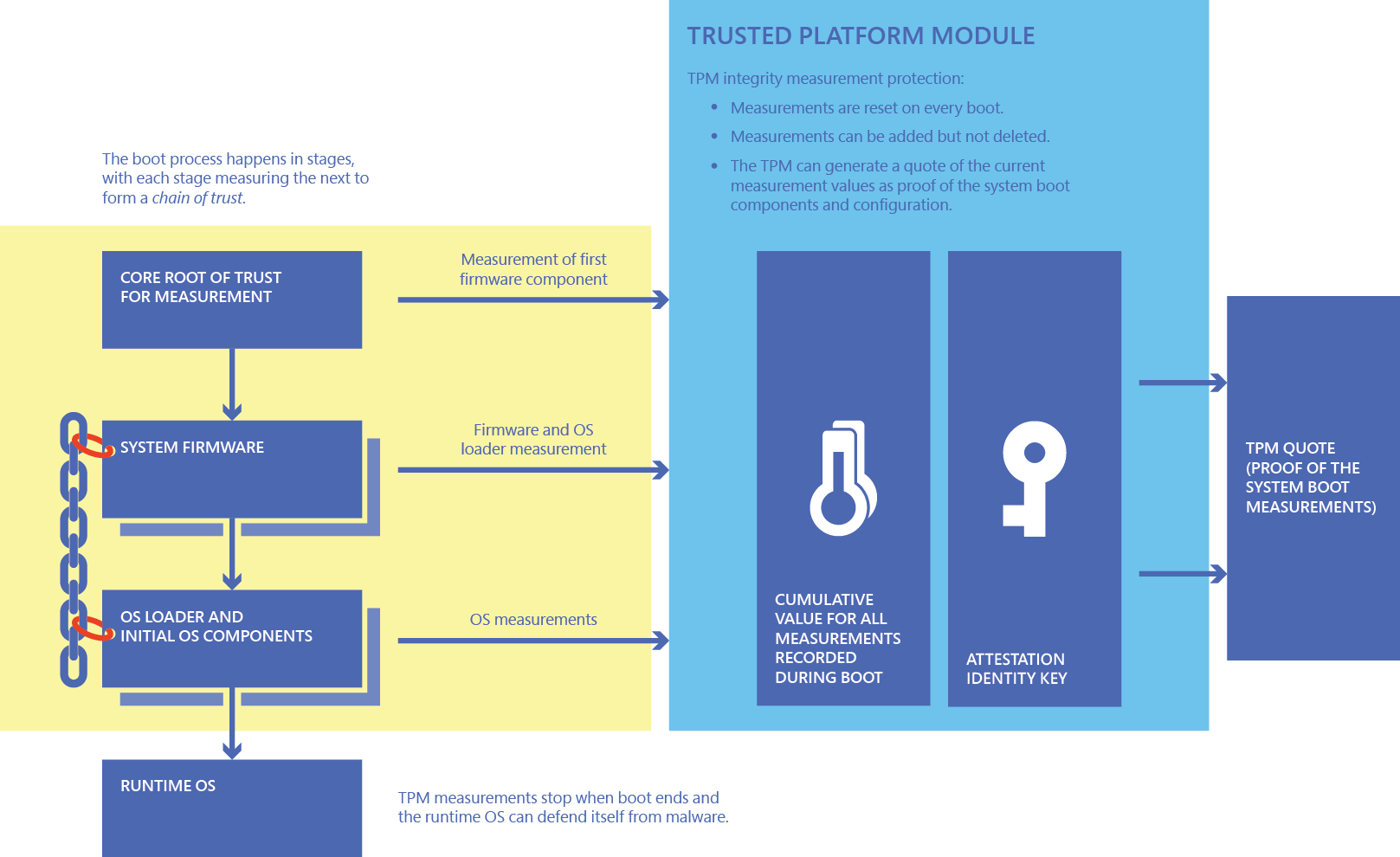
Secure Boot does not encrypt the storage on your device and does not require a TPM. When Secure Boot is enabled, the operating system and any other boot media must be compatible with Secure Boot.
Does TPM 2.0 require Secure Boot?
According to Microsoft, TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot are needed to provide a better security environment and prevent (or at least minimize) sophisticated attacks, common malware, ransomware, and other threats.
Does Secure Boot use the TPM?
One of the many features a TPM enhances is Secure Boot. This feature prevents malware from running when you first start up your computer by only allowing software that’s cryptographically signed to run when you turn it on (though you can turn it off if you need to).
Do you need TPM and Secure Boot for Windows 11?
As part of the system requirements, alongside a Trusted Platform Module (TPM), a device must have “Secure Boot” enabled to install Windows 11.
Is TPM really necessary?
And while it’s not a spectacular piece of hardware, it plays an important role in your computer security. The TPM is a cryptoprocessor that uses a cryptographic key to protect your data. As such, it increases your computer’s security by adding hardware-based security.
Does TPM 2.0 require Secure Boot?
According to Microsoft, TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot are needed to provide a better security environment and prevent (or at least minimize) sophisticated attacks, common malware, ransomware, and other threats.
Does Secure Boot use the TPM?
One of the many features a TPM enhances is Secure Boot. This feature prevents malware from running when you first start up your computer by only allowing software that’s cryptographically signed to run when you turn it on (though you can turn it off if you need to).
Why is Secure Boot unsupported?
Secure Boot Is Unsupported. Sometimes, you may find the Secure Boot State is Unsupported and the BIOS Mode is Legacy. This is because your system is installed on an MBR disk. In general, if your system disk is MBR style, you should use the Legacy (also named BIOS) mode to boot it.
Can TPM be bypassed?
Note that Microsoft also has also created an official registry hack to bypass TPM 2.0 and CPU requirements for an in-place upgrade. However, this method still requires at least TPM 1.2 so, if you have no TPM at all, it’s worthless.
Is Secure Boot same as UEFI?
What is Secure Boot? Secure Boot is one feature of the latest Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) 2.3. 1 specification (Errata C). The feature defines an entirely new interface between operating system and firmware/BIOS.
How do I bypass TPM and Secure Boot?
One such issue is the requirement of ‘Secure Boot’ along with ‘TPM 2.0’ enabled computers. However, if you are using a UEFI BIOS Mode machine, you can pretty straightforwardly bypass TPM on Windows 11. You simply have to go to BIOS settings and enable the ‘Secure Boot’ and ‘TPM 2.0’ options.
What happens if you update to Windows 11 without TPM?
So, even if you get Windows 11 to run without TPM 2.0, you may find that you no longer get any updates in the future, which could put your security at risk. For most people, then, we recommend you don’t force the Windows 11 upgrade on a PC without TPM 2.0.
Does TPM 2.0 require UEFI?
There is no need to enter UEFI/BIOS to check whether your computer has TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot enabled. Windows 10 has a built-in system information tool that shows you all the data you need. Press Win + R and enter the msinfo32 command.
Does TPM 2.0 slow down computer?
Does TPM 2.0 slow down computers? The simple answer is no, TPM has no effects on our computer system because it was built into the motherboard and, once enabled, it just serves as a cryptographic key storage device and performs cryptographic operations on drives.
What happens if TPM is removed?
Clearing the TPM causes you to lose all created keys associated with the TPM, and data protected by those keys, such as a virtual smart card or a sign in PIN. Make sure that you have a backup and recovery method for any data that is protected or encrypted by the TPM.
Does TPM 2.0 require UEFI?
BIOS Mode: The system BIOS is likely set to legacy mode. TPM 2.0 requires that BIOS operates in native UEFI mode.
Does enabling TPM 2.0 do anything?
TPM 2.0 is required to run Windows 11, as an important building block for security-related features. TPM 2.0 is used in Windows 11 for a number of features, including Windows Hello for identity protection and BitLocker for data protection. In some cases, PCs that are capable of running TPM 2.0 are not set up to do so.
Does TPM 2.0 require BitLocker?
BitLocker supports TPM version 1.2 or higher. BitLocker support for TPM 2.0 requires Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) for the device. TPM 2.0 is not supported in Legacy and CSM Modes of the BIOS. Devices with TPM 2.0 must have their BIOS mode configured as Native UEFI only.
Does TPM 2.0 require Secure Boot?
According to Microsoft, TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot are needed to provide a better security environment and prevent (or at least minimize) sophisticated attacks, common malware, ransomware, and other threats.
Does Secure Boot use the TPM?
One of the many features a TPM enhances is Secure Boot. This feature prevents malware from running when you first start up your computer by only allowing software that’s cryptographically signed to run when you turn it on (though you can turn it off if you need to).
Does Secure Boot need to be enabled for UEFI?
Secure Boot must be enabled before an operating system is installed. If an operating system was installed while Secure Boot was disabled, it will not support Secure Boot and a new installation is required. Secure Boot requires a recent version of UEFI.
Can you enable Secure Boot in BIOS?
From the System Utilities screen, select System Configuration > BIOS/Platform Configuration (RBSU) > Server Security > Secure Boot Settings > Secure Boot Enforcement and press Enter. Select a setting and press Enter: Enabled — Enables Secure Boot. Disabled — Disables Secure Boot.