Flywheels are nothing but circular disc-shaped objects which are mainly used to store energy in machines.
What is the moment of inertia of a flywheel?
What is meant by MOI of the flywheel? The moment of inertia of a body has been defined as the object’s resistance to rotational changes. The flywheel flexibly rotates about a horizontal axis. A calliper could be used to measure the radius of the flywheel’s axile.
What is disc type flywheel?
Flywheels have an inertia called the moment of inertia and thus resist changes in rotational speed. The amount of energy stored in a flywheel is proportional to the square of its rotational speed. A flywheel is a spinning wheel or disc with a fixed axle so that rotation is only about one axis.
Is a flywheel a rotor?
There are two basic flywheel configurations. In one type the flywheel is attached to the shaft and both rotate together. This is termed a conventional rotor. The other type consists of a flywheel spinning around a shaft which does not move, also called an inside-out rotor.
Why is it called a flywheel?
But for practical purposes a flywheel would be mounted along its axis with the use of special bearings to minimise the friction. So, it’d be a wheel that flies in the air and stores energy – maybe that’s why it’s called Fly Wheel.
Does the flywheel always spin?
So, you might think the flywheel spins all the time. That’s not true. The flywheel does not spin when in neutral. This is because the input shaft that connects to the clutch plate; then to the pressure plate which connects to the flywheel is designed to spin freely when the vehicle is in neutral.
What do you mean by solid disk and rimmed flywheel?
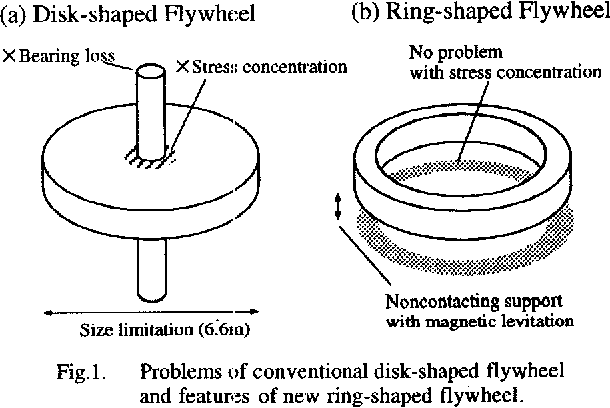
2. Rimmed Flywheel. The rim-type flywheel will explode at a much lower rotary speed than a solid disc-type wheel of equal weight and diameter. For minimal weight and high energy-storage capacity, a flywheel can be formed of high-strength steel and produced as a tapered disk, which is thick in the center.
How do dual mass flywheels work?
It consists of two flywheels that rotate independently of each other. One is attached to the clutch assembly and the other to the engine. Between the two flywheels are a series of springs, which dampen the engine vibrations and prevent most of them from reaching the gearbox.
What is the purpose of flywheel?
flywheel, heavy wheel attached to a rotating shaft so as to smooth out delivery of power from a motor to a machine. The inertia of the flywheel opposes and moderates fluctuations in the speed of the engine and stores the excess energy for intermittent use.
What does a flywheel consist of?
Flywheels are typically made of steel and rotate on conventional bearings; these are generally limited to a maximum revolution rate of a few thousand RPM. High energy density flywheels can be made of carbon fiber composites and employ magnetic bearings, enabling them to revolve at speeds up to 60,000 RPM (1 kHz).
Why does flywheel have large moment of inertia?
That’s because there’s a lot of kinetic energy stored within its spinning mass, and the heavier a flywheel is, the more kinetic energy it contains.
What is the moment of inertia of a flywheel rotating about its diameter?
In phy tb , pg 171 , it has been given that M.I of a flywheel about its axis = 1/2 MR^2 .
How is moment of inertia calculated?
Moments of inertia can be found by summing or integrating over every ‘piece of mass’ that makes up an object, multiplied by the square of the distance of each ‘piece of mass’ to the axis. In integral form the moment of inertia is I=∫r2dm I = ∫ r 2 d m .
Where are flywheels used?
Large vehicles have a larger mass which minimizes the effects of gyroscopic motion. Typically, modern flywheels are found in trains, Semi-trailer trucks, and other large transport trucks. Flywheel braking systems also have applications in Formula one racing.
Who invented flywheels?
But it’s a good thing James Watt, the pioneering 18th-century Scottish engineer, was willing to tinker around with that ancient technology. By using a wheel to convert the up-and-down thrusts of steam-powered pistons into a continuous rotational motion, Watt invented the modern flywheel.
What is a flywheel in simple terms?
A flywheel is a heavy wheel that makes an engine move smoothly by storing kinetic energy and keeping the engine at a constant speed throughout its cycle. Without a flywheel, car engines would be very jerky. The flywheel stores energy and makes the pistons move at a constant speed.
How does a flywheel break?
Riding the clutch pedal while driving, slowly engaging/disengaging the clutch while your foot is on the gas pedal, or quickly disengaging the clutch while at a high RPM (ie: drag racing) are the usual culprits to a worn out flywheel and/or clutch.
How does your flywheel turn?
A flywheel is a machine that reserves rotational energy by resisting changes in rotation speed. The stored energy is proportionate to the square of the speed of the rotation. You can change the machine’s preserved power by applying a torque to grow or reduce its rotational speed.
Can a flywheel power a car?
What is advantage of flywheel?
The advantages of flywheel energy storage systems are high efficiency, high energy and power density, and long life. On the other hand, flywheels are more expensive and require more space than batteries and fuel cells. There are also some safety concerns about flywheels rotating at high speeds.
What is a solid flywheel?
As the name implies, a single or solid mass flywheel is made out of a single, heavy cast piece of steel or metal, has no moving pieces, and provides a direct contact between the clutch assembly and the engine.
What is the difference between flywheel and governor?
Flywheel stores rotational energy when the mechanical energy supplied is more than that’s required for operation, whereas a governor regulates the fuel supply according to the varying load conditions.