A DNS name server is a highly sensitive infrastructure which requires strong security measures, as it can be hijacked and used by hackers to mount DDoS attacks on others: Watch for resolvers on your network — unneeded DNS resolvers should be shut down.
Can a DNS server spy on you?
If you’re on your ISP’s DNS server without a VPN (a service that allows you to change your IP and the server you use), not only can your ISP see your online activity, but depending on the provider, you could be set up on a DNS server that lacks privacy or desirable security measures.
Are DNS servers safe?
It’s safe to change your DNS, as long as you’re changing it to trusted DNS servers. For example, Google’s Public DNS (8.8. 8.8 and 8.8. 4.4) or CloudFlare’s (1.1.
Can you get a virus from a DNS server?
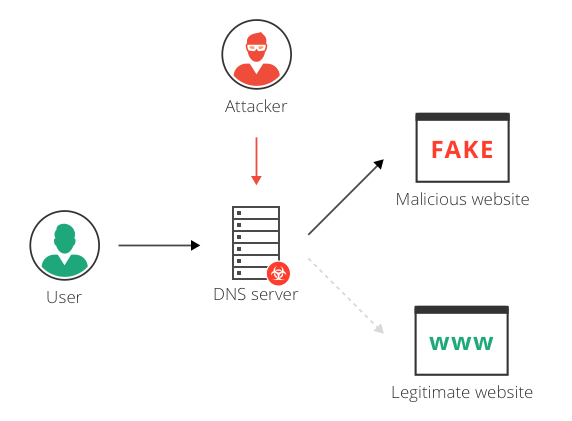
DNS servers convert the domain names into IP addresses. Now the malware, changes the domain name servers used by your computer and uses a different malicious DNS server. This malicious DNS server, swaps IP’s and takes the user to a fake site.
How do you know if my DNS has been hacked?
You’re Redirected to Unintended or Unknown Websites If you’re trying to visit your regular round of websites and you keep getting redirected to websites you weren’t intending to visit, then this could be a sign of a hacked router using DNS hijacking.
Can a DNS server spy on you?
If you’re on your ISP’s DNS server without a VPN (a service that allows you to change your IP and the server you use), not only can your ISP see your online activity, but depending on the provider, you could be set up on a DNS server that lacks privacy or desirable security measures.
What can someone do with my DNS?
A local DNS attack installs malware on the website user’s computer. The malware, usually a trojan malware disguised as legitimate software, gives the cyber thieves access to users’ network systems, enabling them to steal data and change DNS settings to direct the users to malicious websites.
Can you be tracked through DNS?
Tracking and Logging DNS Requests DNS monitoring can also discover and track IP addresses of DNS requests and log every website viewed by a device connected to your network. This helps your network team find out which websites your employees are visiting and how long it takes to complete the DNS request.
Are DNS safer than VPN?
DNS is a better option due to its lightweight nature. It does not use encryption so you can enjoy the full speed of your standard internet connection. However, keep in mind that VPNs don’t always slow down your connection; Working in a government-restricted environment.
Is using 8.8 8.8 DNS safe?
8.8. 8.8 is the primary DNS server for Google DNS. Google DNS is a public DNS service that is provided by Google with the aim to make the Internet and the DNS system faster, safer, secure, and more reliable for all Internet users.
What are the possible attacks on DNS?
For example, DNS tunneling techniques enable threat actors to compromise network connectivity and gain remote access to a targeted server. Other forms of DNS attacks can enable threat actors to take down servers, steal data, lead users to fraudulent sites, and perform Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
Is Google’s DNS safe?
Google Public DNS complies with Google’s main privacy policy, available at our Privacy Center. Your client IP address is only logged temporarily (erased within a day or two), but information about ISPs and city/metro-level locations are kept longer for the purpose of making our service faster, better, and more secure.
What happens when DNS hacked?
In a DNS server hack, your query is redirected in the wrong destination by a DNS server under a hacker’s control. This attack is even more cunning because once the query leaves your device, you have no control whatsoever over the direction your traffic takes.
Can you tell me if I’ve been hacked?
Some of the warning signs that you’ve been hacked include: You receive emails or text messages about login attempts, password resets, or two-factor authentication (2FA) codes that you didn’t request. You see logins from devices and locations you don’t recognize in your account activity or sign-in logs.
What does it look like when your hacked?
Frequent pop-up windows, especially the ones that encourage you to visit unusual sites, or download antivirus or other software. Changes to your home page. Mass emails being sent from your email account. Frequent crashes or unusually slow computer performance.
What is a DNS sniffer?
DNS Query Sniffer is a tool that prints DNS query/response information in a spreadsheet-style view, and allows easy exporting of the data.
Does Google DNS server track you?
Moreover, Google does not use any personal information collected through the Public DNS service to target ads. We do not correlate or associate personal information in Google Public DNS logs with your information from use of any other Google service except for addressing security and abuse.
What happens if your DNS is attacked?
For example, DNS tunneling techniques enable threat actors to compromise network connectivity and gain remote access to a targeted server. Other forms of DNS attacks can enable threat actors to take down servers, steal data, lead users to fraudulent sites, and perform Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
What happens when you visit a website DNS?
After you’ve typed the URL into your browser and pressed enter, the browser needs to figure out which server on the Internet to connect to. To do that, it needs to look up the IP address of the server hosting the website using the domain you typed in. It does this using a DNS lookup.
Can a DNS server spy on you?
If you’re on your ISP’s DNS server without a VPN (a service that allows you to change your IP and the server you use), not only can your ISP see your online activity, but depending on the provider, you could be set up on a DNS server that lacks privacy or desirable security measures.
Can private DNS steal data?
They can steal data like financial credentials, login credentials, security numbers, and other sensitive data. Blocks Device Security Updates. Through DNS poisoning, hackers can even prevent the devices from getting security patch updates. It helps them in long-term control over the device.
Should I delete DNS?
If the old DNS record is no longer in use, I’d recommend deleting old DNS record. This way, you can reuse the name (especially in the case of A / AAAA, and CNAME) in the future if you need to.