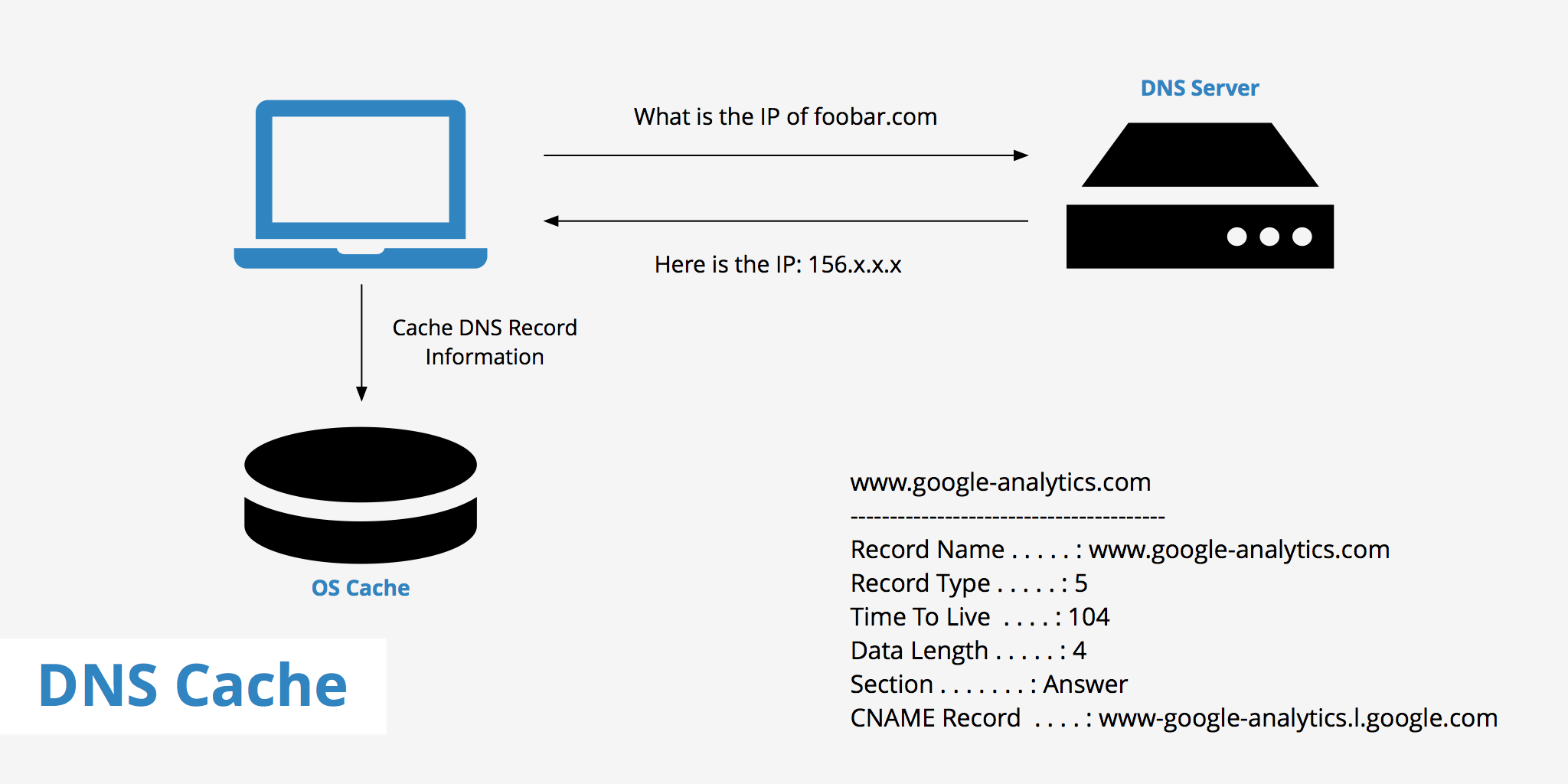
DNS caching allows any DNS server or client to locally store the DNS records and re-use them in the future – eliminating the need for new DNS queries. The Domain Name System implements a time-to-live (TTL) on every DNS record. TTL specifies the number of seconds the record can be cached by a DNS client or server.
Where is DNS cache on server?
dns, located in the WINDOWS\System32\Config folder. If SRV records are missing in your DNS zone, you can reload them automatically by running the Netdiag /fix command at a command prompt.
How long is DNS cache stored?
By default, Windows stores positive responses in the DNS cache for 86,400 seconds (i.e., 1 day) and stores negative responses for 300 seconds (5 minutes). To modify these values, perform the following steps: Start a registry editor (e.g., regedit.exe).
Can you flush DNS cache?
Navigate to All Programs > Accessories and select Command Prompt. In the command line interface, run ipconfig /flushdns . You should receive a confirmation message once the DNS cache is flushed.
What is caching DNS server?
DNS caching allows any DNS server or client to locally store the DNS records and re-use them in the future – eliminating the need for new DNS queries. The Domain Name System implements a time-to-live (TTL) on every DNS record.
Does chrome have DNS cache?
Yes, Google Chrome browser has inbuilt DNS and proxy caching server to improve performance. You can quickly clean out or flush out DNS entries manually on Google Chrome browser.
Why does DNS servers use caches?
DNS cache refers to the temporary storage of information about previous DNS lookups on a machine’s OS or web browser. Keeping a local copy of a DNS lookup allows your OS or browser to quickly retrieve it and thus a website’s URL can be resolved to its corresponding IP much more efficiently.
Do routers have cache?
Each router has a cache reset button, typically located on the rear of the unit. This process is different from resetting a browser cache, or a DNS cache, both of which involve an address bar, command prompt, and IP addresses.
Does rebooting clear DNS cache?
A router can have a DNS cache as well. Which is why rebooting a router is often a troubleshooting step. For the same reason you might flush DNS cache on your computer, you can reboot your router to clear the DNS entries stored in its temporary memory.
How often does a PC flush DNS?
This setting controls when the DNS server rejects refresh requests from hosts and the DHCP service. Most Windows hosts attempt to refresh their records every 24 hours.
How often are DNS records updated?
Common refresh intervals seen on the Internet are anywhere from 30 minutes to a couple of hours, but can vary based on what the administrator for that domain wants to specify. There is another mechanism in the DNS protocol that can make these changes propagate even more quickly.
What does flushing your DNS do?
Whatever the case, you can “flush” your DNS cache to start from scratch, so your computer looks up web addresses on the DNS server again. This process is, of course, different from clearing your web cache from a web browser.
How do I see DNS cache in Windows server?
To display the contents of the DNS resolver cache: Type ipconfig /displaydns and press Enter. Observe the contents of the DNS resolver cache.
What happens when I flush DNS?
What does flush DNS do? Flushing DNS will clear any IP addresses or other DNS records from your cache. This can help resolve security, internet connectivity, and other issues. It’s important to understand that your DNS cache will clear itself out from time to time without your intervention.
How do I view the DNS cache in Chrome?
I understand you can clear and view the Google Chrome DNS cache by navigating to chrome://net-internals/#dns in the browser.
Which command displays the contents of the local DNS cache?
Use ipconfig /displaydns and ipconfig /flushdns to view and manage the local DNS cache. The first command displays the contents of the local DNS cache that Windows maintains and updates every 24 hours.
How does local DNS cache work?
A DNS Cache works by temporarily storing the results of recently browsed websites’ DNS queries, or other FQDNs, on a local file for faster retrieval.
How do DNS servers determine how long to cache records?
DNS TTL (time to live) is a setting that tells the DNS resolver how long to cache a query before requesting a new one. The information gathered is then stored in the cache of the recursive or local resolver for the TTL before it reaches back out to collect new, updated details.
How many DNS servers should I have?
At a minimum, you’ll need two DNS servers for each Internet domain you have. You can have more than two for a domain but usually three is tops unless you have multiple server farms where you would want to distribute the DNS lookup load. It’s a good idea to have at least one of your DNS servers at a separate location.
Does Windows have DNS cache?
Windows contains a client-side DNS cache. Microsoft doesn’t recommend disabling DNS client-side caching on DNS clients. A configuration in which DNS client-side caching is disabled isn’t supported.
Does Windows 10 have a DNS cache?
To improve the speed and performance of your internet connection, Microsoft Windows 10 stores vital domain name resolution information in a temporary file known as the DNS cache.
Does incognito cache DNS?
View incognito history via DNS cache This information is recorded in the DNS cache — even when you’re surfing incognito. The DNS cache helps speed up your browsing by ensuring your browser doesn’t have to check the DNS server every time to revisit a site.